Is the United States an exceptional country that has played a uniquely good role in history? Or is it a typical country, perhaps even a uniquely bad one considering the legacy of slavery and Jim Crow? On this, the Left and Right do not agree.
US History

Liberty’s Secret ~ Excerpt
I have already been challenged on this topic, to wit, the challenge and my response will follow the excerpt.
This following excerpt from Liberty’s Secrets is one that squarely displaces the typical secular attack on Jefferson being a man of faith to some degree. In this excerpt Thomas Paine’s position on Christianity and God is dealt with as an extra bonus, as well as some of the Founders predictions of the then young French Revolution. This is a really good read, and I highly recommend the book.
Before the excerpt, I want to share a favorite sentence that I think best defines the Founders accomplishments in the Constitution. Here it is:
- The Constitution is the integration of ideals with reality, the ideal being human liberty, the reality being human nature. (p. 69)
If that isn’t the best definition in one sentence of the Constitution, I don’t know what is!
GOD AND THE HUMAN SOUL: THE EXISTENCE OF THE UNIVERSE AND MORALITY
Belief in God and the immortality of the human soul was universal among the Founders, which is incontrovertibly evident from the most cursory review of their writings. While not all of them were orthodox Christians, their thoughts on atheism ranged from extreme caution to outright disdain. For them, belief in God was natural to man because it was in accordance with his nature, and they agreed with Tocqueville when he noted (while describing the virtual absence of atheism in America) that “men cannot detach themselves from religious beliefs except by some wrong-headed thinking, and by a sort of moral violence inflicted upon their true nature… Unbelief is an accident; faith is the only permanent state of mankind.”
They saw the fingerprints of God everywhere they looked, and their conclusion that He existed was not even necessarily dependent on the Bible or any specific set of religious dogma but on the very nature of the cosmos. Writing to his friend John Adams toward the end of his life, Jefferson explained his views:
I hold (without appeal to revelation) that when we take a view of the Universe, in its parts general or particular, it is impossible for the human mind not to perceive and feel a conviction of design, consummate skill, and the indefinite power in every atom of its composition… We see, too, evident proofs of the necessity of a superintending power to maintain the Universe in its course and order… So irresistible are these evidences of an intelligent and powerful Agent that, of the infinite numbers of men who have existed through all time, they have believed, in the proportion of a million at least to unit, in the hypothesis of an eternal pre-existence of a creator, rather than in that of a self-existent Universe. Surely this unanimous sentiment renders this more probable than that of a few in the other hypothesis Even Thomas Paine, who in the second half of his life was an ardent opponent of orthodox Christianity (mostly Catholicism) and the clergy and did not believe the Bible was divinely inspired, wrote at the same time, “All the principles of science are of divine origin. Man cannot make or invent or contrive principles. He can only discover them, and he ought to look through the discovery to the Author.”
Paine criticized any teaching of “natural philosophy” (i.e., science) that asserted that the universe was simply “an accomplishment” (i.e., self-existent). He also criticized those teachers who “labor with studied ingenuity to ascribe everything they behold to innate properties of matter and jump over all the rest by saying that matter is eternal” and thereby encouraged the “evil” of atheism. “Instead of looking through the works of creation to the Creator Himself, they stop short and employ the knowledge they acquire to create doubts of His existence,” he lamented. “When we examine an extraordinary piece of machinery, an astonishing pile of architecture, a well-executed statue, or a highly-finished painting… our ideas are naturally led to think of the extensive genius and talent of the artist. When we study the elements of geometry, we think of Euclid. When we speak of gravitation, we think of Newton. How, then, is it that when we study the works of God in creation, we stop short and do not think of God?”
For these reasons, among others, Jefferson rejected being an atheist, “which,” as he put it, “I can never be.” His friend John Adams noted, “I never heard of an irreligious character in Greek or Roman history, nor in any other history, nor have I known one in life who was not a rascal. Name one if you can, living or dead.”” Nor did the Founders see science and religion as opposed to one another, as is all too common today. Rather, as President Adams asserted in a letter to university students, they were not only mutually compatible, but mutually necessary for one another: “When you look up to me with confidence as the patron of science, liberty, and religion, you melt my heart. These are the choicest blessings of humanity; they have an inseparable union. Without their joint influence no society can be great, flourishing, or happy.”
Just as much as the existence of God was essential to their understanding of the physical constitution of the universe, its combination with their belief in the immortality of the soul was crucial to their understanding of the moral constitution of the world, as it was the means by which God judged the good and evil acts committed in this life, whether noticed by man or not. Tocqueville ascribed a great deal of the accomplishments of the Puritans/Pilgrims and their progeny (the Founders) to this belief, which he described as so “indispensable to man’s greatness that its effects are striking,” for it kept him morally anchored, never able to escape ultimate justice. It was for this reason that the Founders considered belief in God as the cornerstone of all morality, but not because man could do no good apart from God commanding him to do so. Quite the contrary: part of their conception of the “law of nature and nature’s God” was the idea that all men had at least portions of this law inscribed into their very being, and that most men knew the basics of right and wrong because God had given them a conscience. The problem was that, because of their fallen nature, they did not obey their consciences as they should. Adams elaborated:
The law of nature would be sufficient for the government of men if they would consult their reason and obey their consciences. It is not the fault of the law of nature, but of themselves, that it is not obeyed; it is not the fault of the law of nature that men are obliged to have recourse to civil government at all, but of themselves; it is not the fault of the ten commandments, but of themselves, that Jews or Christians are ever known to steal, murder, covet, or blaspheme. But the legislator who should say the law of nature is enough, if you do not obey it, it will be your own fault, therefore no other government is necessary, would be thought to trifle.
This brings us to a very important fact that we must remember when it comes to the Founders: they did not believe that religion made men good, but rather that it provided the best encouragement and incentive to be good, for it taught them that their choices had consequences in eternity, not just in the moment. Even if consequences could be avoided in the now, God would exact justice in the hereafter.
This had been a Judeo-Christian teaching from time immemorial and was well known to the Founders. The problem was not that man had no knowledge of good and evil and therefore needed a religious commandment to tell him, but rather that human nature commonly bowed to the dictates of the passions, rather than reason, and thereby abandoned conscience and committed evil anyway. The Founders realized that our human nature could, and often did, pervert the plain dictates of conscience, allowing us to convince ourselves that right is wrong and wrong is right if it suits our own desires. As Adams noted, “Human reason and human conscience, though I believe there are such things, are not a match for human passions, human imaginations, and human enthusiasm.” Our passions would corrupt our minds, our minds would justify our passions, and in turn our passions would become even more corrupt, a deadly cycle with horrific consequences for individuals and society. “Our passions, ambition, avarice, love, resentment, etc. possess so much metaphysical subtlety and so much overpowering eloquence that they insinuate themselves into the understanding and the conscience and convert both to their party,” Adams wrote. “And I may be deceived as much as any of them when I say that power must never be trusted without a check.”
That “check,” at least as far as voluntary self-restraint was concerned, was religion. The Founders understood that mankind’s capacity for self-delusion was boundless; therefore, moral obligations must be placed on a divine rather than a humanistic footing if anyone could assert any truth or notion of right and wrong at all. It was for this reason that religious commandments such as “do not murder,” “do not steal,” and “do not commit adultery” were necessary, not because man was completely incapable of avoiding these sins without God commanding him to, but because, since He had commanded them, man had no intellectual excuse for ever allowing his passions or personal desires to blind his judgment and excuse him of his moral obligations. Religion thus anchored the definition of morality on God and asserted its obligations on man by acting as a powerful regulator of the inherently negative aspects of human nature. James Madison explained the importance of this truth: “The belief in a God All Powerful wise and good, is so essential to the moral order of the world and to the happiness of man, that arguments which enforce it cannot be drawn from too many sources nor adapted with too much solicitude to the different characters and capacities to be impressed with it.”
