(Hat-tip to Wintery Knight’s FACEBOOK) In a lively yet in-depth discussion, Piers Morgan drills down to the core of human existence with Stephen C. Meyer, the prominent ‘intelligent design’ advocate. In this Piers Morgan Uncensored special, Meyers firmly rejects the idea that a scientific worldview leads to atheism, arguing instead that ‘the universe requires a creator or cause’. When Richard Dawkin’s name is mentioned, Meyer claims that he actually really loves the atheist firebrand and admires his intensity. Lastly, Morgan and Meyers agree that the question of God’s existence is tied to more than just cold hard facts, but also human nature itself.
Stephen Meyer


Modern Man’s “Red Herring”
ORIGINALLY POSTED IN JANUARY OF 2014
Jump to Bradley Monton’s Isaac Newton and the methodological method.
- Newton is a leading contributor to the scientific worldview, and yet he does not bind himself by the assumption of uninterruptible natural law ~ Bradley Monton
- The divine art of miracle is not an art of suspending the pattern to which events conform but of feeding new events into that pattern ~ CS Lewis
- Meredith’s whole argument about ID, miracles, and the so-called “breaking” of natural laws is nothing but a red herring. Again, the real issue is about the nature of causation not about natural law ~ Michael Flannery
In the most recent issue of FIRST THINGS (February 2014), Stephen Meredith attempted to critique Intelligent Design theory, by, essentially creating straw-men arguments or by debating issues others have dealt with well.
Later in this “short” review of topics that caught my critical eye, we will see the similar vein John Derbyshire takes in the January/February (2014) issue of The American Spectator in comparing ID to Islam.
AT LEAST American Spectator had the foresight to have an alternative view side-by-side, so you get to see what an erudite, idea filled presentation looks like (Stephen Meyer’s)…
— a portion of which I will publish at the bottom from a magazine I recommend highly —
…alongside another filled with fallacious arguments, non-sequiturs, and a lack of intelligence in laying out a positive case (John Derbyshire).
First, however, my mind went immediately to David Hume and CS Lewis after reading the following from Stephen Meredith in the First Things article:

…The metaphysics of ID is occasionalist. It holds, to abbreviate the doctrine rather drastically, that causation is an illusion; that everything happens because God makes it happen.
Why does ice float on water? Aristotle thought it was a matter of shape (see On the Heavens, IV.6). Science says it’s because ice is less dense than water. The occasionalist says it’s because God wills it so….
…But: Ice floats on water because God wills it so? Oh.
(David Hume: The Essential Philosophical Works, eBook, [2012], pages 662 and 663)
1. Miracles are violations of the laws of nature
2. These laws have been established by ‘firm and unalterable’ experience
3. Therefore, the argument against miracle is as good as any argument from experience can be
B. Argument from the uniformity of experience:
1. Unusual, yet frequently observed, events are not miracles – like a healthy person suddenly dropping dead
2. A resurrection would be a miracle because it has never been observed anywhere at any time
3. There is uniform experience against every miraculous event, otherwise it would not be called miraculous
Dr. Lennox continues:
Argument 1. Hume says that accounts of miracles ‘are observed chiefly to abound among ignorant and barbarous nations’ (op.cit. p.79).
Fallacy. In order to recognize some event as a miracle, there must be some perceived regularity to which that event is an apparent exception! You cannot recognize something which is abnormal, if you do not know what is normal. Example: 1) virgin conception of Jesus; 2) conception of John the Baptist.
Argument 2. Now that we know the laws of nature, belief in miracles is impossible.
Fallacy. The danger of confusion between legal and scientific use of word law. Why it is inaccurate and misleading to say that miracles ‘violate’ the laws of nature. It is rather, that God feeds new events into the system from time to time. There is no alteration to or suspension of the laws themselves.
‘If God annihilates or creates or deflects a unit of matter, He has created a new situation at that point. Immediately all nature domiciles this new situation, makes it at home in her realm, adapts all other events to it. It finds itself conforming to all the laws. If God creates a miraculous spermatozoon in the body of a virgin, it does not proceed to break any laws. The laws at once take over. Nature is ready. Pregnancy follows, according to all the normal laws, and nine months later a child is born’ (C.S Lewis, Miracles. p.63).
By the “laws of Nature” such a man means, I think, the observed course of Nature. If he means anything more than that he is not the plain man I take him for but a philosophic Naturalist and will be dealt with in the next chapter. The man I have in view believes that mere experience (and specially those artificially contrived experiences which we call Experiments) can tell us what regularly happens in Nature. And he finks that what we have discovered excludes the possibility of Miracle. This is a confusion of mind.
Granted that miracles can occur, it is, of course, for experience to say whether one has done so on any given occasion. But mere experience, even if prolonged for a million years, cannot tell us whether the thing is possible. Experiment finds out what regularly happens in Nature: the norm or rule to which she works. Those who believe in miracles are not denying that there is such a norm or rule: they are only saying that it can be suspended. A miracle is by definition an exception.
[….]
The idea that the progress of science has somehow altered this question is closely bound up with the idea that people “in olden times” believed in them “because they didn’t know the laws of Nature.” Thus you will hear people say, “The early Christians believed that Christ was the son of a virgin, but we know that this is a scientific impossibility.” Such people seem to have an idea that belief in miracles arose at a period when men were so ignorant of the cause of nature that they did not perceive a miracle to be contrary to it. A moment’s thought shows this to be nonsense: and the story of the Virgin Birth is a particularly striking example. When St. Joseph discovered that his fiancee was going to have a baby, he not unnaturally decided to repudiate her. Why? Because he knew just as well as any modern gynaecologist that in the ordinary course of nature women do not have babies unless they have lain with men. No doubt the modern gynaecologist knows several things about birth and begetting which St. Joseph did not know. But those things do not concern the main point—that a virgin birth is contrary to the course of nature. And St. Joseph obviously knew that. In any sense in which it is true to say now, “The thing is scientifically impossible,” he would have said the same: the thing always was, and was always known to be, impossible unless the regular processes of nature were, in this particular case, being over-ruled or supplemented by something from beyond nature. When St. Joseph finally accepted the view that his fiancee’s pregnancy was due not to unchastity but to a miracle, he accepted the miracle as something contrary to the known order of nature. All records
[….]
It is therefore inaccurate to define a miracle as something that breaks the laws of Nature. It doesn’t. If I knock out my pipe I alter the position of a great many atoms: in the long run, and to an infinitesimal degree, of all the atoms there are. Nature digests or assimilates this event with perfect ease and harmonises it in a twinkling with all other events. It is one more bit of raw material for the laws to apply to, and they apply. I have simply thrown one event into the general cataract of events and it finds itself at home there and conforms to all other events. If God annihilates or creates or deflects a unit of matter He has created a new situation at that point. Immediately all Nature domiciles this new situation, makes it at home in her realm, adapts all other events to it. It finds itself conforming to all the laws. If God creates a miraculous spermatozoon in the body of a virgin, it does not proceed to break any laws. The laws at once take it over. Nature is ready. Pregnancy follows, according to all the normal laws, and nine months later a child is born. We see every day that physical nature is not in the least incommoded by the daily inrush of events from biological nature or from psychological nature. If events ever come from beyond Nature altogether, she will be no more incommoded by them. Be sure she will rush to the point where she is invaded, as the defensive forces rush to a cut in our finger, and there hasten to accommodate the newcomer. The moment it enters her realm it obeys all her laws. Miraculous wine will intoxicate, miraculous conception will lead to pregnancy, inspired books will suffer all the ordinary processes of textual corruption, miraculous bread will be digested. The divine art of miracle is not an art of suspending the pattern to which events conform but of feeding new events into that pattern.
[….]
A miracle is emphatically not an event without cause or without results. Its cause is the activity of God: its results follow according to Natural law. In the forward direction (i.e. during the time which follows its occurrence) it is interlocked with all Nature just like any other event. Its peculiarity is that it is not in that way interlocked backwards, interlocked with the previous history of Nature. And this is just what some people find intolerable. The reason they find it intolerable is that they start by taking Nature to be the whole of reality. And they are sure that all reality must be interrelated and consistent. I agree with them. But I think they have mistaken a partial system within reality, namely Nature, for the whole.
CS Lewis, Miracles (New York, NY: Touchstone Publishers, 1996), 62-63, 64-65, 80-81, 81-82.
This is mainly the point Michael Flannery makes near the end of this portion of his critique of the First Things article, entitled: “Writing in First Things, Stephen Meredith Offers Confusion in the Guise of Critique“:
1) a faulty view of ID’s relationship to nature, miracles, and the supernatural;
2) no clear definition of what ID really is; and
3) an erroneous view of much of the history related to ID, evolution, and theology.
In company with John Derbyshire, Meredith, insists that ID proponents are “occasionalists,” holding to a particular theological understanding of causation. As occasionalists they do “not credit natural or physical law with enough causal power to enact evolution on its own.” Instead they “educe supernatural causes to do most of the heavy lifting in worldly events.” This is a fundamental misunderstanding. ID does not require the “breaking” of natural law or the notion that a natural law would have done X but instead Y happened. As William A. Dembski has pointed out, ID doesn’t need this “counterfactual substitution.” People act, for example, as intelligent agents not by “breaking” or “suspending” natural laws but by arranging or front-loading laws to suite particular ends (The Design Revolution, pp. 181-182). Meredith seems to argue that ID is incongruous with modern science because it invokes miracles and yields to supernatural causes. Here Meredith is making an old mistake, called out again by Dembski: “The contrast between natural law and supernatural causes is the wrong contrast. The proper contrast is between undirected natural causes on the one hand and intelligent causes on the other” (p. 189).
