Information drives the development of life. But what is the source of that information? Could it have been produced by an unguided Darwinian process? Or did it require intelligent design? The Information Enigma is a fascinating 21-minute documentary that probes the mystery of biological information, the challenge it poses to orthodox Darwinian theory, and the reason it points to intelligent design. The video features molecular biologist Douglas Axe and Stephen Meyer, author of the books Signature in the Cell and Darwin’s Doubt. (See more here)
Stephen Meyer


Information > RNA/DNA | Or, What “IS” Information
- “My whole life has been guided by the principle of Plato’s Socrates: Follow the evidence, wherever it leads.” After chewing on his scientific worldview for more than five decades, Flew concluded, “A super-intelligence is the only good explanation for the origin of life and the complexity of nature.” Previously, in his central work, The Presumption of Atheism (1976), Flew argued that the “onus of proof [of God] must lie upon the theist.” However, at the age of 81, Flew shocked the world when he renounced his atheism because “the argument for Intelligent Design is enormously stronger than it was when I first met it.” Prominent in his conclusion were the discoveries of DNA. | Antony Flew |
What naturalism is is described in the last paragraph. It is also described in a more relational way here, “Love.”
Professor Werner Gitt – Director and professor at the German Federal Institute of Physics and Technology – tells us that:
“The highest information density known to us is that of DNA molecules…. The storage capacity of DNA, the information carriers of living things, is 4.5 x 10 (to the 13th power) times more effective than a megachip!… The sum total of knowledge currently stored in the libraries of the world is estimated at 10(to the 18th power) bits. If this information could be stored in DNA molecules, 1% of the volume of a pinhead would be sufficient for this purpose. If, on the other hand, this information were to be stored with aid of megachips, we would need a pile higher than the distance between the earth and the moon.”
The DNA molecule, of which even the simplest – some would say the most “primitive” – forms of life are composed, is thus 45 million million times more efficient at holding and conveying information than a megachip. This is because the DNA molecule is an incredibly complex three-dimensional information storage system, where the megachip is only two-dimensional. But the DNA molecules ability to store and convey such inconceivably large amounts of information so efficiently does not tell us where the itself comes from. What is the source of that?
Information Theory, of which Professor Gitt is one of the world’s leading exponents, is an important branch of scientific investigation which has shown conclusively and consistently that information cannot and does not arise from any state of non-information, just as life cannot proceed from non-life. Moreover, information has now come to be recognized as the Third Fundamental Quantity of the universe, which hitherto was thought to consist of merely two fundamental quantities, those of matter and energy. The DNA molecule is, of course, matter. Its activities are funded by energy. But the information that it carries is something else entirely. In other words, it is not sufficient to have only matter and energy for DNA to work. What is also required, at least to begin with, is a massive input of information for which matter and energy can give no account, and which neither of them can supply. Again, Professor Gitt:
“According to Norbert Wiener, the founder of cybernetics and information theory, information cannot be of a physical nature, even though it is transmitted by physical means: ‘Information in information, neither matter nor energy. No materialism that fails to take account of this can survive the present day.’”
Because of the increasing disillusionment with the role of chance, a shift took place in the late 60’s and the 70’s to the view that life was somehow the inevitable outcome of nature’s laws at work over vast spans of time. Terms such as “directed chance” and “biochemical predestination” have entered the scientific literature to mean that life was somehow the result of the inherent properties of matter.
But more discomforting still to the materialist, is not just the recent discovery of information to be the Third Fundamental Quantity, but rather the startling realization of its source:
“If a basic code is found in any system, it can be concluded that the system originated from a mental concept, and did not arise by chance…. Meanings always represent mental concepts. They are distinct from matter and energy. They originate from an intelligent source. It is by means of language that information may be stored and transmitted on physical carriers. The information itself is invariant…. The reason for this invariance lies in its non-material nature.”
DNA stores literally coded information || DNA contains codified information || The various codes in the cell
It would seem then that while some materialists have been busy looking in all the wrong places, certain physicists have stumbled upon the Mind of God.
The problem with most of modern science is that the philosophy of reductionism is the ruling paradigm. According to George Williams, a scientist of some stature in the evolutionary community, the crucial object of selection in evolution is inherently non-material:
“Evolutionary biologists have failed to realize that they work with two more or less incommensurable domains: that of information and that of matter…. These two domains can never be brought together in any kind of the sense usually implied by the term ‘reductionism.’ … The gene is a package of information, not an object. The pattern of base pairs in a DNA molecule specifies the gene. But the DNA molecule is the medium, its not the message…. Just the fact that fifteen years ago I started using a computer may have had something to do with my ideas here. The constant process of transferring information from one physical medium to another and then being able to recover the same information in the original medium brings home the separability of information and matter. In biology, when you’re talking about things like genes and genotypes and gene pools, you’re talking about information, not physical objective reality.”
Perhaps evolutionary biologists have avoided noticing that information and matter are fundamentally different things because that insight is fatal to the whole reductionist project in biology. If the message is truly not reducible to the medium, then trying to explain the creation of the information by a materialistic theory is simply a category mistake. One might as well try to explain the origin of a literary work [say, Hamlet] by invoking the chemical laws that govern the combining of ink and paper, and then proposing speculative hypotheses about how those laws (with boost from chance but without intelligence) might have generated meaningful sentences.
Here is some more wonderful information I updated in another post that came from a conversation at Starbucks:
Preliminary Hearing at Starbucks
I had a wonderful conversation with a very nice fellow at Starbucks (I will simply refer to him at times as John D.). The encounter started because of the book I was reading and an unsolicited question about it. It was only AFTER the conversation that I noted why question about the book was asked. The book was “Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is Designed.” (Watch the author speak about the book HERE.) After the conversation had concluded, I realized what drew John D. into engaging me. During the conversation, as you will see, he intimated that he was a lawyer. Hence, the large title that drew him in is “Undeniable.”
Light conversation took place about the book, mainly because I am just beginning the book and do not know the content well enough yet to discuss it specifically. I did steer the conversation towards DNA just a tad — with Stephen Meyer’s book in mind.
For the reader of this post, keep in mind that while I did not go in-depth into the discussion of DNA that immediately follows, I did reference briefly the aspects of information being separate from the means of transmission [matter]:
Evolutionary biologist George Williams observed: “Evolutionary biologists have failed to realize that they work with two more or less incommensurable domains: that of information and that of matter…. The gene is a package of information, not an object. The pattern of base pairs in a DNA molecule specifies the gene. But the DNA molecule is the medium, it’s not the message…. These two domains will never be brought together in any kind of the sense usually implied by the term ‘reductionism. Information doesn’t have mass or charge or length in millimeters. Likewise, matter doesn’t have bytes…. This dearth of shared descriptors makes matter and information two separate domains of existence, which have to be discussed separately, in their own terms.”[1]
As the information theorist Hubert Yockey observes, the “genetic code is constructed to confront and solve the problems of communication and recording by the same principles found . . . in modern communication and computer codes.” Yockey notes that “the technology of information theory and coding theory has been in place in biology for at least 3.85 billion years,” or from the time that life first originated on earth. What should we make of this fact? How did the information in life first arise?[2]
Codes are not matter and they’re not energy. Codes don’t come from matter, nor do they come from energy. Codes are information, and information is in a category by itself.[3]
A great example is a newspaper.[4] If you read an article on a topic that is information being passed on to you by another intelligence. The modern roadblock for today’s naturalist is the problem of looking at the molecules that make up the ink printed page stores information via the 26 letters of the alphabet as somehow related to the origin of the information being passed on. The problem is that the newspaper is merely the medium, for the information. Like a Compact Disc is for music. The CD is merely the medium to carry the information.