Adams asserted the same thing and specifically acknowledged that Judaism, through the Bible, had bequeathed to the world what he considered the most essential ingredient of human civilization:
I will insist that the Hebrews have done more to civilize men than any other nation. If I were an atheist, and believed in blind eternal fate, I should still believe that fate had ordained the Jews to be the most essential instrument for civilizing the nations. If I were an atheist of the other sect, who believe or pretend to believe that all is ordered by chance, I should believe that chance had ordered the Jews to preserve and propagate to all mankind the doctrine of a supreme, intelligent, wise, almighty sovereign of the universe, which I believe to be the great essential principle of all morality, and consequently of all civilization.
For the Founders, the most effective catalyst of virtue was religion, for it reminded man that he is not God and he therefore cannot shape morality according to his own selfish desires. It was the subversion of this principle that they identified as the cause behind the American and French Revolutions taking such radically different courses: it was ultimately a difference of theology.
GOD AND THE AMERICAN AND FRENCH REVOLUTIONS
The Founders believed in the existence of a God, which they deemed the most rational basis for the existence of the universe, morality, and reason itself. The French Revolution was predicated on almost the exact opposite idea.
While many today assume that the notion of blind chance being the operative force in the universe’s creation and development arrived on the scene with Charles Darwin, this is not the case. In fact, it was a notion quite popular among many of the continental European intellectuals of the time, most of whom were French, and most of whom tended to be atheists and/or materialists (which were practically the same). They contended that the universe had not been created but had either existed eternally or was the result of inherent properties in matter itself. But among the French intelligentsia, the one who had the most profound effect on the Founders, Montesquieu, directly contradicted this position in his famous work, The Spirit of the Laws: “Those who have said that a blind fate has produced all the effects that we see in the world have said a great absurdity,” he wrote, “for what greater absurdity is there than a blind fate that could have produced intelligent beings?”
For Montesquieu and the Founders, the universe was simply too full of information, order, and harmony to ascribe it to blind chance. “What is chance?” asked Adams. “It is motion; it is action; it is event; it is phenomenon without cause. Chance is no cause at all; it is nothing.”
In addition to their denial, or at least extreme doubt of the existence of a Creator, many of the French intellectuals in like manner either doubted or denied the existence and immortality of the human soul. They therefore denied the two theological pillars upon which the Founders based their ideas of virtue, and as such, it was no surprise that the French Revolution, which claimed to be the heir of the American Revolution, devolved into a bloodbath of violence and oppression unrestrained by any religious principle.
While both revolutions were similar in their assertion of human rights, they offered fundamentally different explanations of the origin of such rights. The American Revolution was premised on men being “endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable rights,” while the French Revolution asserted man’s rights were based purely on reason, apart from any notions of divinity or religion. A statue of a deified “Reason” was erected in the Notre Dame cathedral in Paris, and the revolution was predicated upon principles that were explicitly and directly opposed to religion, Christianity in particular. Adams noted the differences between the two revolutions when he wrote to his friend Richard Price that “Diderot and D’Alembert, Voltaire and Rousseau,” all French atheists and materialists, “have contributed to this great event more than Sidney, Locke, or Hoadly,” English political philosophers who explicitly asserted that the “laws of nature and nature’s God” were the foundation of man’s rights and moral obligations, and who had a profound impact on the American Revolution. The French, on the other hand, based man’s rights on the consensus of “the nation.” The rights of man were what man, through the nation, had decided they would be. For this reason, Adams admitted to Price as early as 1790, “I own to you, I know not what to make of a republic of thirty million atheists,” and he predicted there would be rampant violence and bloodshed.
But that was not all. Several of the Founders, Adams in particular, believed that the principles of the French Revolution not only directly undermined the basis of human rights and obligations but also destroyed the very idea of human liberty. If man was simply matter in motion, then his entire destiny had already been determined by physical laws and constants (today known as “determinism”), making liberty a meaningless idea. And yet, this was the view of many of the leading French intellectuals. “And what was their philosophy?” Adams inquired:
Atheism—pure, unadulterated atheism…. The universe was matter only, and eternal. Spirit was a word without a meaning. Liberty was a word without a meaning. There was no liberty in the universe; liberty was a word void of sense. Every thought, word, passion, sentiment, feeling, all motion and action was necessary [determinism]. All beings and attributes were of eternal necessity; conscience, morality, were all nothing but fate. This was their creed, and this was to perfect human nature, and convert the earth into a paradise of pleasure… Why, then, should we abhor the word “God,” and fall in love with the word “fate”? We know there exists energy and intellect enough to produce such a world as this, which is a sublime and beautiful one, and a very benevolent one, notwithstanding all our snarling; and a happy one, if it is not made otherwise by our own fault.
Alexander Hamilton, who described the French Revolution as “the most cruel, sanguinary, and violent that ever stained the annals of mankind,” also predicted its failure due to the fact that it was explicitly
opposed to Christianity, “a state of things which annihilates the foundations of social order and true liberty, confounds all moral distinctions and substitutes to the mild and beneficent religion of the Gospel a gloomy, persecuting, and desolating atheism:’
It was precisely because the French Revolution rejected the Judeo-Christian notion of the fallen nature of man in exchange for the idea that he could be perfected by reason that they engaged in the wanton violence and cruelty of the guillotine: it was all worth it because they were creating a new, ideal world that had to be purged of its impure elements.
The French Revolution was thereby founded on principles that fundamentally contradicted the divine basis of the existence of the universe, man’s rights, his moral obligations, and his very liberty, upon which the Founders, partaking of both the classical and Judeo-Christian tradition, asserted them. With God removed, several of the Founders, Adams in particular, predicted the French Revolution would operate according to the bloody principles of “might makes right.” “A nation of atheists,” he had warned, would likely lead to “the destruction of a million of human beings.” Adams explained his prophecy of a forthcoming deluge of blood in biblical terms and ascribed it to the utter rejection of religion by the leaders of the French Revolution:
The temper and principles prevailing at present in that quarter of the world have a tendency to as general and total a destruction as ever befell Tyre and Sidon[,] Sodom and Gomorrah. If all religion and governments, all arts and sciences are destroyed, the trees will grow up, cities will molder into common earth, and a few human beings may be left naked to chase the wild beasts with bows and arrows…. I hope in all events that religion and learning will find an asylum in America.
In this, he disagreed (at the time) with Jefferson. But even Jefferson was forced to admit decades later, after the Reign of Terror, the Napoleonic Wars, and the other violent outbursts that came out of the French Revolution, that Adams had been completely right in his assessment, acknowledging, “Your prophecies… proved truer than mine.” When Jefferson asked Adams why he had predicted what he did, Adams explained that the power of God had been replaced by the arrogant, usurping power of man, and conscience was thereby disconnected from its transcendent anchors. Thus, those in power believed whatever they did was moral: “Power always sincerely, conscientiously, de tres bon foi [“in very good faith”], believes itself right. Power always thinks it has a great soul, and vast views, beyond the comprehension of the weak, and that it is doing God’s service, when it is violating all his laws.” It was for this reason that, as much as religion had been abused for centuries in European history, Adams argued it could not compare with the atrocities committed in the name of “Liberté, Egalité, Fraternité” during the French Revolution: “It is a serious problem to resolve whether all the abuses of Christianity, even in the darkest ages when the Pope deposed princes and laid nations under his interdict, were ever so bloody and cruel, ever bore down the independence of the human mind with such terror and intolerance, or taught doctrines which required such implicit credulity to believe, as the present reign of pretended philosophy in France.”