Furthermore, Meredith’s concern regarding miracles contravening natural laws seems to suggest a position of tension between the miraculous and science itself. However, this is not a scientific position. It is a philosophical one suggestive of methodological naturalism. “Scientists, as scientists,” Norman Geisler explains, “need not be so narrow as to believe that nothing can ever count as a miracle. All a scientist needs to hold is the premise that every event has a cause and that the observable universe operates in an orderly way” (Baker Encyclopedia of Christian Apologetics, p. 467). Meredith’s whole argument about ID, miracles, and the so-called “breaking” of natural laws is nothing but a red herring. Again, the real issue is about the nature of causation not about natural law…
Even atheist philosophers refute the idea that to incorporate a theistic view into nature is NOT anti-science, and works within the scientific paradigm:

Here’s the first of Pennock’s arguments against methodological naturalism that I’ll consider:
allowing appeal to supernatural powers in science would make the scientist’s task too easy, because one would always be able to call upon the gods for quick theoretical assistance…. Indeed, all empirical investigation beyond the purely descriptive could cease, for scientists would have a ready-made answer for everything.
This argument strikes me as unfair. Consider a particular empirical phenomenon, like a chemical reaction, and imagine that scientists are trying to figure out why the reaction happened. Pennock would say that scientists who allow appeal to supernatural powers would have a ready-made answer: God did it. While it may be that that’s the only true explanation that can be given, a good scientist-including a good theistic scientist—would wonder whether there’s more to be said. Even if God were ultimately the cause of the reaction, one would still wonder if the proximate cause is a result of the chemicals that went into the reaction, and a good scientist—even a good theistic scientist—would investigate whether such a naturalistic account could be given.
To drive the point home, an analogy might be helpful. With the advent of quantum mechanics, scientists have become comfortable with indeterministic events. For example, when asked why a particular radioactive atom decayed at the exact time that it did, most physicists would say that there’s no reason it decayed at that particular time; it was just an indeterministic event!’ One could imagine an opponent of indeterminism giving an argument that’s analogous to Pennock’s:
allowing appeal to indeterministic processes in science would make the scientist’s task too easy, because one would always be able to call upon chance for quick theoretical assistance…. Indeed, all empirical investigation beyond the purely descriptive could cease, for scientists would have a ready-made answer for everything.
It is certainly possible that, for every event that happens, scientists could simply say “that’s the result of an indeterministic chancy process; there’s no further explanation for why the event happened that way.” But this would clearly be doing bad science: just because the option of appealing to indeterminism is there, it doesn’t follow that the option should always be used. The same holds for the option of appealing to supernatural powers.
As further evidence against Pennock, it’s worth pointing out that prominent scientists in the past have appealed to supernatural powers, without using them as a ready-made answer for everything. Newton is a good example of this—he is a devout theist, in addition to being a great scientist, and he thinks that God sometimes intervenes in the world. Pennock falsely implies that this is not the case:
God may have underwritten the active principles that govern the world described in [Newton’s] Principia and the Opticks, but He did not interrupt any of the equations or regularities therein. Johnson and other creationists who want to dismiss methodological naturalism would do well to consult Newton’s own rules of reasoning….
But in fact, Newton does not endorse methodological naturalism. In his Opticks, Newton claims that God sometimes intervenes in the world. Specifically, Newton thinks that, according to his laws of motion, the orbits of planets in our solar system are not stable over long periods of time, and his solution to this problem is to postulate that God occasionally adjusts the motions of the planets so as to ensure the continued stability of their orbits. Here’s a relevant passage from Newton. (It’s not completely obvious that Newton is saying that God will intervene but my interpretation is the standard one.)
God in the Beginning form’d Matter in solid, massy, hard, impenetrable, moveable Particles … it became him who created them to set them in order. And if he did so, it’s unphilosophical to seek for any other Origin of the World, or to pretend that it might arise out of a Chaos by the mere Laws of Nature; though being once form’d, it may continue by those Laws for many Ages. For while Comets move in very excentrick Orbs in all manner of Positions, blind Fate could never make all the Planets move one and the same way in Orbs concentrick, some inconsiderable Irregularities excepted, which may have risen from the mutual Actions of Comets and Planets upon one another, and which will be apt to increase, till this System wants a Reformation…. [God is] able by his Will to move the Bodies within his boundless uniform Sensorium, and thereby to form and reform the Parts of the Universe….
A scientist who writes this way does not sound like a scientist who is following methodological naturalism.
It’s worth noting that some contemporaries of Newton took issue with his view of God occasionally intervening in the universe. For example, Leibniz writes:
Sir Isaac Newton and his followers also have a very odd opinion concerning the work of God. According to them, God Almighty needs to wind up his watch from time to time; otherwise it would cease to move. He had not, it seems, sufficient foresight to make it a perpetual motion.”
Note, though, that Leibniz also thought that God intervened in the world:
I hold that when God works miracles, he does not do it in order to supply the wants of nature, but those of grace.
Later investigation revealed that in fact planetary orbits are more stable than Newton thought, so Newton’s appeal to supernatural powers wasn’t needed. But the key point is that Newton is willing to appeal to supernatural powers, without using the appeal to supernatural powers as a ready-made answer for everything.
Pennock says that “Without the binding assumption of uninterruptible natural law there would be absolute chaos in the scientific worldview.” Newton’s own approach to physics provides a good counterexample to this—Newton is a leading contributor to the scientific worldview, and yet he does not bind himself by the assumption of uninterruptible natural law.
Bradley Monton, Seeking God in Science: An Atheist Defends Intelligent Design, (Peterborough, Ontario [Canada]: Broadview Press, 2009), 62-64.
How one can go from the above rational positions by a Christian (CS Lewis), and an atheist (Bradley Monton), to comparing floating ice as an unnatural event held in situ by God’s continuous miraculous intervention. And then compare this straw-man to the Islamic understanding of extreme fideistic occasionalism?
An important object of metaphysical reflection is God’s nature, or the properties of that nature. Is God simple or complex? If omniscience, omnipotence, and beauty are part of the divine perfection, what exactly are these properties? Is timeless eternity part of God’s perfection? Can an omnipotent being will that there be a four-sided triangle or change the past? Does an omniscient being know the future actions of free agents? (If so, how can they be free?) Does an omniscient being who is timelessly eternal know what time it is now?
IN a great presentation from True U. (Focus on the Family store | Discovery Institute), Dr. Stephen Meyer shows how — by using the supposition from Hinduism that the earth sits atop a turtle used by Stephen Hawking’s — the materialist position differs little from this religious supposition. This video is to replace an old, defunct, MRCTV video uploaded early 2014, but here today (11/4/2023). I added a William Provine clip from his 1994 debate with Phillip Johnson at Stanford. The entire debate can be see HERE.
Colin Patterson [1978] (Dr. Patterson was Senior Principal Scientific Officer of the Paleontology Department of the British Museum of Natural History in London.)
Bradley Monton, author of Seeking God in Science: An Atheist Defends Intelligent Design ~ Apologetics315 h/t
Likewise one of the most celebrated pediatric surgeons in the world, whom a movie was made after, “Gifted Hands,” is a young earth creationist. And the inventor of the MRI, a machine that diagnosed my M.S., is also a young earth creationist.
Evolutionary Darwinism is first and foremost an “historical science” that has many presuppositions that precede it, making it a metaphysical belief, a philosophy, as virulent anti-creationist philosopher of science, Michael Ruse explains:
Michael Ruse, “Saving Darwinism from the Darwinians,” National Post (May 13, 2000), p. B-3. (Via ICR)
….Nevertheless, there is a second, and arguably deeper, mystery associated with the Cambrian explosion: the mystery of how the neo-Darwinian mechanism of natural selection and random mutation could have given rise to all these fundamentally new forms of animal life, and done so quickly enough to account for the pattern in the fossil record. That question became acute in the second half of the twentieth century as biologists learned more about what it takes to build an animal.
In 1953 when Watson and Crick elucidated the structure of the DNA molecule, they made a startling discovery, namely, its ability to store information in the form of a four-character digital code. Strings of precisely sequenced chemicals called nucleotide bases store and transmit the assembly instructions—the information—for building the crucial protein molecules that the cell needs to survive. Just as English letters may convey a particular message depending on their arrangement, so too do certain sequences of chemical bases along the spine of a DNA molecule convey precise information. As Richard Dawkins has acknowledged, “the machine code of the genes is uncannily computer-like.” Or as Bill Gates has noted, “DNA is like a computer program, but far, far more advanced than any software ever created.”
The Cambrian period is marked by an explosion of new animals exemplifying new body plans. But building new animal body plans requires new organs, tissues, and cell types. And new cell types require many kinds of specialized or dedicated proteins (e.g., animals with gut cells require new digestive enzymes). But building each protein requires genetic information stored on the DNA molecule. Thus, building new animals with distinctive new body plans requires, at the very least, vast amounts of new genetic information. Whatever happened during the Cambrian not only represented an explosion of new biological form, but it also required an explosion of new biological information.
Is it plausible that the neo-Darwinian mechanism of natural selection acting on random mutations in DNA could produce the highly specificarrangements of bases in DNA necessary to generate the protein building blocks of new cell types and novel forms of life?
According to neo-Darwinian theory, new genetic information arises first as random mutations occur in the DNA of existing organisms. When mutations arise that confer a survival advantage, the resulting genetic changes are passed on to the next generation. As such changes accumulate, the features of a population change over time. Nevertheless, natural selection can only “select” what random mutations first generate. Thus the neo-Darwinian mechanism faces a kind of needle-in-the-haystack problem—or what mathematicians call a “combinatorial” problem. The term “combinatorial” refers to the number of possible ways that a set of objects can be arranged or combined. Many simple bike locks, for example, have four dials with 10 digits on each dial. A bike thief encountering one of these locks faces a combinatorial problem because there are 10 × 10 × 10 × 10, or 10,000 possible combinations and only one that will open the lock. A random search is unlikely to yield the correct combination unless the thief has plenty of time.