The next question is, how much information can the DNA molecule hold?
a) A pinhead made of DNA: Let us imagine we had enough DNA to fill the volume of a pinhead with a diameter of 2 mm. How many paperbacks (each with 189 pages as in [G19]) could be represented by the information held in that amount of DNA? Answer: about 25 trillion. That would be a pile of these paperback books approximately 920 times the distance from the earth to the moon (384,000 km). In 2011, if we were to equally distribute these paperbacks amongst the approximately 6.93 billion people on Earth, every person would receive about 3,600 copies. b) Drawing a wire: Now let us stretch the material of the 2 mm diameter pinhead into a wire of the same thickness as the DNA molecule (2 x 10-6 mm). How long would this wire be? Unbelievably, it would stretch 33 times around the equator, which has a circumference of 24,860 miles (40,000 km). c) One thousandth of a gram of DNA: If we were to take a milligram (1 mg = 10-3 g) of a (double helix) strand of DNA material, it would almost stretch from the earth to the moon![5] (Click to enlarge) Dr. George Church, a pioneering molecular geneticist at Harvard/MIT, informed us in a Sciencexpress article in August of 2012, that the digital-information storage capacity of DNA is “very dense.” How dense? One gram of DNA can store 455 exabytes of information. For those readers like myself whose eyes glaze over as soon as computer nerds start talking about bytes and RAM’s I will put it in simple layman’s terms. One gram of DNA – the weight of two Tylenol – can store the same amount of digitally encoded information as a hundred billion DVD’s. Yes, you read correctly, I said a hundred billion DVD’s. Every single piece of information that exists on the Earth today; from every single library, from every single data base, from every single computer, could be stored in one beaker of DNA. This is the same DNA/Genetic Information/Self-Replication System that exists in humans and in bacteria (which are the simplest living organisms that exist today and have ever been known to exist). In short, our DNA-based genetic code, the universal system for all life on our planet, is the most efficient and sophisticated digital information storage, retrieval, and translation system known to man.[6] I will repeat a line from the above graphic description: Let me give you another example of the same sort of reasoning. Imagine that you have just finished reading a fabulous novel. Wanting to read another book like it, you exclaim to a friend, “Wow! That was quite a book. I wonder where I can get a bottle of that ink?” Of course not! You wouldn’t give the ink and paper credit for writing the book. You’d praise the author, and look for another book by the same writer. By some twist of logic, though, many who read the fabulous DNA script want to give credit to the “ink (DNA base code) and paper (proteins)” for composing the code. In a novel, the ink and paper are merely the means the author uses to express his or her thoughts. In the genetic code, the DNA bases and proteins are merely the means God uses to express His thoughts.[7] Human DNA is like a computer program but far, far more advanced than any software ever created.[8] Information is information, neither matter nor energy. No materialism that fails to take account of this can survive the present day. – Norbert Weiner, MIT Mathematician and Father of Cybernetics[9] [1] This is a fuller quote adapted from two sources: Donald E. Johnson, Probability’s Nature and Nature’s Probability : A Call to Scientific Integrity (Charleston, SC: Booksurge Publishing, 2009), 44; Stephen C. Meyer, Signature in the Cell: DNA and the Evidence for Intelligent Design (New York, NY: Harper One, 2009), 17. [2] Meyer, ibid. [3] Perry Marshall, Evolution 2.0: Breaking the Deadlock Between Darwin and Design (Dallas, TX: Benbella Books, 2016), 187. [4] The graphic to the right of the footnote is from, Werner Gitt, In the Beginning Was Information (Bielefeld, Germany: Christliche Literatur-Verbreitung, 1997), 86. [5] Werner Gitt, Without Excuse (Atlanta, GA: Creation Book Publishers, 2011), 288 (graph from p. 286). [6] Moshe Averick, Atheistic Science is Rapidly Sinking in the Quicksand, algemeiner. [7] Gary Parker, 1.3 The Origin of Life: DNA and Protein, AiG. [8] Bill Gates, The Road Ahead (New York, NY: Penguin Group, 1995), 188. [9] Stan Lennard, So Easy a Caveman Could Do It?, RtB.
Here is a great presentation[s] and a QandA by Stephen Meyer discussing his Signature In The Cell:
ONE MUST INCLUDE THESE OTHER POSTS AS WELL!!!

Preliminary Hearing at Starbucks (Conversation Series)
I had a wonderful conversation with a very nice fellow at Starbucks (I will simply refer to him at times as John D.). The encounter started because of the book I was reading and an unsolicited question about it. It was only AFTER the conversation that I noted why question about the book was asked. The book was “Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is Designed.” (Watch the author speak about the book HERE.) After the conversation had concluded, I realized what drew John D. into engaging me. During the conversation, as you will see, he intimated that he was a lawyer. Hence, the large title that drew him in is “Undeniable.”
Light conversation took place about the book, mainly because I am just beginning the book and do not know the content well enough yet to discuss it specifically. I did steer the conversation towards DNA just a tad — with Stephen Meyer’s book in mind.
For the reader of this post, keep in mind that while I did not go in-depth into the discussion of DNA that immediately follows, I did reference briefly the aspects of information being separate from the means of transmission [matter]:
Evolutionary biologist George Williams observed: “Evolutionary biologists have failed to realize that they work with two more or less incommensurable domains: that of information and that of matter…. The gene is a package of information, not an object. The pattern of base pairs in a DNA molecule specifies the gene. But the DNA molecule is the medium, it’s not the message…. These two domains will never be brought together in any kind of the sense usually implied by the term ‘reductionism. Information doesn’t have mass or charge or length in millimeters. Likewise, matter doesn’t have bytes…. This dearth of shared descriptors makes matter and information two separate domains of existence, which have to be discussed separately, in their own terms.”[1]
As the information theorist Hubert Yockey observes, the “genetic code is constructed to confront and solve the problems of communication and recording by the same principles found . . . in modern communication and computer codes.” Yockey notes that “the technology of information theory and coding theory has been in place in biology for at least 3.85 billion years,” or from the time that life first originated on earth. What should we make of this fact? How did the information in life first arise?[2]
Codes are not matter and they’re not energy. Codes don’t come from matter, nor do they come from energy. Codes are information, and information is in a category by itself.[3]
A great example is a newspaper.[4] If you read an article on a topic that is information being passed on to you by another intelligence. The modern roadblock for today’s naturalist is the problem of looking at the molecules that make up the ink printed page stores information via the 26 letters of the alphabet as somehow related to the origin of the information being passed on. The problem is that the newspaper is merely the mediu, for the information. Like a Compact Disc is for music. The CD is merely the medium to carry the information. The
The next question is, how much information can the DNA molecule hold?