As president, Adams had to deal directly with the revolutionary French government and easily noted the difference between an American society that assented to general religious principles and a French society that rejected them:
You may find the moral principles, sanctified and sanctioned by religion, are the only bond of union, the only ground of confidence of the people in one another, of the people in the government, and the government in the people. Avarice, ambition, and pleasure, can never be the foundations of reformations or revolutions for the better. These passions have dictated the aim at universal domination, trampled on the rights of neutrality, despised the faith of solemn contracts, insulted ambassadors, and rejected offers of friendship.
For the Founders, the purpose of reason—which Adams referred to as “a revelation from its maker” and Jefferson as an “oracle given you by heaven”-was to better align human actions with the “law of nature and nature’s God” by the taming of human passions and the application of knowledge. The leaders of the French Revolution believed precisely the opposite, that God didn’t really exist (and if He did, He was largely irrelevant), and that reason was man’s alone, and thus his to utilize toward whatever ends he himself determined. Though the Founders knew perfection “falls not to the share of mortals,” the French believed that man could be perfected through reason, and therefore any barriers to creating the world of their dreams needed to be destroyed, for this was tantamount to obstructing man’s perfection. The differences between the two revolutions thus turned out to be theological at root, and for this reason, while on the surface they were superficially similar, they were in fact fundamentally different, as Adams prophesied, other Founders criticized, and the facts of history verified.
Joshua Charles, Liberty’s Secrets: The Lost Wisdom of America’s Founders (Washington, DC: WND Books, 2015), 82-91.
Dennis Prager interviews Ann Coulter in regards to her new book, Demonic.” Ann points out a fact I wasn’t aware of in regards to the mob mentality that set the standard for the French Revolution. Much like the misunderstanding in regards to the Crusades, the witch trials, and the like, numbers are not the forte of the left. Nor is putting into context meaning behind them.
Challenges
I posted a link to this at a friends “counter-atheist” page on FaceBook. I posted the following that included a link back to this page:
For those interested, before I head out to drink wine in Cambria, I posted an excerpt from a book I am reading… and it deals with both Jefferson’s, Madison’s, Hamilton’s, Paine’s, view of faith and/or atheists and creation vs. evolutionary thinking (the basis of which reaches back to Greece)
Almost immediately after this was posted this was posted.
- Fascinating!! I never knew Jefferson died before The Origin of Species was written!!
I believe Tim, the author of the above challenge, meant to say “died after” Darwin’s seminal work, not before.
Per the modi operandi of the atheists on this site, they do not read and inculcate what was said. Forgive me as I take time with a though. After reading four books on marijuana addiction and the latest studies (one that followed over a thousand people for 25-years) showing the deleterious affects of this drug (a 8% decrease of the amygdala, and 12% reduction in size of the hippocampus). During this time of reading, a story came out about what amounts to brain damage in a controlled setting by “targeted magnetism” — making more people unable to “believe” in God… by about thirty-percent.
One commentator said it must be embarrassing to the atheist because “the specific part of the brain they frazzled was the posterior medial frontal cortex—the part associated with detecting and solving problems, i.e., reasoning and logic.”
I often wonder aloud to my wife if these guys smoke weed! But I digress… continuing.
I respond:
I am sorry Tim, evolutionary thinking pre-dates Darwin. Take Cicero countering his rivals of the day (as an example). If you read this… what is the opposing viewpoint? [Nothing?]
…suppose that after darkness had prevailed from the beginning of time, it similarly happened to ourselves suddenly to behold the light of day, what should we think of the splendour of the heavens? But daily recurrence and habit familiarize our minds with the sight, and we feel no surprise or curiosity as to the reasons for things that we see always; just as if it were the novelty and not rather the importance of phenomena that ought to arouse us to inquire into their causes.
Marcus Tullius Cicero, Cicero Nature of the Gods Academics (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; Translated by H. Rackam, 2005), 217.
OR,
But if the structure of the world in all its parts is such that it could not have been better whether in point of utility or beauty, let us consider whether this is the result of chance, or whether on the contrary the parts of the world are in such a condition that they could not possibly have cohered together if they were not controlled by intelligence and by divine providence. If then the products of nature are better than those of art, and if art produces nothing without reason, nature too cannot be deemed to be without reason. When you see a statue or a painting, you recognize the exercise of art; when you observe from a distance the course of a ship, you do not hesitate to assume that its motion is guided by reason and by art; when you look at a sun-dial or a water-clock, you infer that it tells the time by art and not by chance; how then can it be consistent to suppose that the world, which includes both the works of art in question, the craftsmen who made them, and everything else besides, can be devoid of purpose and of reason? Suppose a traveller to carry into Scythia or Britain the orrery recently constructed by our friend Posidonius, which at each revolution reproduces the same motions of the sun, the moon and the five planets that take place in the heavens every twenty-four hours, would any single native doubt that this orrery was the work of a rational being? These thinkers however raise doubts about the world itself from which all things arise and have their being, and debate whether it is the product of chance or necessity of some sort, or of divine reason and intelligence;
Marcus Tullius Cicero, Cicero Nature of the Gods Academics (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; Translated by H. Rackam, 2005), 207-209.
And the opening sentence to a Berkeley.EDU paper is this:
✦ Evolutionary theory begins with the Ionian philosopher Anaximander (ca. 611 – 546 B. C. E.). Very little is known about his life, but it is known that he wrote a long poem, On Nature, summarizing his researches. This poem is now lost, and has survived only in extracts quoted in other works. Enough survives, however, that Anaximander’s thought can be reconstructed with some confidence. For Anaximander, the world had arisen from an undifferentiated, indeterminate substance, the apeiron. The Earth, which had coalesced out of the apeiron, had been covered in water at one stage, with plants and animals arising from mud. Humans were not present at the earliest stages; they arose from fish. This poem was quite influential on later thinkers, including Aristotle. ~ Berkeley.edu
Tim responds:
- What’s your point?
This is one of those “bang your head on the keyboard” moments. You see, Tim challenged my statement. I corrected his challenge. He then feigns like I just waded in, off topic. Like I started talking about MPG for city buses where I live. You will notice this is Paley’s watchmaker argument almost 1800-years before Paley lived! Paley pre-dated Darwin. Were there no naturalistic origins hypothesis of his day either? Paley was just “preaching to the quire”? Dumb. Here is my response:
OMG…. sigh….
➣ You said: “Fascinating!! I never knew Jefferson died [after] The Origin of Species was written!!”
I corrected your viewpoint that “evolution” is something Charles Darwin “founded.” He merely reformulated the general idea that “man has evolved,” into, the General Theory of Evolution (GTE).
For more context on defining “evolution,” see my debate with some atheists about the General Theory of Evolution.

Dennis Prager’s Ultimate Issues Hour, with Author, Joshua Charles
In this second interview of author Joshua Charles (see the first here), Josh delves into the Founders faith more so than the first time around via his book, “Liberty’s Secrets: The Lost Wisdom of America’s Founders.” One of the main topics dealt with is Deism (see my post on Deism).
Another enjoyable jaunt through history.
For more clear thinking like this from Dennis Prager… I invite you to visit: http://www.dennisprager.com/ ~ see also: http://www.prageruniversity.com/

Religious Tolerance: Made in America by Protestants
Religious tolerance is a given in the West. But it’s a historical aberration — an ideological revolution created by the Puritans and pre-1776 Americans. What was it that led to the religious tolerance revolution? Was there something unique in Protestantism and Americanism? Or would tolerance have eventually arisen elsewhere, perhaps in Europe? Larry Schweikart, best-selling author and professor of history at the University of Dayton, explains.