Similarly, it is extremely difficult to assemble a new information-bearing gene or protein by the natural selection/random mutation process because of the sheer number of possible sequences. As the length of the required gene or protein grows, the number of possible base or amino-acid sequences of that length grows exponentially.
Here’s an illustration that may help make the problem clear. Imagine that we encounter a committed bike thief who is willing to search the “sequence space” of possible bike combinations at a rate of about one new combination per two seconds. If our hypothetical bike thief had three hours and took no breaks he could generate more than half (about 5,400) of the 10,000 total combinations of a four-dial lock. In that case, the probability that he will stumble upon the right combination exceeds the probability that he will fail. More likely than not, he will open the lock by chance.
But now consider another case. If that thief with the same limited three hour time period available to him confronted a lock with ten dials and ten digits per dial (a lock with ten billion possible combinations) he would now have time only to explore a small fraction of the possible combinations—5,400 of ten billion—far fewer than half. In this case, it would be much more likely than not that he would fail to open the lock by chance.
These examples suggest that the ultimate probability of the success of a random search—and the plausibility of any hypothesis that affirms the success of such a search—depends upon both the size of the space that needs to be searched and the number of opportunities available to search it.
In Darwin’s Doubt, I show that the number of possible DNA and amino acid sequences that need to be searched by the evolutionary process dwarfs the time available for such a search—even taking into account evolutionary deep time. Molecular biologists have long understood that the size of the “sequence space” of possible nucleotide bases and amino acids (the number of possible combinations) is extremely large. Moreover, recent experiments in molecular biology and protein science have established that functional genes and proteins are extremely rare within these huge combinatorial spaces of possible arrangements. There are vastly more ways of arranging nucleotide bases that result in non-functional sequences of DNA, and vastly more ways of arranging amino acids that result in non-functional amino-acid chains, than there are corresponding functionalgenes or proteins. One recent experimentally derived estimate places that ratio—the size of the haystack in relation to the needle—at 1077non-functional sequences for every functional gene or protein. (There are only something like 1065 atoms in our galaxy.)
All this suggests that the mutation and selection mechanism would only have enough time in the entire multi-billion year history of life on Earth to generate or “search” but a miniscule fraction (one ten trillion, trillion trillionth, to be exact) of the total number of possible nucleotide base or amino-acid sequences corresponding to a single functional gene or protein. The number of trials available to the evolutionary process turns out to be incredibly small in relation to the number of possible sequences that need to be searched. Thus, the neo-Darwinian mechanism, with its reliance on random mutation, is much more likely to fail than to succeed in generating even a single new gene or protein in the known history of life on earth. In other words, the neo-Darwinian mechanism is not an adequate mechanism to generate the information necessary to produce even a single new protein, let alone a whole new Cambrian animal….
[….]
Of course, many scientists dismiss intelligent design as “religion masquerading as science.” But the case for intelligent design is not based upon religious or scriptural authority. Instead it is based upon scientific evidence and the same method of scientific reasoning that Darwin himself used in the Origin of Species.
In rejecting the theory as unscientific by definition, evolutionary biologists reveal a deep a priori commitment to methodological naturalism—the idea that scientists must limit themselves to materialistic explanations for all things. Yet, we know from experience that certain types of events and structures—in particular, information-rich structures—invariably arise from minds or personal agents. Indeed, no thinking person would insist that the inscriptions on the Rosetta stone, for example, were produced by strictly materialistic forces such as wind and erosion. Yet, by insisting that all events in the history of life must be explained by reference to strictly materialistic processes evolutionary biologists preclude consideration of a designing intelligence in the history of life, regardless of what the evidence might indicate.
This commitment to a wholly materialistic account of the origins of life also helps to explain the reluctance to criticize the Darwinian theory publicly. Many evolutionary biologists fear that if they do so they will aid and abet the case for intelligent design—a theory they disdain as inherently unscientific. Those of us who support the theory of intelligent design advocate a more open approach to scientific investigation. Not only do we think the public has a right to know about the problems with evolutionary theory, we also think that the rules of science should allow scientists to “follow the evidence wherever it leads”—even if it leads to conclusions that raise deep and unwelcome metaphysical questions.
Can you believe in God and science at the same time? Many claim that belief in religion is at odds with “the science” of today. But is that really true? In this five-part series, Stephen Meyer, Senior Fellow at the Discovery Institute, attempts to answer this existential question.
Series “Broken Out”
- Are Religion and Science in Conflict? — Science and God | Does belief in God get in the way of science? The idea that science and religion are inevitably in conflict is a popular way of thinking today. But the history of science tells a different story.
- How Did the Universe Begin? — Science and God | Was the universe always here, or did it have a beginning? If so, how did it start? Mankind has debated these questions for centuries and has only recently begun to find some answers. And those answers may point to some even more intriguing conclusions.
- Aliens, the Multiverse, or God? — Science and God | Even staunch Darwinists have acknowledged that life in the universe displays an appearance of design, rather than being created out of random chance. If that’s true, where did that design come from? In other words, does a design require a designer?
- What Is Intelligent Design? — Science and God | Chances are if you’ve heard anything about intelligent design, you’ve heard that it’s faith-based, not science-based. Is that true? Or does modern science, in fact, point us in the direction of a designing intelligence?
- What’s Wrong with Atheism? — Science and God | Is there any meaning to life? Or is life nothing more than a cosmic accident? Scientific atheists claim the latter, but ironically, it’s science itself that suggests the former.

Scientific and Anecdotal Evidence for the Beginning of the Universe
(Originally Posted December of 2015)
Please see “Theistic Implications of Big-Bang Cosmology“ for more on this topic.
- The editor of the prestigious weekly science periodical, Nature, John Maddox, wrote an editorial entitled, “Down with the Big Bang,” where he hoped for the downfall of the Big Bang model, because in it, he found it to be “philosophically unacceptable,” quote: “Apart from being philosophically unacceptable, the Big-Bang is an over-simple view of how the Universe began, and it is unlikely to survive the decade ahead.” ~ Maddox, J. 1989. Down with the Big Bang. Nature 340: 425.
- Physicist Hubert Reeves remarked that the Big Bang “involves a certain metaphysical aspect which may be either appealing or revolting” ~ Reeves, H., Andouze, J., Fowler, W. A., and Schramm, D. N. 1973. On the Origin of the Light Elements. Astrophysical Journal 179: 912.
- Cosmologist Christopher Isham: “Perhaps the best argument in favor of the thesis that the Big Bang supports theism is the obvious unease with which it is greeted by some atheist physicists. At times this has led to scientific ideas, such as continuous creation [steady state] or an oscillating universe, being advanced with a tenacity which so exceeds their intrinsic worth that one can only suspect the operation of psychological forces lying very much deeper than the usual academic desire of a theorist to support his/her theory.” ~ Isham, C. 1988. “Creation of the Universe as a Quantum Process,” in Physics, Philosophy, and Theology, A Common Quest for Understanding, eds. R. J. Russell, W. R. Stoeger, and G. V. Coyne, Vatican City State: Vatican Observatory, p. 378.
(SOURCE — see the previous slide as well)
- “The biggest problem with the Big Bang theory of the origin of the universe is philosophical–perhaps even theological–what was there before the bang? This problem alone was sufficient to give a great initial impetus to the Steady State theory; but with that theory now sadly in conflict with the observations, the best way round this initial difficulty is provided by a model in which the universe expands from a singularity, collapses back again, and repeats the cycle indefinitely” (John Gribbin, “Oscillating Universe Bounces Back,” Nature 259 [1976]: 15).
(SOURCE)
Lee Strobel does a great job in relaying the evidence that we live in a finite cosmos and not an infinite one in his discussion with Dr. William Lane Craig [I added J. Warner Wallace as well to this presentation]:
When Albert Einstein developed his general theory of relativity in 1915 and started applying it to the universe as a whole, he was shocked to discover it didn’t allow for a static universe. According to his equations, the universe should either be exploding or imploding. In order to make the universe static, he had to FUDGE his equations by putting in a factor that would hold the universe steady.
In the 1920’s, the Russian mathematician Alexander Friedman and the Belgium astronomer George Lemaitre were able to develop models based on Einstein’s theory. They predicted the universe was expanding. Of course, this meant that if you went backward in time, the universe would go back to a single origin before which it didn’t exist. Astronomer Fred Hoyle derisively called this the Big Bang — and the name stuck! [Later in his career, Fred Hoyle confirmed the expansion through work on the second most plentiful element in the universe, helium.]
Starting in the 1920’s, scientists began to find empirical evidence that supported these purely mathematical models.