a) A pinhead made of DNA: Let us imagine we had enough DNA to fill the volume of a pinhead with a diameter of 2 mm. How many paperbacks (each with 189 pages as in [G19]) could be represented by the information held in that amount of DNA? Answer: about 25 trillion. That would be a pile of these paperback books approximately 920 times the distance from the earth to the moon (384,000 km). In 2011, if we were to equally distribute these paperbacks amongst the approximately 6.93 billion people on Earth, every person would receive about 3,600 copies. b) Drawing a wire: Now let us stretch the material of the 2 mm diameter pinhead into a wire of the same thickness as the DNA molecule (2 x 10-6 mm). How long would this wire be? Unbelievably, it would stretch 33 times around the equator, which has a circumference of 24,860 miles (40,000 km). c) One thousandth of a gram of DNA: If we were to take a milligram (1 mg = 10-3 g) of a (double helix) strand of DNA material, it would almost stretch from the earth to the moon![5] (Click to enlarge) Dr. George Church, a pioneering molecular geneticist at Harvard/MIT, informed us in a Sciencexpress article in August of 2012, that the digital-information storage capacity of DNA is “very dense.” How dense? One gram of DNA can store 455 exabytes of information. For those readers like myself whose eyes glaze over as soon as computer nerds start talking about bytes and RAM’s I will put it in simple layman’s terms. One gram of DNA – the weight of two Tylenol – can store the same amount of digitally encoded information as a hundred billion DVD’s. Yes, you read correctly, I said a hundred billion DVD’s. Every single piece of information that exists on the Earth today; from every single library, from every single data base, from every single computer, could be stored in one beaker of DNA. This is the same DNA/Genetic Information/Self-Replication System that exists in humans and in bacteria (which are the simplest living organisms that exist today and have ever been known to exist). In short, our DNA-based genetic code, the universal system for all life on our planet, is the most efficient and sophisticated digital information storage, retrieval, and translation system known to man.[6] I will repeat a line from the above graphic description: Let me give you another example of the same sort of reasoning. Imagine that you have just finished reading a fabulous novel. Wanting to read another book like it, you exclaim to a friend, “Wow! That was quite a book. I wonder where I can get a bottle of that ink?” Of course not! You wouldn’t give the ink and paper credit for writing the book. You’d praise the author, and look for another book by the same writer. By some twist of logic, though, many who read the fabulous DNA script want to give credit to the “ink (DNA base code) and paper (proteins)” for composing the code. In a novel, the ink and paper are merely the means the author uses to express his or her thoughts. In the genetic code, the DNA bases and proteins are merely the means God uses to express His thoughts.[7] Human DNA is like a computer program but far, far more advanced than any software ever created.[8] Information is information, neither matter nor energy. No materialism that fails to take account of this can survive the present day. – Norbert Weiner, MIT Mathematician and Father of Cybernetics[9] [1] This is a fuller quote adapted from two sources: Donald E. Johnson, Probability’s Nature and Nature’s Probability : A Call to Scientific Integrity (Charleston, SC: Booksurge Publishing, 2009), 44; Stephen C. Meyer, Signature in the Cell: DNA and the Evidence for Intelligent Design (New York, NY: Harper One, 2009), 17. [2] Meyer, ibid. [3] Perry Marshall, Evolution 2.0: Breaking the Deadlock Between Darwin and Design (Dallas, TX: Benbella Books, 2016), 187. [4] The graphic to the right of the footnote is from, Werner Gitt, In the Beginning Was Information (Bielefeld, Germany: Christliche Literatur-Verbreitung, 1997), 86. [5] Werner Gitt, Without Excuse (Atlanta, GA: Creation Book Publishers, 2011), 288 (graph from p. 286). [6] Moshe Averick, Atheistic Science is Rapidly Sinking in the Quicksand, algemeiner. [7] Gary Parker, 1.3 The Origin of Life: DNA and Protein, AiG. [8] Bill Gates, The Road Ahead (New York, NY: Penguin Group, 1995), 188. [9] Stan Lennard, So Easy a Caveman Could Do It?, RtB.
…Continuing
After relaying the basics of information and DNA, I then went through what I have memorized quite well — here are the bullet points:
- Albert Einstein developed his general theory of relativity in 1915;
- Around the same time evidence of an expanding universe was being presented to the American Astronomical Society by Vesto Slipher;
- In the 1920s using Einstein’s theory, a Russian mathematician (Alexander Friedman) and the Belgium astronomer (George Lemaitre) predicted the universe was expanding;
- In 1929, Hubble discovered evidence confirming earlier work on the Red-Light shift showing that galaxies are moving away from us;
- In the 1940’s, George Gamow predicted a particular temperature to the universe if the Big Bang happened;
- In 1965, two scientists (Arno Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson) discovered the universe’s background radiation — and it was only about 3.7 degrees above absolute zero.
(see more)
I mentioned that this information from science supports the Hebrew Scripture’s account of creation ex nihilo [from nothing], whereas, all the other writings from the Egyptians, Sumerian, Greeks, as well as all the major religious texts all posit an eternal universe or matter in some form or another. I relayed this quote roughly, noting Dr. Wilson’s participation in the Big-Bang becoming a widely accepted:
- “Certainly there was something that set it all off. Certainly, if you are religious, I can’t think of a better theory of the origin of the universe to match with Genesis.” ~ Robert Wilson: is an American astronomer, 1978 Nobel laureate in physics, who with Arno Allan Penzias discovered in 1964 the cosmic microwave background radiation.
John D. then steered the conversation towards other matters, giving me some biographical information about himself. He mentioned he was a lawyer. I gave him my card to my site and explained that if you hover over “Home” with your mouse (at the top of my site), to click on “Recommended Reads.” I pulled this page up on my phone and mentioned these top four books are by lawyers or people specialized in evidence… the parameters of which courts use as acceptable. I pointed to the Simon Greenleaf book, and started to explain his background to him…
 |
 |
 |
 |
… I noted that Simon Greenleaf wrote what was a first in American history, giving our court system a 3-volume set on what “is” evidence, thus, divorcing us from the British concepts of what courts should and should not accept as evidence. His work, “A Treatise on the Law of Evidence. 3 Vols.,” is considered a classic of American jurisprudence and is still used in law-schools today as part of the history of law. I included a bit more biographical info before getting to the main part of the point. I mentioned Dr. Greenleaf was an atheist (really I should have said agnostic) as well as a Jew who was skeptical of the Resurrection of Jesus. Continuing I said that Simon Greenleaf took his knowledge of what makes good evidence to respond to a challenge by a student in regards to applying the rules of evidence to the Gospels to prove-or-disprove the Resurrection. After about two-years, Dr. Greenleaf became a Christian and wrote his book, “Testimony of the Evangelists.“
Simon Greenleaf died October 6, 1853. Born of Jewish descent on December 5, 1783, Greenleaf was an agnostic, some say atheist, who believed the resurrection of Jesus Christ was either a hoax or a myth. No stranger to truth, and to the proof of the truth, Greenleaf was a principal founder of the Harvard Law School and a world-renowned expert on evidence. Challenged by one of his students one day to “consider the evidence” for the Resurrection of Jesus Christ, Greenleaf set out to disprove it, but ended up concluding that the Resurrection of Jesus Christ was indeed fact, not fiction. Being a man of conviction and reason, and in accordance with his conclusions, Greenleaf converted from Agnosticism to Christianity. His life and works went on to inspire such scholars as John Warwick Montgomery, Josh McDowell, Ross Clifford and Lee Strobel…. (Biographical Info)
It was when I finished that part of our discussion that he mentioned he was Jewish. “Awesome, I am glad I focused in on Simon Greenleaf then,” I thought to myself. John D. then segued by stating that as a lawyer he would never introduce such hearsay/shabby evidence as what the Old Testament affords people, mentioning specifically the old testament not pre-dating the Dead Sea Scrolls in any written form (they date around 200 B.C. or younger. I did not bring up an earlier example (by 400-years) of a partial scroll of Numbers, instead, I wanted to bring into his court room he was apparently running something along the same lines. Or this recent tech advance allowing the reading of a 2,000 year-old scroll:
This comes by way of END TIME blog:
…Modern Technology Unlocks Secrets of a Damaged Biblical Scroll
Nearly half a century ago, archaeologists found a charred ancient scroll in the ark of a synagogue on the western shore of the Dead Sea. The lump of carbonized parchment could not be opened or read. Its curators did nothing but conserve it, hoping that new technology might one day emerge to make the scroll legible. Just such a technology has now been perfected by computer scientists at the University of Kentucky. Working with biblical scholars in Jerusalem, they have used a computer to unfurl a digital image of the scroll.
So neat! What does the text say?