Enjoy the Show as the Left Eats Itself (Jefferson & Jackson Out)

I have said for quite some time that the Left eats itself. From Hillary and O’Malley having to backtrack for statements that “all lives matter,” to the same activist group interrupting Bernie Sanders (I guess he is not left enough?), to this new occurrence via CT-Post.com:
Thomas Jefferson and Andrew Jackson are history in Connecticut.
Under pressure from the NAACP, the state Democratic Party will scrub the names of the two presidents from its annual fundraising dinner because of their ties to slavery.
Party leaders voted unanimously Wednesday night in Hartford to rename the Jefferson Jackson Bailey dinner in the aftermath of last month’s fatal shooting of nine worshipers at the historic black church in Charleston, S.C….
Maybe this will get Democrats to see their history fully?

Remember When… Nope, Neither Do I
This is painting memorializing the colonists who participated in the first official battle[s] of the Revolutionary War (Battles of Lexington and Concord), with some 2nd Amendment “swerve.”

The Battle Flag of Gen. Robert E. Lee ~ A Quick History
I loved this callers short historical bio of the flag in question. Rush did a short bio of it as well. The Daily Callers original upload on YouTube had a horribly low volume issue. So I corrected it and uploaded it at my Live-Leak and posted it and other issues here:
✦ When Did Republicans Get Involved?
Listen To Larry On-Line at CRN-Talk Radio
For more clear thinking like this from Larry Elder… I invite you to visit: http://www.larryelder.com/ ~AND~ http://www.elderstatement.com/

Some Pleasant Conversation About Democratic Racist History
An older [seasoned] black caller and Larry Elder discuss politely the racial history of the Democratic Party… past and present. Larry Elder was filling in for Dennis, a pleasant conversation.
Listen To Larry On-Line at CRN-Talk Radio
For more clear thinking like this from Larry Elder… I invite you to visit: http://www.larryelder.com/ ~AND~ http://www.elderstatement.com/

Did We Eviscerate the Native Americans? (Whittle, D’Souza, MachoSauce)
In this PJTV series, we look at whether America is a country of hostility or prosperity. The first episode covers the treatment of Native American’s. Should we be ashamed of the way our ancestors treated them?
(ZoNation) Dinsesh D’souza, Bill Whittle, AlfonZo Rachel, and Yaron Brook explore the American experience concerning the Native American. Hear more in this episode of Setting the Record Straight!

Herbert Hoover and the Changing Demographic of Black Voters
See C-SPANS one-hour interview of Bruce Bartlett about the book I quote from below:
By 1914, Tillman was not on the ballot and he used his influence to defeat Blease in the Democratic primary, the only election that mattered in South Carolina after the disenfranchisement of blacks in 1895. Indeed, so intent was Tillman on defeating his former protégé that he threatened to have the literacy tests designed for blacks used against Blease’s poor white followers as well.
Among the more ridiculous tactics Blease used in the 1914 campaign to save his position was an attack on doctors, whom he charged with abusing young women by examining their private parts during physical examinations. He threatened to kill any doctor who examined his daughter against her will and to pardon anyone who did the same. Fearful that other people were not as outraged as he was about doctors simply doing their jobs, Blease implied that doctors were allowing “Negro janitors” to observe their examinations.
Of course, Blease did not avoid attacking blacks directly in his efforts to gin up the votes of ignorant white textile workers. “The Negro race has absolutely no standard of morality,” he declared. “They are, in that respect, a class by themselves as marital infidelity seems to be their more favorite pastime.” Blease said that giving education to a black man would only “ruin a good field hand and make a bad convict.” He warned that “the black ape and baboon” was a constant threat to rape white women whenever the opportunity presented itself.
Partly because of Tillman’s efforts, Blease was defeated in the 1914 Democratic primary and again in 1916. In 1918, Blease retaliated by running against Tillman for the Senate himself. However, Blease misread the mood of the people regarding World War I and ran a strongly pacifist campaign, attacking Woodrow Wilson and opposing American intervention in the war. After voters reacted very negatively to this approach, he tried to switch course, but it was too late and he was defeated.
Six years later, Blease ran again for the Senate; this time winning election. As a U.S. Senator, Blease was best known for continuing the Tillman tradition of making racially inflammatory speeches on the Senate floor. For example, in a 1928 speech, Democrat Blease blasted Republican Commerce Secretary Herbert Hoover:
Republicans are now talking about nominating that man for President of the United States . . . a man who is in favor of making young white girls use the same water-closets as Negro men, making young white girls sit by them day by day. If there was nothing else, Mr. President, a Negro would be offensive because of his natural human smell. You can take a Negro and take a tub of the hottest water you can get him into, and use all the soap you can use, then take him out and cover him with cologne, and in five minutes he will smell just as offensive as he did before you washed him, because it is human nature, and he could not get rid of the odor. Then this man [Hoover], who wants to be President of the United States of America, this Englishman, wants to make white girls associate on equal terms with Negroes. . . . Mr. President, it is a shame, it is a disgrace.
The only disgrace, of course, was that the Democratic voters of South Carolina—the only ones whose votes counted—sent such an obnoxious racist to Washington to represent them. But by 1930, they came to their senses and replaced Blease with James F. Byrnes, a much more genteel racist. Twice more, in 1934 and 1938, Blease attempted to make a comeback as governor, but was rejected by voters both times. He died in 1942.
[….]
There is no mention of blacks in the Democratic Party’s 1932 platform. Much of the black community was, in fact, less than enthusiastic about the Roosevelt-Garner ticket. Said the New York Amsterdam News, a prominent black newspaper, “We fear that equal rights in the National Democratic Party means exactly what they meant in 1913 when the Woodrow Wilson administration came into power—equal rights for the white man but hell and damnation for the colored man.”
From the black perspective, the best thing Roosevelt had going for him in 1932 simply was that he wasn’t Herbert Hoover. Hoover was certainly no racist—he abolished segregation in the Commerce Department while secretary” But he had the tinniest of tin ears when it came to practical politics, especially when it came to blacks. Hoover needlessly alienated them by purging blacks from Republican organizations in the South in order to appeal to whites; nominating a justice to the Supreme Court, John J. Parker, who was widely viewed, rightly or wrongly, as a racist; and allowing the War Department to segregate black Gold Star Mothers during a government-financed trip to European graveyards. Many blacks also believed that Hoover had condoned discriminatory treatment while he was in charge of federal relief after the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927.
[….]
It is impossible to calculate precisely to what extent New Deal policies raised black unemployment above what otherwise would have been the case. But it is revealing that well after the beginning of the Depression but before the New Deal began, unemployment for black workers was actually lower than for whites. In April 1930, the unemployment rate was 6.3 percent for black males and 6.9 percent for white males. Seven years later, in late 1937, after implementation of most New Deal programs, the unemployment rate for black males was well above that for white males: 19.1 percent for the former versus 13.9 percent for the latter.
POLITICAL REALIGNMENT
Despite all of this, black support for Roosevelt grew sharply between 1932 and 1936. Contrary to popular belief, Hoover actually carried a majority of the black vote in 1932. It was not until 1936 that blacks really deserted the Republican Party in large numbers. A key reason appears to have been the federal government’s welfare efforts through the Federal Emergency Relief Administration, which literally put food on the table for a large percentage of black families. According to one estimate, 30 percent of the entire black population was receiving relief in January 1935. As a contemporary analyst explained, blacks were profoundly grateful for this aid, little as it was, and rewarded the political party that delivered the goods:
Many Negroes in Chicago came in for a large share of relief funds and, consequently, were greatly impressed with the humanitarian aims of the New Deal. This sentiment was played upon and encouraged by both the national and local Democratic organizations. It was soon evident that their security was tied up with direct relief.