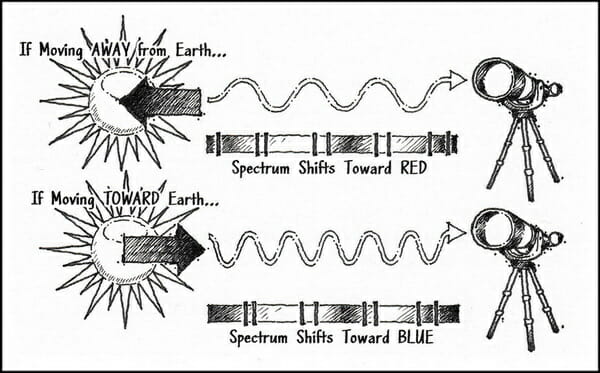
LET US TAKE A QUICK BREAK from this excerpt to fill in some information from another excerpt, and then we will continue: As mathematicians explored the theoretical evidence, astronomers began to make observations confirming the expansion of the universe. Vesto Slipher, an American astronomer working at the Lowell Observatory. in Flagstaff, Arizona, spent nearly ten years perfecting his understanding of spectrograph readings. His observations revealed something remarkable. If a distant object was moving toward Earth, its observable spectrograph colors shifted toward the blue end of the spectrum. If a distant object was moving away from Earth, its colors shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. Slipher identified several nebulae and observed a redshift in their spectrographic colors. If these nebulae were moving away from our galaxy (and one another), as Slipher observed, they must have once been tightly clustered together. In 1914, he offered these findings at a meeting of the American Astronomical Society, proposing them as evidence the universe was expanding. A graduate student named Edwin Hubble seas in attendance and realized the implications of Slipher’s work. Hubble later began working at the Mount Wilson Observatory in Los Angeles. Using the Hooker telescope, he eventually proved Slipher’s nebulae were actually galaxies beyond the Milky Way composed of billions of stars. By 1929, Hubble published findings of his own, verifying Slipher’s observations and demonstrating the speed at which a star or galaxy moves away from us increases with its distance from Earth. This once again confirmed the expansion of the universe. …CONTINUING… For instance, in 1929, the American astronomer Edwin Hubble discovered that the light coming to us from distant galaxies appears redder than it should be, and this is a universal feature of galaxies in all parts of the sky. Hubble explained this red shift as being due to the fact that the galaxies are moving away from us. He concluded that the universe is literally flying apart at enormous velocities. Hubble’s astronomical observations were the first empirical confirmation of the predictions by Friedman and Lemaitre. Then in the 1940’s, George Gamow predicted that if the Big Bang really happened, then the background temperature of the universe should be just a few degrees above absolute zero. He said this would be a relic from a very early stage of the universe. Sure enough, in 1965, two scientists accidentally discovered the universe’s background radiation — and it was only about 3.7 degrees above absolute zero. There’s no explanation for this apart from the fact that it is a vestige of a very early and a very dense state of the universe, which was predicted by the Big Bang model. The third main piece of the evidence for the Big Bang is the origin of light elements. Heavy elements, like carbon and iron, are synthesized in the interior of stars and then exploded through supernova into space. But the very, very light elements, like deuterium and helium, cannot have been synthesized in the interior of the stars, because you would need an even more powerful furnace to create them. These elements must have been forged in the furnace of the Big Bang itself at temperatures that were billions of degrees. There’s no other explanation. So predictions about the Big Bang have been consistently verified by the scientific data. Moreover, they have been corroborated by the failure of every attempt to falsify them by alternative models. Unquestionably, the Big Bang model has impressive scientific credentials… Up to this time, it was taken for granted that the universe as a whole was a static, eternally existing object…. At the time an agnostic, American astronomer Robert Jastrow was forced to concede that although details may differ, “the essential element in the astronomical and Biblical accounts of Genesis is the same; the chain of events leading to man commenced suddenly and sharply, at a definite moment in time, in a flash of light and energy”…. Einstein admitted the idea of the expanding universe “irritates me” (presumably, said one prominent scientist, “because of its theological implications”)
This should be put in bullet points for easy memorization:
- Albert Einstein developed his general theory of relativity in 1915;
- Around the same time evidence of an expanding universe was being presented to the American Astronomical Society by Vesto Slipher;
- In the 1920s using Einstein’s theory, a Russian mathematician (Alexander Friedman) and the Belgium astronomer (George Lemaitre) predicted the universe was expanding;
- In 1929, Hubble discovered evidence confirming earlier work on the Red-Light shift showing that galaxies are moving away from us;
- In the 1940’s, George Gamow predicted a particular temperature to the universe if the Big Bang happened;
- In 1965, two scientists (Arno Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson) discovered the universe’s background radiation — and it was only about 3.7 degrees above absolute zero.
“In speaking of the fear of religion, I don’t mean to refer to the entirely reasonable hostility toward certain established religions and religious institutions, in virtue of their objectionable moral doctrines, social policies, and political influence. Nor am I referring to the association of many religious beliefs with superstition and the acceptance of evident empirical falsehoods. I am talking about something much deeper–namely, the fear of religion itself. I speak from experience, being strongly subject to this fear myself: I want atheism to be true and am made uneasy by the fact that some of the most intelligent and well-informed people I know are religious believers.
I want atheism to be true and am made uneasy by the fact that some of the most intelligent and well-informed people I know are religious believers. It isn’t just that I don’t believe in God and, naturally, hope that I’m right in my belief. It’s that I hope there is no God! I don’t want there to be a God; I don’t want the universe to be like that.”
In this extended conversation released as part of the Science Uprising series, best-selling author Stephen Meyer discusses the big bang, whether you can have an expanding universe without a beginning, and the most common ways scientists have tried to avoid a beginning to the universe. Along the way, Meyer addresses the ideas of Albert Einstein, Stephen Hawking, Edwin Hubble, Lawrence Krauss, Sean Carroll, and more.
Here I will post a portion of a response to a local author on the issue that part of the above was likewise used:
(You can click top enlarge)
Here are just two (of the many examples I can provide) of an atheist and an agnostic commenting on the above evidence:
➤ “The essential element in the astronomical and biblical accounts of Genesis is the same; the chain of events leading to man commenced suddenly and sharply, at a definite moment in time, in a flash of light and energy…. The Hubble Law is one of the great discoveries in science; it is one of the main supports of the scientific story of Genesis.”
>> Robert Jastrow: American astronomer and physicist. Founding director of NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies, he is the director of the Mount Wilson Institute and Hale Solar Laboratory. He is also the author of Red Giants and White Dwarfs (1967) and God and the Astronomers (2nd ed., 2000).
➤ “Certainly there was something that set it all off. Certainly, if you are religious, I can’t think of a better theory of the origin of the universe to match with Genesis.”
>> Robert Wilson: is an American astronomer, 1978 Nobel laureate in physics, who with Arno Allan Penzias discovered in 1964 the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB)…. While working on a new type of antenna at Bell Labs in Holmdel Township, New Jersey, they found a source of noise in the atmosphere that they could not explain. After removing all potential sources of noise, including pigeon droppings on the antenna, the noise was finally identified as CMB, which served as important corroboration of the Big Bang theory.
The previous well accepted model was the Steady State theory… and this was accepted without a single piece of experimental verification; its appeal was purely metaphysical [footnote #21]:
- As Jaki points out, Hoyle and his colleagues were inspired by “openly anti-theological, or rather anti-Christian motivations” (Stanley L. Jaki, Science and Creation [Edinburgh: Scottish Academic Press, 1974), p. 347. Martin Rees recalls his mentor Dennis Sciama’s dogged commitment to the Steady State Model: “For him, as for its inventors, it had a deep philosophical appeal–the universe existed, from everlasting to everlasting, in a uniquely self-consistent state. When conflicting evidence emerged, Sciama therefore sought a loophole (even an unlikely seeming one) rather as a defense lawyer clutches at any argument to rebut the prosecution case” (Martin Rees, Before the Beginning, with a Foreword by Stephen Hawking [Reading, Mass.: Addison-Wesley, 1997], p. 41). The phrase “from everlasting to everlasting” is the Psalmist’s description of God (Ps. 90.2). Rees gives a good account of the discoveries leading to the demise of the Steady State Model.
Some more evidence to support the theistic position in the Big-Bang:
- Stephen Joseph Willams, What Your Atheist Professor Doesn’t Know (But Should) — CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform (May 23, 2013)
Dr. George Smoot, Particle Physicist, Nobel Prize winner, and team leader from the Lawrence-Berkeley Laboratory, regarding the 1992 observations from COBE (the NASA satellite Cosmic Background Explorer): “It’s like looking at God.”(8)
A somewhat more “sober” assessment of the findings was given by Frederick Burnham, a science-historian. He said, “These findings, now available, make the idea that God created the universe a more respectable hypothesis today than at any time in the last 100 years.”(9)
Dr. Stephen Hawking (Theoretical Physicist) described the big bang ripples observations as “the scientific discovery of the century, if not all time.”(10)
Dr. George Greenstein (Professor of Astronomy at Amherst.): “As we survey all the evidence, the thought insistently arises that some supernatural agency – or, rather, Agency – must be involved. Is it possible that suddenly, without intending to, we have stumbled upon scientific proof of the existence of a Supreme Being? Was it God who stepped in and so providentially crafted the cosmos for our benefit?”(11)
Sir Arthur Eddington (British Astrophysicist): “The idea of a universal mind or Logos would be, I think, a fairly plausible inference from the present state of scientific theory.”(12)
Dr. Arno Penzias (Nobel Prize winner in physics, co-discoverer of the microwave background radiation from the Big Bang): “Astronomy leads us to a unique event, a universe which was created out of nothing, one with the very delicate balance needed to provide exactly the conditions required to permit life, and one which has an underlying (one might say ‘supernatural’) plan.”(13)
Sir Roger Penrose (Physicist, Emeritus Rouse Ball Professor of Mathematics at the Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford, and joint developer of the Hawking-Penrose Theorems): “I would say the universe has a purpose. It’s not there just somehow by chance.”(14)
Dr. Robert Jastrow (Founding director of NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies): “For the scientist who has lived by his faith in the power of reason, the story ends like a bad dream. He has scaled the mountains of ignorance; he is about to conquer the highest peak; as he pulls himself over the final rock, he is greeted by a band of theologians who have been sitting there for centuries.”(15)
Dr. Frank Tipler (Professor of Math and Physics at Tulane University): “When I began my career as a cosmologist some twenty years ago, I was a convinced atheist. I never in my wildest dreams imagined that one day I would be writing a book purporting to show that the central claims of Judeo-Christian theology are in fact true, that these claims are straightforward deductions of the laws of physics as we now understand them. I have been forced into these conclusions by the inexorable logic of my own special branch of physics.”(16) Tipler since has actually converted to Christianity, resulting in his latest book, The Physics Of Christianity.