It turns out to hold a fragment identical to the Masoretic text of the Hebrew Bible and, at nearly 2,000 years old, is the earliest instance of the text. … The scroll’s content, the first two chapters of the Book of Leviticus, has consonants — early Hebrew texts didn’t specify vowels — that are identical to those of the Masoretic text, the authoritative version of the Hebrew Bible and the one often used as the basis for translations of the Old Testament in Protestant Bibles.
So the authoritative 1000 year old Masoretic text is identical to this 2000 year old text found and examined by computer? Those tenth century monks who precisely copied and instituted rules for further copying so as to ensure perfection of the texts is proved 100% reliable by computer forensics in this millennial age? Even more neat!
“We have never found something as striking as this,” Dr. Tov said. “This is the earliest evidence of the exact form of the medieval text,” he said, referring to the Masoretic text.
It is striking, that a 2000 year old text from Leviticus is exact as to the Masoretic texts copied in 1000 AD! So thrilling…
I mentioned that in the Dead Sea Scrolls was an intact copy of Isaiah. At the time the oldest manuscript the Church had was dated at A.D. 980. When the Dead Sea Scrolls were found we had a copy dated to 125 B.C. — that is just about 1,100 years apart. Only one single word was added to the text that was likewise previously confirmed by the LXX.
The word “light”
He will see it[a] out of His anguish,
and He will be satisfied with His knowledge.
My righteous Servant will justify many,
and He will carry their iniquities.
Footnotes: [a] Isaiah 53:11 DSS [Dead Sea Scrolls],
LXX [Septuagint] read see light
Here we see the ending paragraphs giving an overview of the issue in the excellent book by Dr.’s Geisler and Nix:
With the discovery of the Dead Sea Scrolls, scholars have Hebrew manuscripts one thousand years earlier than the great Masoretic Text manuscripts, enabling them to check on the fidelity of the Hebrew text. The result of comparative studies reveals that there is a word-for-word identity in more than 95 percent of the cases, and the 5 percent variation consists mostly of slips of the pen and spelling. To be specific, the Isaiah scroll (1Q Isa) from Qumran led the Revised Standard Version translators to make only thirteen changes from the Masoretic Text; eight of those were known from ancient versions, and few of them were significant. More specifically, of the 166 Hebrew words in Isaiah 53 only seventeen Hebrew letters in 1Q Isb differ from the Masoretic Text. Ten letters are a matter of spelling, four are stylistic changes, and the other three compose the word for “light” (add in v. 11), which does not affect the meaning greatly. Furthermore that word is also found in that verse in the LXX and 1Q Isa.
CONCLUSION
The [many] thousands of Hebrew manuscripts, with their confirmation by the LXX and the Samaritan Pentateuch, and the numerous other crosschecks from outside and inside the text provide overwhelming support for the reliability of the Old Testament text. Hence, it is appropriate to conclude with Sir Frederic Kenyon’s statement, “The Christian can take the whole Bible in his hand and say without fear or hesitation that he holds in it the true word of God, handed down without essential loss from generation to generation throughout the centuries.”
Norman Geisler and William Nix, A General Interdiction to the Bible (Chicago, IL: Moody, 1986), 382.
I mentioned that in our case the court would not worry about the amount of years between the two documents, rather they would show precedence that very little has changed between the two. So In a court all that would matter to the jury is how these texts are transmitted and if this transmission is done well/accurately. John D. even mentioned the telephone game where one kid whispers into another kids ear… and by the end of circle you are left with something different. I would note as politely as possible that that analogy is a non-sequitur, and leave it at that.
(By the way, introducing Detective Wallace’s work always allows me to give my testimony. While I was one of the early inmates to super-max here in my town, he connected with that in that before it officially opened, he got to tour the facility.)
The odd thing is — at least to me — is that he made a comment about hearsay testimony after I mentioned J. Warner Wallace’s BOOK and discussed some of his biographical background. John D. mentioned that to bring into to court a person that hadn’t had a police officer immediately (or very close to the event) write down the witness’ description of events that the testimony would be thrown out.
I was shocked.
So I brought up a hypothetical crime done in a neighborhood where people typically keep silent, whether out of fear, culture, whatever. Lets say it was a murder. Some months later [even years] some witnesses start coming forward… four of them, and described the events. Each a little different because of recollection, vantage point, their demeanor, and the like. But the witnesses describe something that fit well with the forensic evidence. I was politely blunt with John when I said of course you could easily get a conviction of this murderer. He agreed, mentioning circumstantial evidence. Which is really what we are talking about.
My friends started showing up for the Bible study I was early for… but John had to tell me a story about Jewish tradition and children. “Seders” was the topic and children were the true scribes of tradition. Which is partially true… that is how the Jewish tradition and culture has lasted for all this time – memorization and habit. I even write that Christians should take their Gospel studies as seriously. He discussed how innocent children are not knowing how to even lie to about 4-years old. I did not interrupt him, even though the Bible (see “A”) and studies of children (see “B”) show this not to be the case, I wanted him to say what he needed to say.
Before I said my final statements… as he wanted to get his coffee and go (we had talked almost half-an-hour). I simply reiterated his statement to me near the beginning of the conversation that he had yet to see evidence that he would make him consider or take the Bible seriously (a rough recap of his statement). I got him to admit that he hasn’t gone out of his way to do so, and that if I got him a single book — if he would take it as a gift and consider reading it when he has the time.
To which he agreed.
I then concluded with my final thoughts to close us out. I mainly went over the conversation in bullet point form; mentioning of the evidences we discussed (scientific evidences as well as manuscript evidences) which I added go a long way to build a case for the Bible and the Judeo-Christian faith. I then pointed him back to what he wanted. That is, he shared a colloquial story from his family (which is fine), but his lovely “story” about the innocence of children and their faithful transmission of tradition was no part of what a court would accept.
At that he went his way. John is a regular and I look forward to future discussions with him if he wishes. But more than that, even though I am using a pseudo name for him PLEASE PRAY that the Holy Spirit quicken his heart to His truths. As he reads the book I got him pray that he follows some of the references/resources to further look into the claims of this Jesus.
I hope as well me adding to the conversation and linking out to other resources is a help for your future conversations.
…The total depravity of man is seen throughout the Bible. Man’s heart is “deceitful and desperately wicked” (Jeremiah 17:9). The Bible also teaches us that man is born dead in transgression and sin (Psalm 51:5, Psalm 58:3, Ephesians 2:1-5). The Bible teaches that because unregenerate man is “dead in transgressions” (Ephesians 2:5), he is held captive by a love for sin (John 3:19; John 8:34) so that he will not seek God (Romans 3:10-11) because he loves the darkness (John 3:19) and does not understand the things of God (1 Corinthians 2:14). Therefore, men suppress the truth of God in unrighteousness (Romans 1:18) and continue to willfully live in sin. Because they are totally depraved, this sinful lifestyle seems right to men (Proverbs 14:12) so they reject the gospel of Christ as foolishness (1 Corinthians 1:18) and their mind is “hostile toward God; for it does not subject itself to the law of God, for it is unable to do so” (Romans 8:7).
The Apostle Paul summarizes the total depravity of man in Romans 3:9-18. He begins this passage by saying that “both Jews and Greeks are all under sin.” Simply put, this means that man is under the control of sin or is controlled by his sin nature (his natural tendency to sin)…
Whether lying about raiding the biscuit tin or denying they broke a toy, all children try to mislead their parents at some time. Yet it now appears that babies learn to deceive from a far younger age than anyone previously suspected.
Behavioural experts have found that infants begin to lie from as young as six months. Simple fibs help to train them for more complex deceptions in later life.
Until now, psychologists had thought the developing brains were not capable of the difficult art of lying until four years old.
Following studies of more than 50 children and interviews with parents, Dr Vasudevi Reddy, of the University of Portsmouth’s psychology department, says she has identified seven categories of deception used between six months and three-years-old.