This same analyst quoted a Republican precinct captain in Chicago, who explained his party’s loss of the black vote this way: “That Abe Lincoln was a Republican is not near so important as their daily bread.’ It didn’t matter that the disbursement of aid was in the hands of local officials who often discriminated severely against blacks. They were grateful that they were getting something, even if it was less than whites received. “Let Jesus lead me and welfare feed me,” Depression-era blacks would say.
Ironically, on August 14, 1935, Roosevelt signed into law the biggest expansion of social welfare in American history—the Social Security Act—and left most blacks out of it. Although initially proposed as universal legislation that would benefit all workers, the bill Roosevelt ultimately signed excluded most blacks by exempting domestic and agricultural workers from coverage. For this reason, many historians today view the original law as inherently racist. As Robert Lieberman of Columbia University recently wrote:
The Old-Age Insurance provisions of the Social Security Act were founded on racial exclusion. In order to make a national program of old-age benefits palatable to powerful Southern congressional barons, the Roosevelt administration acceded to a Southern amendment excluding agricultural and domestic employee from OAI coverage. This provision alone eliminated more than half of the African Americans in the labor force and over three-fifths of black Southern workers.
While Roosevelt himself was not responsible for the provision that limited Social Security coverage for blacks, it is also a fact that he didn’t fight very hard to prevent his proposal from being watered down this way Nor can Roosevelt be excused for ignorance. The NAACP even testified against the Social Security Act before the Senate Finance Committee. Said the NAACP representative, Charles H. Houston, the more the organization studied the legislation, “the more holes appeared, until from a Negro’s point of view it looks like a sieve with the holes just big enough for the majority of Negroes to fall through.”
Bruce Bartlett, Wrong on Race: The Democratic Party’s Buried Past (New York, NY: Palgrave MacMillan, 2008), 54-55, 112, 118-119.

The Constitution Does Not Allow For Social Programs
Here is Walter William’s article Larry Elder mentions:
Now that we’re about to decide the White House’s next occupant, let’s speculate about how previous presidents might fare were they standing for election in today’s America. What would be the presidential prospects of Thomas Jefferson or James Madison, our third and fourth presidents? Here’s my bet: They’d go down in an unprecedented landslide defeat. I could see the likes of a Joseph Stalin or a Mao Zedong winning long before a Jefferson or Madison. Let’s look at it.
In 1792, Congress appropriated $15,000 to assist some French refugees. James Madison wrote disapprovingly, “I cannot undertake to lay my finger on that article of the Constitution which granted a right to Congress of expending, on objects of benevolence, the money of their constituents.” Even though our Constitution hasn’t been amended to authorize Congress to spend on the objects of benevolence, I can’t imagine today’s Americans electing a president who’d share Madison’s view. Such a candidate would be labeled mean-spirited, racist, sexist and homophobic.
Today’s politicians might argue that James Madison, the acknowledged father of our Constitution, is all wrong. They’d say spending on the objects of benevolence (legalized theft) is authorized by the Constitution’s “promote the general welfare” clause. James Madison spoke to that argument saying, “With respect to the words general welfare, I have always regarded them as qualified by the detail of powers [enumerated in the Constitution] connected with them. To take them in a literal and unlimited sense would be a metamorphosis of the Constitution into a character which there is a host of proofs was not contemplated by its creators.”
Today’s Americans wouldn’t elect Thomas Jefferson either. He’d be labeled an extremist and a gun nut. Jefferson warned, “The issue today is the same as it has been throughout all history, whether man shall be allowed to govern himself or be ruled by a small elite.” Today, he’d be referring to the White House, Congress, the U.S. Supreme Court and federal regulatory agencies. Because of elite proclivities, Thomas Jefferson urged, “No man shall ever be debarred the use of arms. The strongest reason for the people to retain the right to keep and bear arms is, as a last resort, to protect themselves against tyranny in government.” Jefferson wasn’t referring to just any old government; he was referring to the U.S. federal government.
Franklin Pierce, our 14th president, took actions that would be political suicide today. In 1854, he vetoed a bill to help the mentally ill saying, “I cannot find any authority in the Constitution for public charity,” adding that to approve such spending, “would be contrary to the letter and the spirit of the Constitution and subversive to the whole theory upon which the Union of these States is founded.”
In 1887, President Grover Cleveland, our 22nd and 24th president, said when vetoing an appropriation to help drought-stricken counties in Texas, “I feel obliged to withhold my approval of the plan to indulge in benevolent and charitable sentiment through the appropriation of public funds . . . I find no warrant for such an appropriation in the Constitution.”
Today’s politicians can’t be held fully responsible for our growing constitutional contempt. We might blame them for not being statesmen. The lion’s share of the blame rests with 270 million Americans. Our elected officials simply mirror our contempt for constitutional principles and our desire to live at the expense of our fellow American. It’s unreasonable to expect a congressman, or a president to live up to his oath of office, to protect, defend and bear true allegiance to the Constitution, if doing that means political suicide.

Defense Department Fails History In Lieu Of Class Warfare
This is with a h/t to Rick David via Facebook, and comes by way of The Godfather of Politics:
The Daily Caller reports:
“Those three cherished texts all count as ‘historical influences that allow sexism to continue,’ according to a presentation prepared by the Defense Equal Opportunity Management Institute, whose mission is to give a ‘world-class human relations education.’”
Here’s a screen shot of one of the slides:
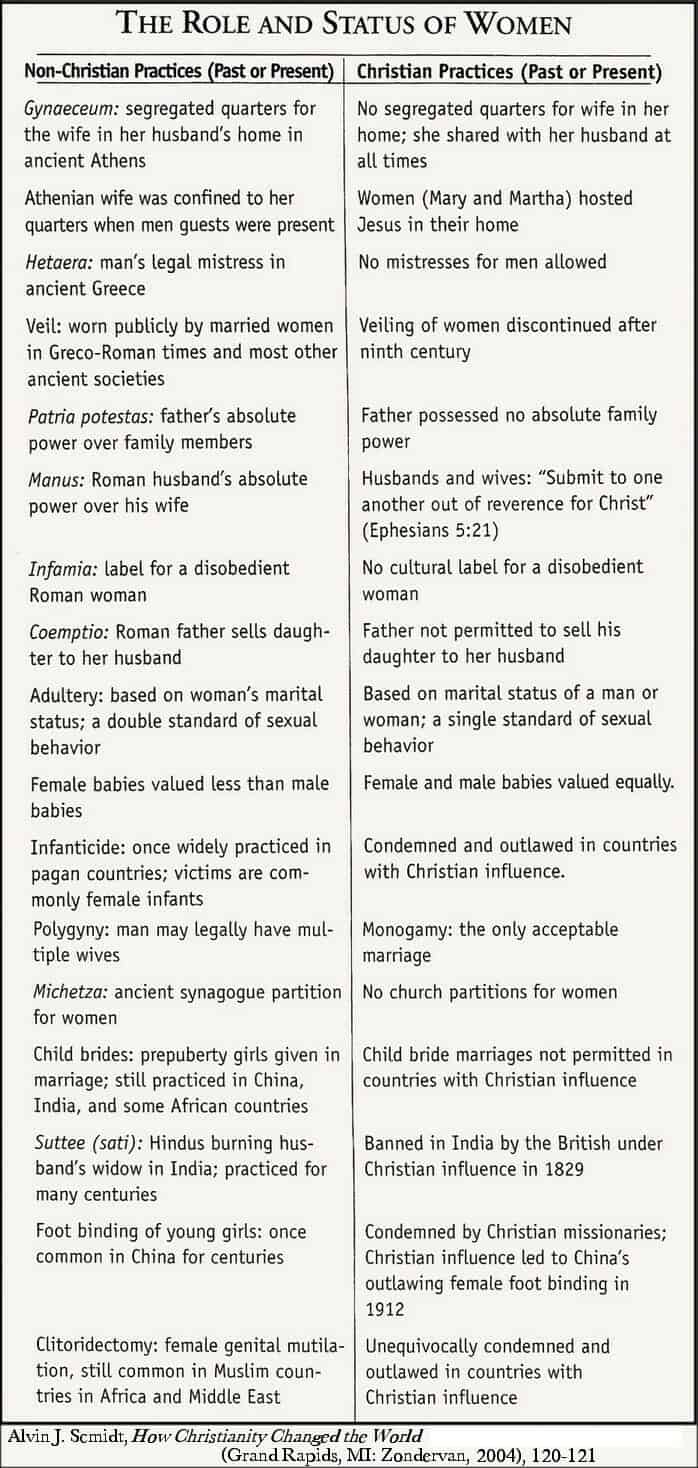
Here I will add to some of the good commentary by Godfather from my own chapter via my book where I challenge in-class ideas from a CSUN professor who was a self-proclaimed Gnostic and feminist. In this excerpt I will show that women, for the first time in history, were looked at as EQUAL to men and their endeavor to spread the Gospel message. NO pagan belief system to date allowed such thinking, and this was the basis for the future suffrage movements, coupled with the freedoms enumerated in America’s Founding documents:
Another reason that Christianity succeeded over that of the other ideologies of its day is partly due to – I believe – the high regard given to woman as compared to the pagan religions of the day, Gnosticism included. This topic is dealt with in the book How Christianity Changed the World, by Alvin J. Schmidt. His chapter entitled “Women Receive Freedom and Dignity” is very revealing.[76] [See his image below.] Paul, for instance, had a high regard for women as coworkers, which is amply demonstrated in other letters.[77] Barbara Geller points out that “during the Byzantine era, female leadership was exercised largely within the hierarchical structures of women’s monastic communities.” She continues, however, that,
…the letters of Paul and the Book of Acts suggest that in the earliest phase of emerging Christianity, the opportunities for women were far greater. The closing chapter of Paul’s letter to the church at Rome, following the epistolary conventions of that period, includes greetings and personal commendations. Paul mentions ten women, the first of whom is Phoebe, described in Greek as diakonos and a prostates, correctly translated in the New Revised Standard Version as “deacon” and “benefactor” (Rom 16:1-2). Older translations erroneously rendered these words as “deaconess” and “helper”; thus, generations of translators ignored the plain sense of the text because of their assumption that women could not have exercised significant roles in the early church. Ancient Inscriptions suggest, moreover, that prostates was not only a benefactor or patron, but also frequently the president or head of an association.[78]
As is common, persons today with an agenda misinterpret Scripture to bolster a political position or to live comfortably within their own worldview. Paul, in his letters, interprets the role of women more liberally than his antagonists say he does. Even the Gospels portray women as being more spiritually perceptive than men.[79] So it is hardly surprising that early Christianity proved to have a deep appeal for women, as one scholar observes:
“It is probable that Jesus’ teachings attracted women in part because of the new roles and equal status they were granted in the Christian community. There were many cults in Greece and Rome that were for men only, or at best, allowed women to participate in very limited ways [as prostitutes, for instance, in the fertility cults within ‘goddism’]…. Judaism offered women proselytes a circumscribed place at best, for they were faced with the Jewish restrictions that limited participation in religious functions. While women were not allowed to make up the quorum[80] necessary to found a synagogue, nor to receive the Jewish covenant sign (circumcision), these limitations did not exist in the Christian community.”[81]
The Book of Acts is another indicator of the early church’s emphasis on the important role of women. In fact, Peter’s speech to the Pentecost crowd included portions of the Old Testament book of Joel: “And it shall come to pass in the last days, says God, that I will pour out my spirit on all flesh, your sons and your daughters will prophesy…. And on My menservants, I will pour out my Spirit in those days…” (Acts 2:17-18). In the beginnings of this new church founded by Jesus of Nazareth we find women mentioned at the very beginning of Christianities historical book, Acts. In 1:14 of Acts we find the disciples were constantly in prayer “along with the women and Mary the mother of Jesus.” The first convert in Philippi, for instance, was Lydia, a dealer in purple cloth (Acts 16:14). The Philippi church meets first in her home (Acts 16:40). Then Priscilla is introduced (18:2), who was a Jewish evangelist! Together with her husband, Aquila, she is mentioned four times in Acts, always being the first mentioned.[82] Likewise, In Romans 16:3 we find Paul mentioning first Priscilla and then her husband, Aquila – mentioning that both are equal in Christ: “Greet Priscilla and Aquila, my fellow workers in Christ Jesus.” In fact, Priscilla is always mentioned prior to her husband except for once, another key to the overturning of patriarchal customs up to that point.[83]
Luke makes mention of when Paul visited the evangelist Philip in Caesarea, that he had four daughters who prophesied. Far from Paul and the church being oppressive to women, this type of universality that included women was a departure from both Jewish norms as well Roman norms. The Romans in fact, could have used this early equalizing as being socially subversive to their social order, in this case to the patriarchy. Likewise, the Jewish leaders who rejected Jesus and the teachings of the early church, including Paul at first, severely restricted the role of women.[84] Paul and the other writers of the New Testament telling men that they should cherish their wives (Ephesians 5), that marriage is a financial partnership (I Timothy 5:8), that the husband is to honor his wife (I Peter 3:7), and that the male should be a part of raising their children within the family unit was essentially unheard of until then. In contradistinction, the Gospel of Thomas “is clearly influenced by the kind of Gnosticism we know was prevalent in the second and third centuries, but not in the first.”[85] For example, we find Jesus of the Gospel of Thomas responding to Peter, let’s read:
114: Simon Peter said to them, “Let Mary leave us, for women are not worthy of life.” Jesus said, “I myself shall lead her in order to make her male, so that she too may become a living spirit resembling you males. For every woman who will make herself male will enter the kingdom of heaven.”
“This demeaning view of women was common within Gnosticism, but utterly foreign to the historical Jesus.”[86] The fact that the canonical Gospels were written a century or two earlier than those of Gnosticism is at least a good preliminary indication that they could possibly also be more authoritative. O. C. Edwards agrees:
“It is precisely as history that I find her [Pagels] work most unsatisfactory. Nowhere, for instance, does she give the impression that the basic picture of Jesus given in the New Testament gospels did not arise contemporaneously with the Gnostic portrait, but antedated it by at least a century. As historical reconstructions [go,] there is no way that the two can claim equal credentials.”[87]
To ignore the century before Gnosticism started, seems to me, like a tell in poker. That is when the opposing player does something or makes an odd move to show the other players that he or she is bluffing, verbal or not. In this case, the total disregard for pre-Gnostic history and roots is telling.
FOOTNOTES
[76] The following list, “The Role and Status of Women” (Grand Rapids, MI: Zondervan, 2004), 120-121.