Dr. Alexander Polyakov (String Theorist, Princeton): “We know that nature is described by the best of all possible mathematics because God created it.”(17)
Dr. Edward Milne (British Astrophysicist, former Rouse Ball Professor of Mathematics, Oxford): “As to the cause of the Universe, in context of expansion, that is left for the reader to insert, but our picture is incomplete without Him [God].”(18)
Dr. Arthur L. Schawlow (Professor of Physics at Stanford University, 1981 Nobel Prize in physics): “It seems to me that when confronted with the marvels of life and the universe, one must ask why and not just how. The only possible answers are religious…. I find a need for God in the universe and in my own life.”(19)
Dr. Wernher von Braun (German-American Pioneer Rocket Scientist) “I find it as difficult to understand a scientist who does not acknowledge the presence of a superior rationality behind the existence of the universe as it is to comprehend a theologian who would deny the advances of science.”(20)
Dr. Frank Tipler (Professor of Math and Physics at Tulane University): “From the perspective of the latest physical theories, Christianity is not a mere religion, but an experimentally testable science.”(21)
Footnotes for these quotes
8) Thomas H. Maugh, II (April 24, 1992). “Relics of Big Bang, Seen for First Time”. Los Angeles Times: pp. Al, A30.
9) The Los Angeles Times, Saturday 2nd May 1992.
10) Smoot, George, Wrinkles in Time, 2007 edition , cover.
11) Greenstein, G. 1988. The Symbiotic Universe. New York: William Morrow, p.27.
12) Heeren, F. 1995. Show Me God. Wheeling, IL, Searchlight Publications, p. 233.
13) Margenau, H and R.A. Varghese, ed. 1992. Cosmos, Bios, and Theos. La Salle, IL, Open Court, p. 83.
14) Penrose, R. 1992. A Brief History of Time (movie). Burbank, CA, Paramount Pictures, Inc.
15) Jastrow, R. 1978. God and the Astronomers. New York, W.W. Norton, p. 116.
16) Tipler, F.J. 1994. The Physics Of Immortality. New York, Doubleday, Preface.
17) Gannes, S. October 13, 1986. Fortune. p. 57
18) Heeren, F. 1995. Show Me God. Wheeling, IL, Searchlight Publications, p. 166-167.
19) Margenau, H. and R. A. Varghese, eds. Cosmos, Bios, Theos: Scientists Reflect on Science, God, and the Origins of the Universe, Life, and Homo Sapiens (Open Court Pub. Co., La Salle, IL, 1992).
20) McIver, T. 1986. Ancient Tales and Space-Age Myths of Creationist Evangelism. The Skeptical Inquirer 10:258-276.
21) McIver, T. 1986. Ancient Tales and Space-Age Myths of Creationist Evangelism. The Skeptical Inquirer 10:258-276.
So, far from atheism being supported by science, the theistic worldview has been exemplified above all other models of interpretation (perceptions) of reality. Mind you this isn’t “proof” how the naturalist wrongly interprets the empirical method (scientific positivism), but it is a probability that exceeds others. (I suggest taking time, about an hour, and listen to this presentation by William Lane Craig on the evidences for theism over other worldviews.) Here John makes one of his signature jumps from one topic to a completely different one. I sometimes feel — shot in the dark again — he does this with the idea that he is saying something “scientific” and that everyone should credit his knowledge in on this particular topic (which is not the case), and then he brings that “trust” into a completely different topic.
I hope this helps a little bit to those searching for answers. Also, note that many people attack Genesis for light being created BEFORE the sun and stars. Here is a great look at what was most likely (according to physicists) in this event. LIGHT is ENERGY:
Two Recent Discoveries Confirm Einstein
Two recent discoveries support for the beginning of the universe (the Big-Bang) and General Relativity. This adds an almost unassailable position of creation ex nihilo as well as more evidence against multiverses… which have no evidence.
GRAVITY WAVES:
BINARY PULSAR:
Binary Pulsar Affirms General Relativity and Cosmic Creation Event
The most rigorous and compelling proof that the universe was created by an Agent that transcends space and time comes from the theory of general relativity. The best confirmation that general relativity is a true theory comes from measurements on the binary pulsar B1913+16. Thanks to a new study, that best confirmation has now become even better.
Astronomers have been studying the binary pulsar PSR B1913+16 for nearly four decades. In a recent issue of the Astrophysical Journal, astronomers Joel Weisberg and Yuping Huang published their analysis of 9,257 pulse times-of-arrival measurements taken over 35 years on PSR B1913+16.1
PSR B1913+16 is a pair of neutron stars where one of the neutron stars is a pulsar. The two neutron stars orbit one other with a period of 7.75 hours and an orbital separation of just 3 light seconds (a little more than twice the separation of the moon from Earth or about 2/3 the diameter of the sun). The pulsar rotates on its axis about 17 times per second. Thus, it sends out a strong pulse of radiation every 59 milliseconds.
The theory of general relativity predicts that neutron stars orbiting close to one another will radiate gravitational waves. This radiation will cause the neutron stars to experience a decay in their orbit—that is, the neutron stars will orbit closer and closer to one another as gravitational energy is radiated away by the gravitational waves.
The easiest and most accurate way to measure the orbital decay is to determine changes in the timing of periastron of the orbit. Periastron refers to the position in the orbit at which two stars orbiting one another are closest to one another. The orientation of periastron in PSR B1913+16’s orbit has been observed to change by 4.2° per year. Figure 1 shows the observed change in the timing of periastron with date from 1975–2003 compared to what the theory of general relativity would predict.2
[….]

[….]
The most potent of the space-time theorems, the one proven by Arvind Borde, Alexander Vilenkin, and Alan Guth, states that all cosmological models are subject to an initial space-time singularity, regardless of assumptions about homogeneity, isotropy (or lack thereof), or energy conditions, including cosmological models that invoke an early hyper-inflation event.9 This beginning of space and time implies that an Agent operating from beyond space and time must have caused the universe to exist.
About a year after the publication of the theorem, Alexander Vilenkin wrote in a book, “With the proof now in place, cosmologists can no longer hide behind the possibility of a past eternal universe. There is no escape, they have to face the problem of a cosmic beginning.”10 That problem is a causal Agent who transcends space and time. Such a causal Agent matches the description of the God of the Bible.
[1] Joel Weisberg and Yuping Huang, “Relativistic Measurements from Timing the Binary Pulsar PSR B1913+16,” Astrophysical Journal 829 (September 2016): id. 55, doi:10.3847/0004-637X/829/1/55.
[2] Joel Weisberg, David Nice, and Joseph Taylor, “Timing Measurements of the Relativistic Binary Pulsar PSR B1913+16,” Astrophysical Journal 722 (September 2010): 1030–34,doi:10.1088/0004-637X/722/2/1030.
[….]
[10] Alexander Vilenkin, Many Worlds in One: The Search for Other Universes (New York: Hill & Wang, 2007), 176.
- RPT “Editors” Note: for more on Vilenkin, see this post: Dr. William Lane Craig Discusses the Borde-Guth-Vilenkin Theorem

The Cost of Materialism (Nihilism)
Hat-tip to EVOLUTION NEWS & SCIENCE TODAY for this.
The role played by the Judeo-Christian tradition in the rise of Western science is a contentious topic — but not an obviously emotional one. Or so you might think. Stephen Meyer spoke on the subject at our most recent Dallas Conference on Science and Faith. The video is up now. In a new presentation using the story of Isaac Newton and his investigation of the nature of gravitation as a case study, Meyer recalls an earlier talk he gave at the Dallas Conference on related themes where a young woman, a member of the video crew, broke down in tears as Steve spoke. She later confessed in a communication to us:
Throughout my college career, professors would constantly lecture that based on the evidence they had provided…there should be no way that anyone in the class could believe in God. They’d argue that the science was proven… and God was hence a myth. I was not equipped to present a valid opposition in a debate. I was desperate to find a commonality between my beliefs and my [scientific] education. [Emphasis added.]
“Desperate” is a remarkable word. How many young people are being educated to believe that thinking scientifically means discarding a relationship with God?
[….]
As these comments suggest, the nihilism that is being sown by materialism is not just an intellectual problem. The desperation that goes with it cuts to the heart of many people. If you have children in college, as I do, it’s a very scary thing. Many thanks to Steve Meyer for tackling the science-versus-faith “warfare” myth directly. One viewer notes that he sent the lecture to his “agnostic brother” who is “really into the sciences.” Good idea.
Bestselling author Stephen Meyer explores how three key Judeo-Christian presuppositions encouraged the rise of modern science, and he explores the influence of faith on the life and work of Sir Isaac Newton. Meyer is Director of the Center for Science and Culture at Discovery Institute and author of Return of the God Hypothesis. This talk was presented at the 2022 Dallas Conference on Science and Faith in January 2022.

5-Part Series: Science and God | Stephen Meyer
Can you believe in God and science at the same time? Many claim that belief in religion is at odds with “the science” of today. But is that really true? In this five-part series, Stephen Meyer, Senior Fellow at the Discovery Institute, attempts to answer this existential question.
Series “Broken Out”
- Are Religion and Science in Conflict? — Science and God | Does belief in God get in the way of science? The idea that science and religion are inevitably in conflict is a popular way of thinking today. But the history of science tells a different story.