Infants quickly learnt that using tactics such as fake crying and pretend laughing could win them attention. By eight months, more difficult deceptions became apparent, such as concealing forbidden activities or trying to distract parents’ attention.
By the age of two, toddlers could use far more devious techniques, such as bluffing when threatened with a punishment.
Dr Reddy said: “Fake crying is one of the earliest forms of deception to emerge, and infants use it to get attention even though nothing is wrong. You can tell, as they will then pause while they wait to hear if their mother is responding, before crying again.
“It demonstrates they’re clearly able to distinguish that what they are doing will have an effect. This is essentially all adults do when they tell lies, except in adults it becomes more morally loaded.”…
UPDATE — LEVITICUS
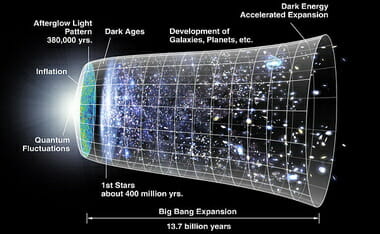
Theistic Implications of Big-Bang Cosmology
Please see my post on the “Scientific and Anecdotal Evidence for the Beginning of the Universe“
WINTERY KNIGHT notes some of the topics via the above video/lecture:
Topics:
- Up until the the last 100 years or so, everyone agreed that the universe was eternal
- This is at odds with the traditional Christian view that God created the universe
- Materialism, the view that matter is all there is, requires eternally existing matter
- Discovery #1: Hubble discovers that the universe is expanding (redshift observation)
- The expanding universe was resisted by proponents of the eternal universe, like Einstein
- Some naturalists even proposed speculative static models like the steady-state model
- However, not of the speculative models fit with observations and experimental results
- Discovery #2: Penzias and Wilson discover the cosmic microwave background radiation
- Measurements of this background radiation confirmed a prediction of the Big Bang theory
- The steady-state theory was falsified of by the discovery of this background radiation
- The oscillating model was proposed to prevent the need for an absolute beginning
- But the oscillating model is not eternal, it loses energy on each “bounce”
- A paper by Alan Guth and Marc Sher from 1982 proved that our universe will not bounce
- In addition, experiments reveal that the universe will expand forever, and not contract
- The beginning of the universe is more at home in a theistic worldview than an atheistic one
- The beginning of the universe fits in well with the Bible, e.g. – Genesis 1, Titus 1, etc.
In case you are wondering about what the evidence is for the Big Bang, here are that are most commonly offered:
Three main observational results over the past century led astronomers to become certain that the universe began with the big bang. First, they found out that the universe is expanding—meaning that the separations between galaxies are becoming larger and larger. This led them to deduce that everything used to be extremely close together before some kind of explosion. Second, the big bang perfectly explains the abundance of helium and other nuclei like deuterium (an isotope of hydrogen) in the universe. A hot, dense, and expanding environment at the beginning could produce these nuclei in the abundance we observe today. Third, astronomers could actually observe the cosmic background radiation—the afterglow of the explosion—from every direction in the universe. This last evidence so conclusively confirmed the theory of the universe’s beginning that Stephen Hawking said, “It is the discovery of the century, if not of all time.”
(MORE)

Michael Behe & Stephen Meyer Destroy Challenge to Flagellum Motor
The idea that Behe’s flagellum motor has been answered is wishful thinking at best, and corrupt science at it’s worst (scientism: which is an insertion of a metaphysical principle stating things like “the only quantifiable reality known is the one made up of atoms, and, science [thus defined] is the best means to understanding said reality”). Really, then, it is an “evolution-of-the-gaps” type thinking.
✿ Ken Miller’s challenge can be read here;
✿ Responses to it and derivatives to it can be found here.
But as one can see… these giants of I.D. did truly wipe the floor with their critics [full exchange].
By-the-way, all this just got WAY MORE complex. For instance, here is the fast-swimming magnetotactic bacterium MO-1… it has 7-flagellum motors… with counter gears:
Here is a basic animation:
One should see Malcolm Bowden’s presentation on YouTube of the bacterium MO-1 as well.
And NOW even more complex is the fact that quantum mechanics may play a role (unrelated to the DNA or RNA) that folds these proteins into the shape for pieces to the whole of the working part.

What’s Behind it all? God, Science and the Universe
A post appeared on an I.D. Facebook group with this introduction:
Given the fact that he is a staunch Darwinist who fully accepts the basic tenets of the mainstream theory of evolution, you might expect Larry Moran (who, after all, did coin the derisive term “IDiots” in reference to Intelligent Design proponents) to have nothing but sneering contempt for Stephen Meyer.
Turns out, however, he met Stephen Meyer and the two got along surprisingly well, despite their deep ideological divide.
I went to the Moran’s blog and wanted to post his thoughts on Lawrence Krauss:
- Krauss tried to hammer Meyer on the “ID is not science” issue using quotes from a judge based on things said by lawyers in the Dover trial….. Lawrence Krauss is an expert on cosmology but he’s very weak on biology. I know it’s common for physicists to think they are experts in everything but that’s just not true. It was demonstrated in last night’s debate.

Are Miracles Even Possible? David Hume
Here is Hume’s basic premise:
“And certainly, there’s no doubt about it, that in the past, and I think also in the present, for many evolutionists, evolution has functioned as something with elements which are, let us say, akin to being a secular religion … And it seems to me very clear that at some very basic level, evolution as a scientific theory makes a commitment to a kind of naturalism, namely, that at some level one is going to exclude miracles and these sorts of things come what may.”
~ Ruse, Michael. (1993) “Nonliteralist Antievolution” AAAS Symposium: “The New Antievolutionism,” February 13, 1993, Boston, MA
Video Description Resources:
- Join us at: http://www.inspiringphilosophy.org
- To help support this ministry click here.
Are Miracles even possible events in the natural world? Theists claim miracles have happened, but is there any reason to think they could even occur? This video answers these questions.
Sources:
- An Enquiry Concerning Human Understanding – David Hume (Article)
- Lecture 12: Does God Really Act? (Video)
- The Blackwell Companion to Natural Theology (Book)
Chapter 9 – Kai-Man Kwan
Chapter 11 – Timothy and Lydia McGrew
- Miracles – CS Lewis (Book)
- Hume’s Abject Failure – John Earman (Book)
- Summa Contra Gentiles – Thomas Aquinas (Books)
- John Lennox – Science And Miracles (Video)
- Divine Action – Keith Ward (Book)
- Philosophical Foundations for a Christian Worldview – JP Moreland & William Lane Craig (Book)
- Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Cosmology and Biological Evolution – Hilary D. Regan and Mark Worthing (Book)
If science is based on the law of causality then do miracles get in the way? Scientist and philosopher John Lennox explores this question, which was made popular by David Hume.
Some quotes:
Professor: “Miracles are impossible Sean, don’t you know science has disproven them, how could you believe in them [i.e., answered prayer, a man being raised from the dead, etc.].”
Student: “for clarity purposes I wish to get some definitions straight. Would it be fair to say that science is generally defined as ‘the human activity of seeking natural explanations for what we observe in the world around us’?”
Professor: “Beautifully put, that is the basic definition of science in every text-book I read through my Doctoral journey.”
Student: “Wouldn’t you also say that a good definition of a miracle would be ‘and event in nature caused by something outside of nature’?”
Professor: “Yes, that would be an acceptable definition of ‘miracle.’”
Student: “But since you do not believe that anything outside of nature exists [materialism, dialectical materialism, empiricism, existentialism, naturalism, and humanism – whatever you wish to call it], you are ‘forced’ to conclude that miracles are impossible”
Norman L. Geisler & Peter Bocchino, Unshakable Foundations: Contemporary Answers to Crucial Questions about the Christian Faith (Minneapolis, MN: Bethany House, 2001), 63-64.