[77] Dale & Sandy Larsen, 7 Myths about Christianity (Wheaton, IL: InterVarsity Press, 1998), see chpt. 2, “Christianity Suppresses Women”; also all one has to do is read 1 Corinthinas 7:1-16, here Paul puts the male and female on equal terms and status, unheard of in the ancient pagan world… until that is, the New Testament and the Christian community. In fact, Wayne Grudem makes this new distinction apparent when he points out the role of women in the early church:
Perhaps the best example of a woman well trained in knowledge of the Bible is Priscilla. When Paul went to Corinth, he stayed with Aquila and Priscilla: “because he was of the same trade he stayed with them and worked, for they were tentmakers by trade” (Acts 18:3). Paul stayed a year and six months at Corinth (Acts 18:11), and we may ponder just how much Bible and theology Priscilla would have learned while having the apostle Paul as a house guest and business partner during that time! Then Priscilla and Aquila went with Paul to Ephesus (Acts 18:1819). It was at Ephesus in A.D. 51 that Priscilla and Aquila together “explained” to Apollos “the way of God more accurately” (Acts 18:26). So in A.D. 51 Priscilla knew Scripture well enough to help instruct Apollos. After that, Priscilla probably learned from Paul for another three years while he stayed at Ephesus teaching “the whole counsel of God” (Acts 20:27; compare 1 Cor. 16:19, where Priscilla is called Prisca, and Paul sends greetings to Corinth from Aquila and Prisca and the church that meets “in their house”). By the end of Paul’s three-year stay in Ephesus, Priscilla bad probably received four and a half years of teaching directly from the apostle Paul. No doubt many other women in Ephesus also learned from Paul—and from Priscilla! Aquila and Priscilla went to Rome sometime later (Rom. 16:3, perhaps around A.D. 58), but they returned to Ephesus, for they were in Ephesus again at the end of Paul’s life (in 2 Tim. 4:19, Paul writes to Timothy at Ephesus, “Greet Prisca and Aquila”). Now, 2 Timothy was probably written in A.D. 66 or 67 (Eusebius says that Paul died in A.D. 67), and 1 Timothy a short time before that, perhaps in A.D. 65. In addition, before he wrote 1 Timothy, Paul seems to have been in Ephesus and it seems he had told Timothy to remain there when he left for Macedonia (see 1 Tim. 1:3: “As I urged you when I was going to Macedonia, remain at Ephesus…”). Therefore, both because 1 Timothy is near in time to 2 Timothy, and because Paul had recently been in Ephesus to know who was there before he wrote 1 Timothy or 2 Timothy, it seems likely that Aquila and Priscilla were back in Ephesus by the time Paul wrote 1 Timothy, about A.D. 65. This was fourteen years after Priscilla and Aquila had explained the way of God to Apollos in Ephesus.
Evangelical Feminism: A New Path to Liberalism (Wheaton, IL: Crossway Books, 2006), 175-176.
[78] Michael D. Coogan, ed., The Oxford History of the Biblical World (2001 paperback edition; New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 1998), 429-430.
[79] Compare Mark 4:40 and 6:52 to Mark 5:25-30. See also Mark 7:24-30 and 12:41-44.
[80] “The number of members of a group or organization required to be present to transact business legally, usually a majority.” Random House Webster’s Unabridged CD-ROM Dictionary, (1999).
[81] Ben Witherington, Women and the Genesis of Christianity (New York, NY: Cambridge University Press, 1990), 246. For those who are not familiar with the Gospel and assume this to reference female circumcision, it does not. Just a quick perusal of Colossians shows that there is freedom found in Christ (Colossians 2:9-15; 3:11-12, NIV):
For in Christ all the fullness of the Deity lives in bodily form, and you have been given fullness in Christ, who is the head over every power and authority. In him you were also circumcised, in the putting off of the sinful nature, not with a circumcision done by the hands of men but with the circumcision done by Christ, having been buried with him in baptism and raised with him through your faith in the power of God, who raised him from the dead. When you were dead in your sins and in the uncircumcision of your sinful nature, God made you alive with Christ. He forgave us all our sins, having canceled the written code, with its regulations, that was against us and that stood opposed to us; he took it away, nailing it to the cross. And having disarmed the powers and authorities, he made a public spectacle of them, triumphing over them by the cross…. Here there is no Greek or Jew, circumcised or uncircumcised, barbarian, Scythian, slave or free, but Christ is all, and is in all. Therefore, as God’s chosen people, holy and dearly loved, clothe yourselves with compassion, kindness, humility, gentleness and patience.
Circumcision was not a sign of salvation or status. We are set free to love and live for Christ Jesus. Freedom is a wonderful thing, both spiritually and economically, and this is the point, modern-day feminism lacks the understanding for both, as we shall see.
[82] John W. Mauck, Paul on Trial: The Book of Acts as a Defense of Christianity (Nashville, TN: Thomas Nelson, 2001), 56.
[83] Acts 18:2, 18, 19, 26; Romans 16:3; 2 Timothy 4:19.
[84] Mauck, Paul on Trial, 56.
[85] Gregory A. Boyd, Jesus Under Siege (Wheaton, IL: Victor Books, 1995), 118.
[86] Ibid., 118.
[87] O. C. Edwards, “A Surprising View of Gnosticism,” New Review of Books and Religion, May 1980, 27. Quoted in, Gary R. Habermas, The Historical Jesus: Ancient Evidence for the Life of Christ (Joplin, MS: College Press, 1996), 107.
Theologian/professor Wayne Grudem has this nugget tucked away in his wonderful seminary-level treatment of culture and the Bible:
Historian Alvin Schmidt points out how the spread of Christianity and Christian influence on government was primarily responsible for outlawing infanticide, child abandonment, and abortion in the Roman Empire (in AD 374); outlawing the brutal battles-to-the-death in which thousands of gladiators had died (in 404); outlawing the cruel punishment of branding the faces of criminals (in 315); instituting prison reforms such as the segregating of male and female prisoners (by 361); stopping the practice of human sacrifice among the Irish, the Prussians, and the Lithuanians as well as among other nations; outlawing pedophilia; granting of property rights and other protections to women; banning polygamy (which is still practiced in some Muslim nations today); prohibiting the burning alive of widows in India (in 1829); outlawing the painful and crippling practice of binding young women’s feet in China (in 1912); persuading government officials to begin a system of public schools in Germany (in the sixteenth century); and advancing the idea of compulsory education of all children in a number of European countries.
During the history of the church, Christians have had a decisive influence in opposing and often abolishing slavery in the Roman Empire, in Ireland, and in most of Europe (though Schmidt frankly notes that a minority of “erring” Christian teachers have supported slavery in various centuries). In England, William Wilberforce, a devout Christian, led the successful effort to abolish the slave trade and then slavery itself throughout the British Empire by 1840.
In the United States, though there were vocal defenders of slavery among Christians in the South, they were vastly outnumbered by the many Christians who were ardent abolitionists, speaking, writing, and agitating constantly for the abolition of slavery in the United States. Schmidt notes that two-thirds of the American abolitionists in the mid-1830s were Christian clergymen, and he gives numerous examples of the strong Christian commitment of several of the most influential of the antislavery crusaders, including Elijah Lovejoy (the first abolitionist martyr), Lyman Beecher, Edward Beecher, Harriet Beecher Stowe (author of Uncle Tom’s Cabin), Charles Finney, Charles T. Torrey, Theodore Weld, William Lloyd Garrison, “and others too numerous to mention.” The American civil rights movement that resulted in the outlawing of racial segregation and discrimination was led by Martin Luther King Jr., a Christian pastor, and supported by many Christian churches and groups.
There was also strong influence from Christian ideas and influential Christians in the formulation of the Magna Carta in England (1215) and of the Declaration of Independence (1776) and the Constitution (1787) in the United States. These are three of the most significant documents in the history of governments on the earth, and all three show the marks of significant Christian influence in the foundational ideas of how governments should function.
Wayne Grudem, Politics According to the Bible [Grand Rapids, MI: Zondervan, 2010], 49-50.
Godfather has this great point about both the Constitution and the Bible being “forward thinking documents”:
Those who pushed for the Equal Rights Amendment argued “that “women were left out of the Constitution.” Robert A. Goldwin, writing in “Why Blacks, Women & Jews Are Not Mentioned in the Constitution,” states the following:
“The fact is, however, that women were not left out; they have always been included in all of the constitutional protections provided to all persons, fully and equally, without any basis in the text for discrimination on the basis of sex. How were they included without being mentioned?