- How Did the Universe Begin? — Science and God | Was the universe always here, or did it have a beginning? If so, how did it start? Mankind has debated these questions for centuries and has only recently begun to find some answers. And those answers may point to some even more intriguing conclusions.
- Aliens, the Multiverse, or God? — Science and God | Even staunch Darwinists have acknowledged that life in the universe displays an appearance of design, rather than being created out of random chance. If that’s true, where did that design come from? In other words, does a design require a designer?
- What Is Intelligent Design? — Science and God | Chances are if you’ve heard anything about intelligent design, you’ve heard that it’s faith-based, not science-based. Is that true? Or does modern science, in fact, point us in the direction of a designing intelligence?
- What’s Wrong with Atheism? — Science and God | Is there any meaning to life? Or is life nothing more than a cosmic accident? Scientific atheists claim the latter, but ironically, it’s science itself that suggests the former.
The Naturalistic Origin Of Life (RNA World Critiqued)
The Origin of Life, two world views, Darwinian evolution theory vs Biblical Creation.
The RNA World Hypothesis is presented in the first half of this video from Dr. Pierre Durand, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg. PhD student Nisha Dhar Quote (Via TImes Live):
- ‘RNA molecules were the first molecules which could have given rise to life.’
- ‘This event is believed to have taken place possibly 4 billion years ago, at a time when a young earth was a hostile place with a volcanic activity and an atmosphere that had yet to contain oxygen. RNA, said Durand, was hardy and would have survived these kinds of conditions.’
Presenting the Biblical Creation science explanation for the origin of life, Dr. James M. Tour (PhD., T. T., and W. F. Chao Professor of Chemistry Professor of Computer Science Professor of Materials Science and Nano Engineering — Rice University. Smalley-Curl Institute and the NanoCarbon Center.)
APOLOGETIC PRESS notes this of the RNA World Hypothesis:
- [Editor’s Note: The following article was written by A.P. auxiliary staff scientist Will Brooks and one of his students. Dr. Brooks holds a Ph.D. in Cell Biology from the University of Alabama at Birmingham and serves as Assistant Professor of Biology at Freed-Hardeman University.]
….Evolutionists would have us to believe that non-living elements and molecules joined together and developed increasing biological capabilities. Those who believe in intelligent design reject this hypothesis, insisting that neither RNA nor living cells are able to evolve spontaneously. While some disagreement exists among those in the evolutionary community on the time frame for such alleged reactions to occur, the consensus is that, given large amounts of time, single-celled bacteria were formed. But all known biological principles militate against this notion. Even billions of years could not provide mechanisms for the reaction products to evolve advantageous characteristics and form DNA and cell proteins, let alone create strings of RNA nucleotides, arriving at just the right sequence in order to code for a functional protein. The four nucleotide bases that form RNA (adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil) can be arranged in an exponential array of combinations and lengths. For an actual, functional protein to be coded, a precise sequence of nucleotides must be obtained. Forming the code for even one protein by evolutionary means is impossible, without even considering the necessity of the number that work together in a single cell.
There is no scientific evidence to suggest that RNA is spontaneously being created and capable of forming pre-cellular life today. While some artificial ribozymes have been created in the laboratory (reviewed in Chen, et al., 2007), there are still significant holes in reproducing an RNA world to support the hypothesis. The ribozymes created artificially lack the abilities to sufficiently process themselves, and there is no evidence of them producing large quantities of advantageous nucleotide sequences. Moreover, no system has ever created cellular life. There is even significant debate among scientists over the conditions and constituents of a “prebiotic Earth” model.
The RNA World Hypothesis is simply another attempt by scientists to explain the origin of life to the exclusion of the divine Creator. Given the absolute impossibility of life originating from the reactions of non-living matter, it can be justified that RNA did not predate other biological molecules. All biological molecules were created together to work in concert. RNA was designed to be the essential intermediate between DNA and proteins, making our cells capable of sustaining life as it was created. The designer of this system must be the intelligent Designer, the God of the Bible.
FOLLOW UP ARTICLES
- About That RNA World Hypothesis (EVOLUTION NEWS & SCIENCE TODAY)
- Evolutionist Criticisms Of The RNA World Conjecture (CREATION.COM)
- The RNA World: A Critique (ORIGINS & DESIGN 17:1)
- The RNA World Hypothesis: The Worst Theory Of The Early Evolution Of Life (except for all the others) (US NATIONAL LIBRARY OF MEDICINE
NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH)
Stephen C. Meyer | The Ben Shapiro Show (Intelligent Design)
Stephen C. Meyer, geophysicist, Vice President of the Discovery Institute, and author of the New York Time’s best seller “Darwin’s Doubt,” joins Ben to discuss philosophy, the origins of life, the overlap of science and religion, and much more. (Hat-Tip to WINTERY KNIGHT). See also RPT:
- Not Enough Evolutionary Time For Simple Life
- Dr. Stephen Meyer and Dennis Prager Discuss Theistic Evolution
- RNA/DNA = Information | Or, What “IS” Information
- DNA by Design – Stephen Meyer (not RPT, but YouTube)
More [hard work] from WINTERY:
- 1:34 What is your scientific background? Science undergraduate degree, professional geologist, later did a PhD in philosophy of science from Cambridge University.
- 2:39 What is the difference between intelligent design and creationism? Creationism starts from the Bible and posits a shorter history of the universe. ID starts from the data of the natural world and is neutral about the age of the Earth / universe. Meyer accepts the old-Earth.
- 3:36 How is Intelligent Design a scientific theory? The discovery of DNA reveals that code is central to living systems. Intelligent design uses the method of “inference to the best explanation” in order to argue that the best explanation for the code is an intelligent agent.
- 6:10 What evidence would have to arise to make Intelligent Design Falsifiable? If a naturalistic mechanism was discovered that could produce biological information using the probabilistic resources of the universe, and the time available, then intelligent design would be falsified.
- 7:26 Is religion separate from science or intertwined within it? There are three views: science is totally separate from religion, science is in total conflict with religion, science and religion agree on some issues, e.g. – the origin of the universe and Genesis 1:1. There are areas where science and religion overlap.
- 9:55 Why are the most prominent Darwinians also militant atheists? Evolution is a theory that tries to explain nature using naturalistic mechanisms, so it is compatible with atheism.
- 10:45 What does the theory of evolution say? The term evolution has multiple meanings, and should be defined before discussions. It can refer to change over time. It can refer to animals changing slightly to adapt to enviromental changes. It can refer to the idea that all animals evolved from simpler life forms, and that there is a tree of life showing how different types of organisms share common ancestors. And it can refer to the idea that purely undirected processes can explain the history of life using purely materialistic forces. It’s that final view that intelligent design challenges.
- 13:15 Where is the discontinuity in naturalistic processes in the development of life? The first discontinuity is the origin of simple life from non-living components. The second discontinuity is the sudden appearance of different body plans in a very narrow window of time in the Cambrian era.
- 15:42 Why does information theory suggest that code requires some sort of designer? DNA is a true information-bearing system identical to the software in computers, e.g. – operating system, applications.
- 19:45 Can information be created by random mutation, and favorable mutations preserved by natural selection? Just as in software code, instructions must be added in order to develop new functionality. Random additions of characters will almost always degrade biological function. The number of possible sequences that do nothing useful is vastly higher than the number of sequences that perform biological functions. Doug Axe did research on this at Cambridge University, and he found that the number of functional sequences of amino acids is 1 in 10 to the 77th power. Given the probabilistic resources (replicating organisms)and the time available, it is extremely unlikely to find sequences that have functional information by chance.
- 25:05 What about Stephen Jay Gould’s model of punctuated equilibrium – doesn’t it explain the sudden jumps in information? Gould’s mechanism is accurate according to the fossil record, which shows a lot of jumps. But he did not have a naturalistic explanation for sudden jumps in biological function. Darwinian mechanisms work slowly and would (in theory) produce different body plans gradually. But this is not what the fossil record shows.
- 27:22 What is the mechanism for injecting information in the theory of intelligent design? The information comes in from an intelligence when new major body plans appear, and minor variations within types could be explained by evolution.
- 29:25 Does the Miller-Urey experiment provide a naturalistic explanation for the building blocks necessary for the origin of life? The MU experiment only produced a few types of amino acids, it doesn’t say anything about how to sequence the amino acids in order to form protein folds that can perform biological functions. The MU experiment also pre-supposes conditions on the early Earth (reducing gases) that do not match what was there (oxidyzing or neutral gases).
- 32:00 Is the RNA world hypothesis is a good explanation for the origin of life? Evolution requires that replication already be in place, because evolution assumes that mutations appear during the replication. The RNA world hypothesis suggests that sequences contain information, but also catalyze origin of life chemistry. The problem with RNA world is that it starts with self-replicating systems. And those replicating systems require the scientist to inject information into the system to get even the simplest replication started.
- 34:56 How do scientists respond to the critiques of Darwinism proposed by intelligent design advocates? By and large, they accept them. They think that mutation and selection works once living systems are in place, but they realize it has no explanation for the origin of life or the sudden origin of body plans. (Tells about the conference of the Royal Society, where problems with Darwinian mechanisms were discussed, and the 2003 MIT Press book by Muller and Newman).
- 37:16 Why do people hold to Darwinian evolution in the face of these problems? Many scientists presuppose methodological naturalism, which requires that any explanation for the origin of life and the origin of major body plans involve materialist explanations only. No intelligent agents are allowed. The problems occur when assumption of naturalism causes scientists to propose incorrect explanations for what we observe in nature. It’s also not clear how naturalistic mechanisms could produce organisms who are capable of reason and free will.