Christians claim that the birth, death, resurrection and ascension of Jesus Christ is the central chapter of world history. How do you measure such a one-off event? The writer, C.S. Lewis develops a reliable test: Does this “Grand Miracle” fit in with the rest of the Author’s other work – Nature itself?
The first Red Herring is this. Any day you may hear a man (and not necessarily a disbeliever in God) say of some alleged miracle, “No. Of course I don’t believe that. We know it is contrary to the laws of Nature. People could believe it in olden times because they didn’t know the laws of Nature. We know now that it is a scientific impossibility.”
By the “laws of Nature” such a man means, I think, the observed course of Nature. If he means anything more than that he is not the plain man I take him for but a philosophic Naturalist and will be dealt with in the next chapter. The man I have in view believes that mere experience (and specially those artificially contrived experiences which we call Experiments) can tell us what regularly happens in Nature. And he finks that what we have discovered excludes the possibility of Miracle. This is a confusion of mind.
Granted that miracles can occur, it is, of course, for experience to say whether one has done so on any given occasion. But mere experience, even if prolonged for a million years, cannot tell us whether the thing is possible. Experiment finds out what regularly happens in Nature: the norm or rule to which she works. Those who believe in miracles are not denying that there is such a norm or rule: they are only saying that it can be suspended. A miracle is by definition an exception.
[….]
The idea that the progress of science has somehow altered this question is closely bound up with the idea that people “in olden times” believed in them “because they didn’t know the laws of Nature.” Thus you will hear people say, “The early Christians believed that Christ was the son of a virgin, but we know that this is a scientific impossibility.” Such people seem to have an idea that belief in miracles arose at a period when men were so ignorant of the cause of nature that they did not perceive a miracle to be contrary to it. A moment’s thought shows this to be nonsense: and the story of the Virgin Birth is a particularly striking example. When St. Joseph discovered that his fiancee was going to have a baby, he not unnaturally decided to repudiate her. Why? Because he knew just as well as any modern gynaecologist that in the ordinary course of nature women do not have babies unless they have lain with men. No doubt the modern gynaecologist knows several things about birth and begetting which St. Joseph did not know. But those things do not concern the main point—that a virgin birth is contrary to the course of nature. And St. Joseph obviously knew that. In any sense in which it is true to say now, “The thing is scientifically impossible,” he would have said the same: the thing always was, and was always known to be, impossible unless the regular processes of nature were, in this particular case, being over-ruled or supplemented by something from beyond nature. When St. Joseph finally accepted the view that his fiancee’s pregnancy was due not to unchastity but to a miracle, he accepted the miracle as something contrary to the known order of nature. All records
[….]
It is therefore inaccurate to define a miracle as something that breaks the laws of Nature. It doesn’t. If I knock out my pipe I alter the position of a great many atoms: in the long run, and to an infinitesimal degree, of all the atoms there are. Nature digests or assimilates this event with perfect ease and harmonises it in a twinkling with all other events. It is one more bit of raw material for the laws to apply to, and they apply. I have simply thrown one event into the general cataract of events and it finds itself at home there and conforms to all other events. If God annihilates or creates or deflects a unit of matter He has created a new situation at that point. Immediately all Nature domiciles this new situation, makes it at home in her realm, adapts all other events to it. It finds itself conforming to all the laws. If God creates a miraculous spermatozoon in the body of a virgin, it does not proceed to break any laws. The laws at once take it over. Nature is ready. Pregnancy follows, according to all the normal laws, and nine months later a child is born. We see every day that physical nature is not in the least incommoded by the daily inrush of events from biological nature or from psychological nature. If events ever come from beyond Nature altogether, she will be no more incommoded by them. Be sure she will rush to the point where she is invaded, as the defensive forces rush to a cut in our finger, and there hasten to accommodate the newcomer. The moment it enters her realm it obeys all her laws. Miraculous wine will intoxicate, miraculous conception will lead to pregnancy, inspired books will suffer all the ordinary processes of textual corruption, miraculous bread will be digested. The divine art of miracle is not an art of suspending the pattern to which events conform but of feeding new events into that pattern.
[….]
A miracle is emphatically not an event without cause or without results. Its cause is the activity of God: its results follow according to Natural law. In the forward direction (i.e. during the time which follows its occurrence) it is interlocked with all Nature just like any other event. Its peculiarity is that it is not in that way interlocked backwards, interlocked with the previous history of Nature. And this is just what some people find intolerable. The reason they find it intolerable is that they start by taking Nature to be the whole of reality. And they are sure that all reality must be interrelated and consistent. I agree with them. But I think they have mistaken a partial system within reality, namely Nature, for the whole.
CS Lewis, Miracles (New York, NY: Touchstone Publishers, 1996), 62-63, 64-65, 80-81, 81-82.
STREAMING IN FROM SPACE, light reaches the human eye and deposits its information on the stippled surface of the retina. Directly thereafter I see the great lawn of Golden Gate Park; a young woman, nose ring twitching; a panting puppy; a rose bush; and beyond, a file of cars moving sedately toward the western sun. A three-dimensional world has been conveyed to a two-dimensional surface and then reconveyed to a three-dimension image.
This familiar miracle suggests, if anything does, the relevance of algorithms to the actual accomplishments of the mind; indeed, the transformation of dimensions is precisely the kind of activity that might be brought under the control of a formal program, a system of rules cued to the circumstances of vision as it takes place in a creature with two matched but somewhat asymmetrical eyes. David Marr, for example, provides (in Vision, 1982) an extraordinary account of the complex transformations undertaken in the mind’s cockpit in order to allow the eyes to see things stereoptically.
[.…]
CHANCE ALONE,” THE NOBEL Prize-winning chemist Jacques Monod once wrote, “is at the source of every innovation, of all creation in Me biosphere. Pure chance, absolutely free but blind, is at the very root of the stupendous edifice of creation.”
The sentiment expressed by these words has come to vex evolutionary biologists. “This belief,” Richard Dawkins writes, “that Darwinian evolution is ‘random,’ is not merely false. It is the exact opposite of the truth.” But Monod is right and Dawkins wrong. Chance lies at the beating heart of evolutionary theory, just as it lies at the beating heart of thermodynamics.
It is the second law of thermodynamics that holds dominion over the temporal organization of the universe, and what the law has to say we find verified by ordinary experience at every turn. Things fall apart. Energy, like talent, tends to squander itself. Liquids go from hot to lukewarm. And so does love. Disorder and despair overwhelm the human enterprise, filling our rooms and our lives with clutter. Decay is unyielding. Things go from bad to worse. And overall, they go only from bad to worse.
These grim certainties the second law abbreviates in the solemn and awful declaration that the entropy of the universe is tending toward a maximum. The final state in which entropy is maximized is simply more likely than any other state. The disintegration of my face reflects nothing more compelling than the odds. Sheer dumb luck.
But if things fall apart, they also come together. Life appears to offer at least a temporary rebuke to the second law of thermodynamics. Although biologists are unanimous in arguing that evolution has no goal, fixed from the first, it remains true nonetheless that living creatures have organized themselves into ever more elaborate and flexible structures. If their complexity is increasing, the entropy that surrounds them is decreasing. Whatever the universe-as-a-whole may be doing-time fusing incomprehensibly with space, the great stars exploding indignantly—biologically things have gone from bad to better, the show organized, or so it would seem, as a counterexample to the prevailing winds of fate.
How so? The question has historically been the pivot on which the assumption of religious belief has turned. How so? “God said: ‘Let the waters swarm with swarms of living creatures, and let fowl fly above the earth in the open firmament of heaven.”‘ That is how so. And who on the basis of experience would be inclined to disagree? The structures of life are complex, and complex structures get made in this, the purely human world, only by a process of deliberate design. An act of intelligence is required to bring even a thimble into being; why should the artifacts of life be different?