“The place to start is that famous provision we considered previously, Article I, section 2, clause 3, describing who will be counted for purposes of representation in the House of Representatives. The phrase ‘the whole number of free persons’ is chiefly where the women are, but they are also among ‘those bound to service for a term of years,’ and even among taxed Indians and ‘all other persons.’ It is quite remarkable that they are not excluded from any one of these groups because, in 1787, women did not vote or hold office anywhere in the United States and were excluded from every level of government. What would be unremarkable, and typical of the time, would be a clear exclusion of women.”
Compare the Constitution to the Northwest Ordinance, which was drafted in the same year as the Constitution, where the phrase “free male inhabitants, of full age, in the district . . . shall receive authority . . . to elect representatives . . . to represent them in the general assembly. . . . Provided also, that a freehold in fifty acres of land . . . shall be necessary to qualify a man as an elector of a representative.”2
Goldwin continues in his very informative article that everybody should read, especially those at the Defense Department:
“In the original Constitution, unlike the Northwest Ordinance, the words ‘man’ or ‘male’ do not occur, nor does any other noun or adjective denoting sex. By not mentioning women or men, speaking instead only of persons, the Constitution must mean that every right, privilege, and protection afforded to persons in the Constitution is afforded to female persons as well as male persons, equally.”
The Bible and the Constitution are very forward-thinking documents…
Not only are these documents forward thinking, for instance, in the early church you had for the first time slaves and slave owners being made equal. NOT in the “workplace,” but when they went to the same place to worship, the slave may have better works-kills as well as task setting for running a meeting place. SO in fact, the slave may have been relied on more and in a leadership position of asking his master to do certain tasks to help the meeting run smooth.
Some of the early letter to the church dealt with this new [first time in history] interaction (see: The Bible and Slavery).
Other issues here is that the Left and class warfare type courses simplify history in order to make a point they are making, stick. It is similar to taking a verse from the Bible out of it’s historical setting, the surroundings, the people it was meant for, the language and idioms/colloquial understandings used in the text — and forcing 21st-century typology onto it (eisegesis).
We see for instance that the early history of our natiuon was more complicated than the Defense Deptartment’s slide and the details in the course. Professor Thomas West points this out in his excellent book, Vindicating The Founders:
It is not only radical feminists who deplore the Founders’ supposed indifference to women’s rights. Mainstream textbooks also paint a gloomy picture. “When Jefferson spoke [in the Declaration of Independence] of `the people,'” writes Lorna Mason in her eighth-grade history textbook, “he meant only free white men.” Cummings and Wise’s Democracy under Pressure, a college political science text, says, “And today, two centuries later, . . . women in America are still struggling for the full freedom and equality denied them by the framers.” No effort is made in these books to understand how the Founders could have viewed women as equal without guaranteeing them the right to vote. Instead, it is assumed that the Founders were insincere or confused when they professed that all human beings have the same rights. Or else it is denied that they believed in equality at all
[….]
James MacGregor Burns’s Government by the People has gone through fifteen editions, but it still mistakenly claims that “All states [in 1787] barred women from voting.” Other textbooks mention that some women voted, only to dismiss the fact as irrelevant. But it is of the highest importance for understanding the Founders’ view of the matter.
The most remarkable case was that of New Jersey. It shows that, on this question at any rate, the Founders were hardly the bigots they have been made out to be. Women voted in large numbers in that state during the late 1790s and early 1800s.
The New Jersey state constitution of 1776 stated that “all inhabitants of this colony, of full age, who are worth fifty pounds proclamation money,… and have resided within the county… for twelve months… shall be entitled to vote.” Some historians speculate that this language was accidental, and that those who wrote it meant males. This is guesswork. There is little evidence on either side. We do know that New Jersey’s 1790 revision of its voting law dutifully implemented the constitution’s literal “all inhabitants” by referring to voters as “he or she.” A 1796 law governing voting in federal elections, used the same language: “No person shall be entitled to vote in any other township or precinct, than that in which he or she doth actually reside…. Every voter shall openly, and in full view, deliver his or her ballot….” Neither of these laws aroused any particular opposition or controversy.
We must pause briefly and note the extraordinary character of this event. For the first time in history, the women of a political community shared with men the right, stated in public law, to select their rulers. There can be only one explanation of why it happened in the United States at this particular time, and in no other country at any previous time. Most Americans, including the members of the New Jersey legislature, believed in the fundamental principle of the Revolution, that all men are created equal. No other government had ever been grounded on this idea. This belief by itself was not enough to bring about female suffrage. But it made it thinkable as an option, while it had been unthinkable for most of human history. Historians have shown that partisan calculations led New Jersey politicians to take advantage of the gender-neutral wording of the state constitution and bring women to the polls in growing numbers. But partisan motivations over the previous three thousand years of Western history had never led to such a result. Clearly, a new idea—the equality idea—changed the terms of what was politically possible. A further sign of this is that female voting generated little controversy in New Jersey for some years.
We know that at least some New Jersey women voted in the year of the Constitutional Convention. Historian Richard McCormick writes, “A Burlington poll list of 1787 contained the names of Iona Curtis and Selve-ria Lilvey, presumably women.” The first newspaper discussion of female voting in New Jersey did not occur until 1797, when the Federalist candidate in a hotly contested election to the state legislature was supported (unsuccessfully) by the women of Elizabethtown. In the Adams-Jefferson presidential election of 1800, and in other subsequent elections, women voted in large numbers throughout the state.
Strictly speaking, only women (and men) who owned property were eligible to vote under the New Jersey law. That meant single women or widows. Married women were not counted as property owners because property within a marriage was legally credited to the husband. In practice, however, the property qualification for voting was carelessly enforced. Married women and even female slaves were often admitted to vote.
In 1800 the New Jersey Assembly considered a law that would have stated, “the inspectors of elections shall not refuse the vote of any widow or unmarried woman of full age:’ One representative wrote: “The House unanimously agreed that this section would be clearly within the meaning of the [New Jersey] Constitution, and as the Constitution is the guide of inspectors, it would be entirely useless to insert it into the law. The motion was negatived. Our Constitution gives this right to maids or widows, black or white It was later said that the votes of two or three women of color swung the election of a state legislator in 1802.
Female voting came to an end in 1807. A close electoral battle between Newark and Elizabeth over the location of a new courthouse inspired massive voting fraud on both sides. Women (and of course men) were in the thick of it. “Women and girls, black and white, married and single, with and without qualifications, voted again and again.” This episode became the excuse for an 1807 law that restricted the franchise to free white males. This law directly violated New Jersey’s constitution, which the courts thereafter dishonestly refused to acknowledge. The representative who promoted the new law most vigorously was the same Jeffersonian Republican who had nearly been defeated in 1797 by the Federalist women of Elizabeth. One partisan pamphleteer had complained that “towns and populous villages [where Federalists had greater strength] gain an unfair advantage over the country by the greater facility they enjoy over the latter, in drawing out their women to the election.”
Women also voted elsewhere in America during the founding era. Robert Dinkin, a historian of early American voting, writes, “Records from a few Massachusetts towns show that a number of widows who owned substantial property did exercise the franchise on occasion” during the colonial period. A New York newspaper reported that “two old widows tendered, and were admitted to vote” in 1737. Records are sparse, so it is likely that other incidents of female voting occurred in these and other states, both before and after the Revolution.
Thomas G. West, Vindicating The Founders: Race, Sex, Class, And Justice In Origins Of America (New York, NY: Rowman & Littlefield, 1997), 71, 75-77.
I could go on, but the ideas portrayed in the course will surely fall apart under inspection of history without the lens of cultural Marxist ideology blinding the course writers.
Back to Text