- 40:43 Does naturalistic evolution have an answer for conscious minds, reasoning, free will? No, consider the work of atheist scholar Thomas Nagel, who argues in his book “Mind and Cosmos” (Oxford University Press 2012) that the existence of mind is a disproof of the neo-Darwinian explanation for life. Darwinism stops us from accepting the reality of minds.
- 42:06 So do naturalistic evolutionists have to explain away the mind as an illusion? First, we humans have immediate experience of consciousness, reason and free will. Second, our whole legal system is based on the idea free will, because you can’t hold someone guilty unless they chose to do something they knew was wrong. Third, we have an epidemic of suicide among young people. This is caused by a crisis of meaning. Intelligent design opens up the possibility of their being a mind behind the universe, who we could have a relationships with.
- 44:53 Why aren’t schools allowed to be honest about the problems with neo-Darwinian evolution? The intellignt design view is to that teachers should be allowed to teach all the vidence for Darwinian evolution, and also discuss some of the problems with the theory. Students learning science should not be told that everything is solved. Students learn science better when they are presented with peer-reviewed evidence for and against a theory, rather than being indoctrinated.
- 47:37 Is intelligent design theory connected to God? Intelligent design infers from the information content in nature that a mind with capabilities like ours injected information into living systems. Intelligent design is agnostic about the designer, because in principle, embodied or unembodied agents could inject information into living systems. Intelligent design is friendly to theism, because theists will immediately identify the mind as God. Furthermore, the fine-tuning in the initial conditions of the universe is another intelligent design argument. In that case, since the design occurs at the beginning of the universe, the intelligent agent acting prior to the creation of the universe would have to be supernatural, i.e. – God.
- 50:53 Can naturalists say that the imposition of “function” on a sequence is arbitrary, in the same way that the English language is arbitrary? This won’t work, because biological function is not arbitrary in the same way as language. Biological function is not arbitrary, because sequences can be tested for function objectively by observing whether sequences can perform functions necessary for life, e.g. – replication.
- 52:43 Doesn’t the multiverse explain away the improbabilities of the fine-tuning, the origin of life, and the development of life? No, because all models of the multiverse require fine-tuning in the mechanism that generates the different universes.
- 55:42 What about cosmological models that eliminate the beginning of the universe? The standard Big Bang model and the inflationary model both posit a beginning of the universe. There is also the Borde-Guth-Vilenkin theory which proves that any universe that is expanding requires a beginning. The only chance for naturalists is quantum cosmologies, but this doesn’t work because 1) it requires an abstract reality of mathematics to actualize the physical universe, but this presupposes a mind. 2) The model requires an earlier input of information, which can only have come from a mind.

The “Problem” of God and Science (Romans 1:20 + Psalm 19)
HAT-TIP to UNCOMMON DESCENT
- Stephen Meyer: The More Science Advances, The More Science Points To Design
(Another MUST LISTEN TO piece can be found at WINTERY KNIGHT)
A clipping from a post of mine elsewhere on this “fine establishments” zeros and ones (RELIGIO-POLITICAL TALK):
✂ SNIP ✂
Lee Strobel does a great job in relaying the evidence that we live in a finite cosmos and not an infinite one in his discussion with Dr. William Lane Craig [I added J. Warner Wallace as well to this presentation]:
When Albert Einstein developed his general theory of relativity in 1915 and started applying it to the universe as a whole, he was shocked to discover it didn’t allow for a static universe. According to his equations, the universe should either be exploding or imploding. In order to make the universe static, he had to FUDGE his equations by putting in a factor that would hold the universe steady.
In the 1920’s, the Russian mathematician Alexander Friedman and the Belgium astronomer George Lemaitre were able to develop models based on Einstein’s theory. They predicted the universe was expanding. Of course, this meant that if you went backward in time, the universe would go back to a single origin before which it didn’t exist. Astronomer Fred Hoyle derisively called this the Big Bang — and the name stuck! [Later in his career, Fred Hoyle confirmed the expansion through work on the second most plentiful element in the universe, helium.]
Starting in the 1920’s, scientists began to find empirical evidence that supported these purely mathematical models.
LET US TAKE A QUICK BREAK from this excerpt to fill in some information from another excerpt, and then we will continue: As mathematicians explored the theoretical evidence, astronomers began to make observations confirming the expansion of the universe. Vesto Slipher, an American astronomer working at the Lowell Observatory. in Flagstaff, Arizona, spent nearly ten years perfecting his understanding of spectrograph readings. His observations revealed something remarkable. If a distant object was moving toward Earth, its observable spectrograph colors shifted toward the blue end of the spectrum. If a distant object was moving away from Earth, its colors shifted toward the red end of the spectrum. Slipher identified several nebulae and observed a redshift in their spectrographic colors. If these nebulae were moving away from our galaxy (and one another), as Slipher observed, they must have once been tightly clustered together. In 1914, he offered these findings at a meeting of the American Astronomical Society, proposing them as evidence the universe was expanding. A graduate student named Edwin Hubble seas in attendance and realized the implications of Slipher’s work. Hubble later began working at the Mount Wilson Observatory in Los Angeles. Using the Hooker telescope, he eventually proved Slipher’s nebulae were actually galaxies beyond the Milky Way composed of billions of stars. By 1929, Hubble published findings of his own, verifying Slipher’s observations and demonstrating the speed at which a star or galaxy moves away from us increases with its distance from Earth. This once again confirmed the expansion of the universe. …CONTINUING… For instance, in 1929, the American astronomer Edwin Hubble discovered that the light coming to us from distant galaxies appears redder than it should be, and this is a universal feature of galaxies in all parts of the sky. Hubble explained this red shift as being due to the fact that the galaxies are moving away from us. He concluded that the universe is literally flying apart at enormous velocities. Hubble’s astronomical observations were the first empirical confirmation of the predictions by Friedman and Lemaitre. Then in the 1940’s, George Gamow predicted that if the Big Bang really happened, then the background temperature of the universe should be just a few degrees above absolute zero. He said this would be a relic from a very early stage of the universe. Sure enough, in 1965, two scientists accidentally discovered the universe’s background radiation — and it was only about 3.7 degrees above absolute zero. There’s no explanation for this apart from the fact that it is a vestige of a very early and a very dense state of the universe, which was predicted by the Big Bang model. The third main piece of the evidence for the Big Bang is the origin of light elements. Heavy elements, like carbon and iron, are synthesized in the interior of stars and then exploded through supernova into space. But the very, very light elements, like deuterium and helium, cannot have been synthesized in the interior of the stars, because you would need an even more powerful furnace to create them. These elements must have been forged in the furnace of the Big Bang itself at temperatures that were billions of degrees. There’s no other explanation. So predictions about the Big Bang have been consistently verified by the scientific data. Moreover, they have been corroborated by the failure of every attempt to falsify them by alternative models. Unquestionably, the Big Bang model has impressive scientific credentials… Up to this time, it was taken for granted that the universe as a whole was a static, eternally existing object…. At the time an agnostic, American astronomer Robert Jastrow was forced to concede that although details may differ, “the essential element in the astronomical and Biblical accounts of Genesis is the same; the chain of events leading to man commenced suddenly and sharply, at a definite moment in time, in a flash of light and energy”…. Einstein admitted the idea of the expanding universe “irritates me” (presumably, said one prominent scientist, “because of its theological implications”)
This should be put in bullet points for easy memorization:
- Albert Einstein developed his general theory of relativity in 1915;
- Around the same time evidence of an expanding universe was being presented to the American Astronomical Society by Vesto Slipher;
- In the 1920s using Einstein’s theory, a Russian mathematician (Alexander Friedman) and the Belgium astronomer (George Lemaitre) predicted the universe was expanding;
- In 1929, Hubble discovered evidence confirming earlier work on the Red-Light shift showing that galaxies are moving away from us;
- In the 1940’s, George Gamow predicted a particular temperature to the universe if the Big Bang happened;
- In 1965, two scientists (Arno Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson) discovered the universe’s background radiation — and it was only about 3.7 degrees above absolute zero.
Not Enough Evolutionary Time For Simple Life
OTHER EVIDENCES TO CONSIDER
Not Enough Time
It’s even in the title of Charles Darwin’s most popular book, On the Origin of Species By Means of Natural Selection. But what Darwin didn’t know then was that natural selection can’t create brand-new genetic information. It’s never been observed to do this. In the case of the bacterium we looked at, it either LOST information or gained already existing information. Nothing brand-new was created! So, if natural selection can never create the brand-new information that evolution needs, how can it be considered the driving force of evolution? Just one more scientific reason that you shouldn’t believe in molecules-to-man evolution. It takes a LOT of faith.
Proof that God (a non-random process) exists and random chance evolutionary processes do not explain our origins.
Stephen C. Meyer appearing in Darwin’s Dilemma talks about Richard Dawkins’s “climbing Mt. Improbable.”
Biologist Ann Gauger discusses the challenge posed to Darwinian natural selection by the process of metamorphosis found in butterflies and other creatures. Gauger is featured in the science documentary “Metamorphosis,” which deals with butterflies, evolution, and intelligent design.

Dr. Stephen Meyer and Dennis Prager Discuss Theistic Evolution
Dennis talks to Stephen Meyer, Director of the Center for Science and Culture at the Discovery Institute in Seattle, about his latest book (one of the editors) which is a collection of essays by two dozen highly credentialed scientists, philosophers, and theologians from Europe and North America, this volume contests this proposal, documenting evidential, logical, and theological problems with theistic evolution—making it the most comprehensive critique of theistic evolution yet produced. Here it is at AMAZON: “Theistic Evolution: A Scientific, Philosophical, and Theological Critique.”