Darwin’s theory of evolution rejects this counsel of experience and intuition. Instead, the theory forges, at least in spirit, a perverse connection with the second law itself, arguing that precisely the same force that explains one turn of the cosmic wheel explains another: sheer dumb luck.
If the universe is for reasons of sheer dumb luck committed ultimately to a state of cosmic listlessness, it is also by sheer dumb luck that life first emerged on earth, the chemicals in the pre-biotic seas or soup illuminated and then invigorated by a fateful flash of lightning. It is again by sheer dumb luck that the first self-reproducing systems were created. The dense and ropy chains of RNA—they were created by sheer dumb luck, and sheer dumb luck drove the primitive chemicals of life to form a living cell. It is sheer dumb luck that alters the genetic message so that, from infernal nonsense, meaning for a moment emerges; and sheer dumb luck again that endows life with its opportunities, the space of possibilities over which natural selection plays, sheer dumb luck creating the mammalian eye and the marsupial pouch, sheer dumb luck again endowing the elephant’s sensitive nose with nerves and the orchid’s translucent petal with blush.
Amazing. Sheer dumb luck.
David Berlinski, The Deniable Darwin & Other Essays (Seattle, WA: Discovery Institute Press, 2009), 37, 47-49.
Philosophical Naturalism and the Modern Worldview
The second modern factor that has contributed to the widespread understanding that religious belief is private, practical, and relative, and need not be related to truth and reason is the widespread acceptance of philosophical naturalism as an expression of scientism. Philosophical naturalism is the idea that reality is exhausted by the spatio-temporal world of physical entities that we can investigate in the natural sciences. The natural causal Fabric of physical reality within the boundaries of space and time is all there is, was, or ever will be. The supernatural doesn’t exist except, perhaps, as a belief in people’s minds. On this view, religious beliefs are simply ways of looking at things in our search for meaning and purpose; they are not ideas that correspond to a mind-independent reality.
Philosophical naturalism is an expression of an epistemology (i.e., a theory of knowledge and justified or warranted belief) known as scientism. Scientism is the view that the natural sciencesare the very paradigm of truth and rationality. If something does not square with currently well-established beliefs, if it is not within the domain of entities appropriate for scientific investigation, or if it is not amenable to scientific methodology then it is not true or rational. Everything outside of science is a matter of mere belief and subjective opinion, of which rational assessment is impossible. Applied to the question of the historical origins of Christianity, scientism implies that since we live in the modern scientific world where the sun is the center of the solar system, the wireless is available for our use, and the atoms power has been harnessed, we can no longer believe in a biblical worldview with its miracles, demons, and supernatural realities.
Obviously, it is impossible in the brief space of an introduction to critique adequately scientism and naturalism. Still, a few cursory remarks need to be expressed.
(1) Scientism is simply false for three reasons. (a) It is self-refining, i.e., it falsifies itself. Why? Scientism is itself a statement of philosophy about knowledge and science; it is not a statement ofscience itself. Moreover, it is a statement of philosophy that amounts to the claim that no statements outside scientific ones, including scientism itself (because it is a statement of philosophy), can be true or supported by rational considerations. (b) Science itself rests on a number of assumptions: the existence of a theory-independent external world, the orderly nature of the external world, the existence of truth and the reliability of our senses and rational faculties to gather truth about the world in a trustworthy manner, the laws of logic and the truths of mathematics, the adequacy of language (including mathematical language) to describe the external world, the uniformity of nature, and soon. Now, each one of these assumptions is philosophical in nature. The task of stating, criticizing, and defending the assumptions of science rests in the field of philosophy. Scientism fails to leave room for these philosophical tasks and, thus, shows itself to be a foe and not a friend of science. (c) There are many things we know in religion, ethics, logic, mathematics, history, art, literature, and so on that are simply not matters of science. For example, we all know that two is an even number, that Napoleon lived, that torturing babies for fun is wrong, that if A is larger than B and B is larger than C, then A is larger than C, and so on. None of these items of knowledge are scientific in nature, and scientism is falsified by their reality.
(2) Philosophical naturalism is false as well. For one thing, philosophical naturalism rules out the existence of a number of things that do, in fact, exist. And while we cannot defend their existence here, suffice it to say that, currently, a number of intellectuals have offered convincing arguments for the reality of universals and other abstract objects such as numbers, the laws of logic, values, the soul and its various mental states (including the first person point of view), other minds, libertarian or full-blown freedom of the will, and so on. None of these items can be classified as mere physical objects totally within the causal fabric of the natural spatio-temporal universe. In fact, it is not an exaggeration to say that there is not a single issue of importance to human beings that is solely a matter of scientific investigation or that can be satisfactorily treated by philosophical naturalists.
(3) Philosophical naturalism fails to explain adequately the fact that there are a number of arguments and pieces of evidence that make belief in God more reasonable than disbelief. Some of this evidence actually comes from science: the fact that the universe had a beginning based on the Big Bang theory and the second law of thermodynamics, the existence of biological information in DNA that is closely analogous to intelligent language and that cannot arise from the accidental collisions of physical entities according to laws of nature, the reality of the mental and of free will according to a number of emerging psychological theories of the self, the delicate fine-tuning of the universe, and so on.”
Like it or not, a significant and growing number of scientists, historians of science, and philosophers of science see more scientific evidence now for a personal creator and designer than was available fifty years ago. In light of this evidence, it is false and naive to claim that modern science has made belief in the supernatural unreasonable. Such a view can be called ostrich naturalism—a position that requires its advocate to keep his or her head in the sand and not to acknowledge real advances in science. The plain truth is that science itself makes no statements about all of reality anyway, nor does science itself offer any support for philosophical naturalism. What does support philosophical naturalism are the ideological claims of naturalists themselves regarding what science ought to say if we assume philosophical naturalism to begin with.
In sum, it matters much that our religious beliefs are both true and reasonable. Moreover, there simply are no sufficient reasons for not believing in the supernatural, and there are in fact a number of good reasons (including but going beyond scientific ones) for believing in the supernatural. As we have said, space considerations do not permit us to defend this last claim here. But we will list some sources in the bibliography that adequately justify this claim. If you are an honest inquirer about the truth of religion, moral and intellectual integrity unite in placing a duty on you to read these works as a sincere seeker of the truth. It is well past time to rest content with the politically correct, unjustified assertions of scientism and philosophical naturalism. University libraries are filled with books that show the weaknesses of these views, and the fellows of the Jesus Seminar show virtually no indication that they have so much as interacted with the arguments they contain, much less have they refuted their claims.
Regarding Jesus of Nazareth, all of this means the following: Prior to investigating the historical evidence about his life, deeds, sayings, and significance, there is no good reason to bring to the evidence a prior commitment to naturalism. As later chapters will show, such a commitment is Procrustean in that it often forces the evidence of history to fit an unjustified anti-supernatural bias. But when the evidence is evaluated on its own terms, and when such an evaluation is combined with the rigorous case for supernatural theism already available in the literature, then the claims of historic, orthodox Christianity can be reasonably judged to be true.
Michael J. Wilkins, ed., Jesus Under Fire: Modern Scholarship Reinvents the Historical Jesus (Grand Rapids, MI: Zondervan, 1996), 8-10.
FOLLOWING SUPERNATURALISM MAKES THE SCIENTIST’S TASK TOO EASY
Here’s the first of Pennock’s arguments against methodological naturalism that I’ll consider:
- allowing appeal to supernatural powers in science would make the scientist’s task too easy, because one would always be able to call upon the gods for quick theoretical assistance…. Indeed, all empirical investigation beyond the purely descriptive could cease, for scientists would have a ready-made answer for everything.
This argument strikes me as unfair. Consider a particular empirical phenomenon, like a chemical reaction, and imagine that scientists are trying to figure out why the reaction happened. Pennock would say that scientists who allow appeal to supernatural powers would have a ready-made answer: God did it. While it may be that that’s the only true explanation that can be given, a good scientist-including a good theistic scientist—would wonder whether there’s more to be said. Even if God were ultimately the cause of the reaction, one would still wonder if the proximate cause is a result of the chemicals that went into the reaction, and a good scientist—even a good theistic scientist—would investigate whether such a naturalistic account could be given.
To drive the point home, an analogy might be helpful. With the advent of quantum mechanics, scientists have become comfortable with indeterministic events. For example, when asked why a particular radioactive atom decayed at the exact time that it did, most physicists would say that there’s no reason it decayed at that particular time; it was just an indeterministic event!’ One could imagine an opponent of indeterminism giving an argument that’s analogous to Pennock’s:
- allowing appeal to indeterministic processes in science would make the scientist’s task too easy, because one would always be able to call upon chance for quick theoretical assistance…. Indeed, all empirical investigation beyond the purely descriptive could cease, for scientists would have a ready-made answer for everything.
It is certainly possible that, for every event that happens, scientists could simply say “that’s the result of an indeterministic chancy process; there’s no further explanation for why the event happened that way.” But this would clearly be doing bad science: just because the option of appealing to indeterminism is there, it doesn’t follow that the option should always be used. The same holds for the option of appealing to supernatural powers.
As further evidence against Pennock, it’s worth pointing out that prominent scientists in the past have appealed to supernatural powers, without using them as a ready-made answer for everything. Newton is a good example of this—he is a devout theist, in addition to being a great scientist, and he thinks that God sometimes intervenes in the world. Pennock falsely implies that this is not the case:
- God may have underwritten the active principles that govern the world described in [Newton’s] Principia and the Opticks, but He did not interrupt any of the equations or regularities therein. Johnson and other creationists who want to dismiss methodological naturalism would do well to consult Newton’s own rules of reasoning….
But in fact, Newton does not endorse methodological naturalism. In his Opticks, Newton claims that God sometimes intervenes in the world. Specifically, Newton thinks that, according to his laws of motion, the orbits of planets in our solar system are not stable over long periods of time, and his solution to this problem is to postulate that God occasionally adjusts the motions of the planets so as to ensure the continued stability of their orbits. Here’s a relevant passage from Newton. (It’s not completely obvious that Newton is saying that God will intervene but my interpretation is the standard one.)
- God in the Beginning form’d Matter in solid, massy, hard, impenetrable, moveable Particles … it became him who created them to set them in order. And if he did so, it’s unphilosophical to seek for any other Origin of the World, or to pretend that it might arise out of a Chaos by the mere Laws of Nature; though being once form’d, it may continue by those Laws for many Ages. For while Comets move in very excentrick Orbs in all manner of Positions, blind Fate could never make all the Planets move one and the same way in Orbs concentrick, some inconsiderable Irregularities excepted, which may have risen from the mutual Actions of Comets and Planets upon one another, and which will be apt to increase, till this System wants a Reformation…. [God is] able by his Will to move the Bodies within his boundless uniform Sensorium, and thereby to form and reform the Parts of the Universe….
A scientist who writes this way does not sound like a scientist who is following methodological naturalism.
It’s worth noting that some contemporaries of Newton took issue with his view of God occasionally intervening in the universe. For example, Leibniz writes:
- Sir Isaac Newton and his followers also have a very odd opinion concerning the work of God. According to them, God Almighty needs to wind up his watch from time to time; otherwise it would cease to move. He had not, it seems, sufficient foresight to make it a perpetual motion.”
Note, though, that Leibniz also thought that God intervened in the world:
- I hold that when God works miracles, he does not do it in order to supply the wants of nature, but those of grace.
Later investigation revealed that in fact planetary orbits are more stable than Newton thought, so Newton’s appeal to supernatural powers wasn’t needed. But the key point is that Newton is willing to appeal to supernatural powers, without using the appeal to supernatural powers as a ready-made answer for everything.
Pennock says that “Without the binding assumption of uninterruptible natural law there would be absolute chaos in the scientific worldview.” Newton’s own approach to physics provides a good counterexample to this—Newton is a leading contributor to the scientific worldview, and yet he does not bind himself by the assumption of uninterruptible natural law.
Bradley Monton, Seeking God in Science: An Atheist Defends Intelligent Design, (Peterborough, Ontario [Canada]: Broadview Press, 2009), 62-64.
Signature in the Cell: Stephen Meyer Faces his Critics (Parts 1 & 2)

Science and Intelligent Design Defined
This is a good working definition for Intelligent Design via New World Encyclopedia:
Intelligent design (ID) is the view that it is possible to infer from empirical evidence that “certain features of the universe and of living things are best explained by an intelligent cause, not an undirected process such as natural selection” [1] Intelligent design cannot be inferred from complexity alone, since complex patterns often happen by chance. ID focuses on just those sorts of complex patterns that in human experience are produced by a mind that conceives and executes a plan. According to adherents, intelligent design can be detected in the natural laws and structure of the cosmos; it also can be detected in at least some features of living things.
Greater clarity on the topic may be gained from a discussion of what ID is not considered to be by its leading theorists. Intelligent design generally is not defined the same as creationism, with proponents maintaining that ID relies on scientific evidence rather than on Scripture or religious doctrines. ID makes no claims about biblical chronology, and technically a person does not have to believe in God to infer intelligent design in nature. As a theory, ID also does not specify the identity or nature of the designer, so it is not the same as natural theology, which reasons from nature to the existence and attributes of God. ID does not claim that all species of living things were created in their present forms, and it does not claim to provide a complete account of the history of the universe or of living things.
ID also is not considered by its theorists to be an “argument from ignorance”; that is, intelligent design is not to be inferred simply on the basis that the cause of something is unknown (any more than a person accused of willful intent can be convicted without evidence). According to various adherents, ID does not claim that design must be optimal; something may be intelligently designed even if it is flawed (as are many objects made by humans).
ID may be considered to consist only of the minimal assertion that it is possible to infer from empirical evidence that some features of the natural world are best explained by an intelligent agent. It conflicts with views claiming that there is no real design in the cosmos (e.g., materialistic philosophy) or in living things (e.g., Darwinian evolution) or that design, though real, is undetectable (e.g., some forms of theistic evolution). Because of such conflicts, ID has generated considerable controversy.
[1] Discovery Institute, Center for Science and Culture, Questions about Intelligent Design: What is the theory of intelligent design? Retrieved March 18, 2007.

Socrates in the City ~ Darwin’s Doubt: Interview with Stephen Meyer
Video Description: Darwin, the scientific method, Danny DeVito, and Cher all manage to find a place in this mind-boggling and entertaining conversation between Eric Metaxas and Stephen Meyer, at the Union League Club in New York City on September 12, 2013. Buy Meyer’s book here.

An I.D. Theorist, Stephen Meyer, Defines His Position on the Dennis Miller Show
Stephen Meyer was interviewed on the Dennis Miller Show.

Stephen Meyer and Michael Medved Discuss Censorship In Science
On the Michael Medved’s “Science & Culture Update,” he and Stephen C. Meyer talk about censorship in science, and calls are taken challenging I.D. — much of which are straw-men positions. In other words, intelligent design is miss-defined and then this position [miss-defined] is attacked.
For more clear thinking like this from Michael Medved… I invite you to visit: http://www.michaelmedved.com/
- 2 of 3
- « Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Next »