BTW, it seems Prager has not hear of the sciences detecting intelligence. One of the best examples is STILL the Golden Arm, by William Dembski: “Man With The Golden Arm ~ Eliminating Chance Statistically.”
For more information on Natural Selection and the neo-Darwinian model waning, see my posts here:
✦ Evolution is “Evolving” ~ The Failure of Neo-Darwinism
✦ Natural Selection ~ D.O.A.
✦ Not Enough Evolutionary Time For Simple Life
DISCOVERY INSTITUTE – Twitter: @DiscoveryCSC

DNA by DESIGN
Antibiotic Resistance Evidence of “Devolution”
The issue involved in the above video is not evolution, but in fact, DEVOLUTION. In other words, “no newly evolved complex information has been demonstrated,” EVOLUTION NEWS AND VIEWS continues with a quote and then some commentarry [I am working on getting the graphic mentioned]:
A key aspect of bacterial survival is the ability to evolve while migrating across spatially varying environmental challenges. Laboratory experiments, however, often study evolution in well-mixed systems. Here, we introduce an experimental device, the microbial evolution and growth arena (MEGA)-plate, in which bacteria spread and evolved on a large antibiotic landscape (120 × 60 centimeters) that allowed visual observation of mutation and selection in a migrating bacterial front. While resistance increased consistently, multiple coexisting lineages diversified both phenotypically and genotypically. Analyzing mutants at and behind the propagating front, we found that evolution is not always led by the most resistant mutants; highly resistant mutants may be trapped behind more sensitive lineages. The MEGA-plate provides a versatile platform for studying microbial adaption and directly visualizing evolutionary dynamics.
The key to understanding the paper is its Figure 3C. There it shows the genes that have undergone more than one mutation across tested bacteria. They break the mutations down into silent changes, changes of amino acids (point mutations), and insertion-deletion or nonsense mutations, which almost certainly are loss of function (LOF). Over half of genes contain such LOF mutations, along with some point mutations, which likely also degrade or destroy function. In other words, devolution….
In another post over at EVOLUTION NEWS AND VIEWS, it is mentioned that “Evolutionists often speak in generalities about beneficial mutations. They may be rare, we are assured, but they happen.” But is this the case? Continuing we read:
…when they do [happen], “natural selection is daily and hourly scrutinising, throughout the world, every variation, even the slightest; rejecting that which is bad, preserving and adding up all that is good; silently and insensibly working, whenever and wherever opportunity offers, at the improvement of each organic being in relation to its organic and inorganic conditions of life” (Darwin, Origin of Species). All right, we have some data to look at. We can put a number to the frequency of beneficial mutations in a large sample. The number is zero.
Genome sequencing technology has progressed very rapidly in only the last few years. NATURE just published results of the Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC), the largest survey of human genes to date. (An “exome” is the portion of the genome that codes for proteins.) The exomes from 60,706 individuals from a variety of ethnic groups have been collected and analyzed. If we multiply 60,000 people by the 20,000 genes in the human genome (the lowest estimate), we get a minimum of 1.2 billion genes that have been examined by ExAC for variants. That sounds like a pretty good sample size for scrutinizing some of those beneficial variations that Darwin said his law of natural selection could add up and preserve.
Large-scale reference data sets of human genetic variation are critical for the medical and functional interpretation of DNAsequence changes. Here we describe the aggregation and analysis of high-quality exome (protein-coding region) DNA sequence data for 60,706 individuals of diverse ancestries generated as part of the Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC). This catalogue of human genetic diversity contains an average of one variant every eight bases of the exome, and provides direct evidence for the presence of widespread mutational recurrence. We have used this catalogue to calculate objective metrics of pathogenicity for sequence variants, and to identify genes subject to strong selection against various classes of mutation; identifying 3,230 genes with near-complete depletion of predicted protein-truncating variants, with 72% of these genes having no currently established human disease phenotype. Finally, we demonstrate that these data can be used for the efficient filtering of candidate disease-causing variants, and for the discovery of human ‘knockout’ variants in protein-coding genes. [Emphasis added.]
Out of this high ratio of variants (one in eight bases shows variation, they said), there should be some proportion, even if small, that improves fitness. But we search the paper in vain for any mention of beneficial mutations. There’s plenty of talk about disease. The authors only mention “neutral” variants twice. But there are no mentions of beneficial mutations. You can’t find one instance of any of these words: benefit, beneficial, fitness, advantage (in terms of mutation),improvement, innovation, invention, or positive selection.
They mention all kinds of harmful effects from most variants: missense and nonsense variants, frameshift mutations, proteins that get truncated on translation, and a multitude of insertions and deletions. Quite a few are known to cause diseases. There are probably many more mutations that never survive to birth. As for natural selection, the authors do speak of “negative selection” and “purifying selection” weeding out the harmful mutations, but nowhere do they mention anything worthwhile that positive selection appears to be preserving…
Yep. I note this “devolution” in a conversation with a biology graduate student in regards to evidences for the GENERAL THEORY OF EVOLUTION (GTE).
▼ It has been proven that resistance to many modern antibiotics was present decades before their [the antibiotics] discovery. In 1845, sailors on an ill-fated Arctic expedition were buried in the permafrost and remained deeply frozen until their bodies were exhumed in 1986. Preservation was so complete that six strains of nineteenth-century bacteria found dormant in the contents of the sailors’ intestines were able to be revived! When tested, these bacteria were found to possess resistance to several modern-day antibiotics, including penicillin. Such traits were obviously present prior to penicillin’s discovery, and thus could not be an evolutionary development. (Medical Tribune, December 29, 1988, p. 1, 23.)
In 1998, the National Academy of Sciences published and distributed a book to public schools and other institutions entitled Teaching About Evolution and the Nature of Science. Jonathan Sarfati, Ph.D., F.M., wrote a book, Refuting Evolution, which is a topic by topic rebuttal to this Academy of Sciences publication. Under the evidence for evolution in the evolutionist text is the following quote:
▼ Similar episodes of rapid evolution are occurring in many different organisms. Rats have developed resistance to the poison warfain. Many hundreds of insect species and other agricultural pests have evolved resistance to the pesticides used to combat them – even to chemical defenses genetically engineered into plants.
(Sarfati’s reply – any words in the [boxes] are mine):
▼ However, what has this to do with the evolution of new kinds with new genetic information? Precisely nothing. What has happened in many cases is that some bacteria already had the genes for resistance to the antibiotics. In fact, some bacteria obtained by thawing sources which had been frozen before man developed antibiotics have shown to be antibiotic-resistant [6 different antibiotics in fact, penicillin in modern doses – which is way beyond the strength of natural penicillin found in nature]. When antibiotics are applied to a population of bacteria, those lacking resistance are killed, and any genetic information they carry is eliminated. The survivors carry less information [or specificity], but they are all resistant. The same principle applies to rats and insects “evolving” resistance to pesticides. Again, the resistance was already there, and creatures without resistance are eliminated.
[Much like if we killed all dogs (including Canis Domesticus and Canis Lupus) except for Chihuahuas, we would permanently lose the information of the parent population. You could then breed Chihuahuas for a millennium and not get an Irish Wolfhound]
▼ …In other cases, antibiotic resistance is the result of a mutation, but in all known cases, this mutation has destroyed information. It may seem surprising that destruction of information can sometimes help. But one example is resistance to the antibiotic penicillin. Bacteria normally produce an enzyme, penicillinase, which destroys penicillin. The amount of penicillinase is controlled by a gene. There is normally enough produced to handle any penicillin encountered in the wild, but the bacterium is overwhelmed by the amount given to patients. A mutation disabling this controlling gene results in much more penicillinase being produced.
[Thus, the bacteria found frozen in 1845 already had the mutation to overcome modern medical doses of penicillin. So the mutation wasn’t the result of the penicillin in modern doses, thus seemingly becoming resistant… it already had the resistant mutation – informational or specificity losing – in the population. In other words, no new information was added to the parent population!]
(See more in this entire chapter discussing the issue: “VARIATION AND NATURAL SELECTION VERSUS EVOLUTION“)

Updated info with a h-t to TOMI AALTO’S site and it comes by way of PHYS.ORG:
Excerpt: “Pioneering work being carried out in a cave in New Mexico by researchers at McMaster University and The University of Akron, Ohio, is changing the understanding of how antibiotic resistance may have emerged and how doctors can combat it in the future.
In research published in Nature Communications today, the scientists examined one bacterium found 1,000 feet underground (called Paenibacillus) that demonstrated resistance to most antibiotics used today, including so-called ‘drugs of last resort’ such as daptomycin. These microorganisms have been isolated from the outside world for more than four million years within the cave.
The results show the bacterium is resistant to 18 different antibiotics and uses identical methods of defense as similar species found in soils.
Among the different ways that the bacteria could be resistant to antibiotics, the scientists identified five novel pathways that were of potential clinical concern. Finding these new pathways is particularly valuable, as it gives researchers time to develop new drugs to combat this type of resistance, potentially decades before it will become a problem for doctors and their patients.
“The diversity of antibiotic resistance and it’s its prevalence in microbes across the globe should be humbling to everyone who uses these lifesaving drugs,” said Gerry Wright, an author of the paper and scientific director of McMaster’s Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Infectious Disease Research.
“It reflects the fact that we must understand that antibiotic use and resistance go hand in hand.”
My [Tomi’s] comment: How could anyone talk about bacterium evolution after this finding? We can’t observe evolution, we can only observe reaction and adaptation. We can also see strong evolutionary stasis here. Bacteria have not experienced changes in assumed millions of years. They have not evolved the ability to rapidly adapt to modern medicines. Instead, they already have all necessary genomic information and capabilities for ecological adaptation. These features are built in by Intelligent source and the Creator. The evolutionary theory is a dangerous heresy.