This is an old video, but someone just posted it on a Facebook group — what follows is my Facebook response as well as additional thoughts. Here is the video that prompted the below:
On the surface I can understand how someone would FEEL this describes reality. But our body politic is more complex than the above video would like to prescribe as reality. In fact, the video sets up a straw man [something that does not exist], and then attacks it as if it were the case.
Here is my response on Facebook:
FACEBOOK RESPONSE
Hey, I know our system is corrupted… but the video notes at around the 30-second mark:
- This axis represents the likelihood of Congress passing a law that reflects any of these ideas from 0% to a 100% chance on this graph, an ideal republic would look like this: if 50% of the public supports an idea, there’s a 50% chance of it becoming law. If 80% of US support something, there’s an 80% chance.
I am sorry. That idea is explaining an ideal Democracy, which our Founders wholeheartedly rejected.
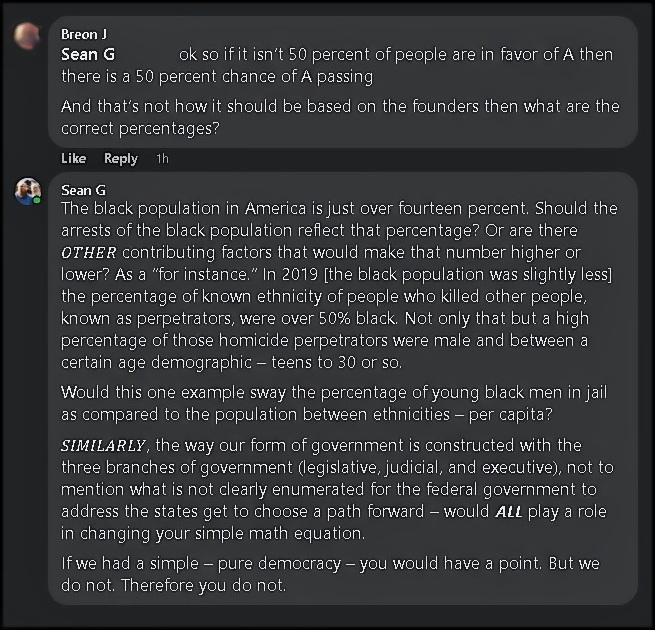
It reminds me of a call of a young black man into the Larry Elder Show where Larry was getting clarification [if he had misheard the young man], or, confirmation [if he had heard the man correctly].
Larry mentioned that “Ferguson is 57% black. What percentage of the arrest should be black people?
The caller responded: “57.”
Larry goes on to make an analogy about the NBA being a majority black players and asks – rhetorically – why the NBA isn’t 70% white? He answers himself by saying that the NBA is based on merit…
Similarly, Larry notes, arrests are based on crime. Not race. Arrests are merit based. So the PERCENTAGES don’t always match population.
Just like in a Republic. You have three forms of “checks and balances” that are supposed to be based in the Constitutional limiting of federal government powers and metering out state control over what is not clearly enumerated for the federal government to act on.
THIS has become corrupted over time, granted, but the “exact percentage” of something “becoming law” [in this video] does not reflect at all – all the variabilities in the struggle to pass something. The Founders didn’t want it easy like 60% says “a” therefore “a” should happen or become law.
In a pure Democracy however, the percentages would match. This video is made during a time where the Dems were [and still believe] pushing for the Electoral College to be abolished. This would effectively be a main driver to getting us to a pure Democracy. Something no one should want:
James Madison (fourth President, co-author of the Federalist Papers and the “father” of the Constitution) – “Democracies have ever been spectacles of turbulence and contention; have ever been found incompatible with personal security, or the rights of property; and have, in general; been as short in their lives as they have been violent in their deaths.”
John Adams (American political philosopher, first vice President and second President) – “Remember, democracy never lasts long. It soon wastes, exhausts, and murders itself. There never was a democracy yet that did not commit suicide.”
Benjamin Rush (signer of the Declaration) – “A simple democracy… is one of the greatest of evils.”
Fisher Ames (American political thinker and leader of the federalists [he entered Harvard at twelve and graduated by sixteen], author of the House language for the First Amendment) – “A democracy is a volcano which conceals the fiery materials of its own destruction. These will provide an eruption and carry desolation in their way.´ / “The known propensity of a democracy is to licentiousness [excessive license] which the ambitious call, and the ignorant believe to be liberty.”
Governor Morris(signer and penman of the Constitution) – “We have seen the tumult of democracy terminate… as [it has] everywhere terminated, in despotism…. Democracy! Savage and wild. Thou who wouldst bring down the virtous and wise to thy level of folly and guilt.”
John Quincy Adams (sixth President, son of John Adams [see above]) – “The experience of all former ages had shown that of all human governments, democracy was the most unstable, fluctuating and short-lived.”
Noah Webster (American educator and journalist as well as publishing the first dictionary) – “In democracy… there are commonly tumults and disorders….. therefore a pure democracy is generally a very bad government. It is often the most tyrannical government on earth.”
John Witherspoon (signer of the Declaration of Independence) – “Pure democracy cannot subsist long nor be carried far into the departments of state – it is very subject to caprice and the madness of popular rage.”
Zephaniah Swift (author of America’s first legal text) – “It may generally be remarked that the more a government [or state] resembles a pure democracy the more they abound with disorder and confusion.”
Take note that as well Article IV, Section 4 of the Constitution reads:
- “The United States shall guarantee to every state in this union a republican form of government…“
Not “republican,” as one “political party, the GOP,” but as a “form” of government. So what is an example of the corruption of the “Consent of the Governed”?
[….]
Having discussed issues FOR YEARS with those on the other side of the aisle, I knew the response would still be similar to the caller into the Larry Elder Show. There is a “disconnect” on the Left that just doesn’t pick up simple underlying ideas. Here is the response as well as me responding…
[….]
…END OF MY FB RESPONSE… adding more info for my reader.
An important phrase in my mind’s eye is the phrase, “Consent of the Governed.” That is found in the Declaration of Independence. Here is an excerpt of the idea/phrase via the Declaration of Independence:
- We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness.–That to secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed, –That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the Right of the People to alter or to abolish it, and to institute new Government, laying its foundation on such principles and organizing its powers in such form, as to them shall seem most likely to effect their Safety and Happiness.
Here are two large excerpts about this from THE HERITAGE FOUNDATION that I wish to share so the reader understands that the topic isn’t as “neat and tidy, or, simple” as the OP video makes it out to be with simple percentages.
[CONSENT]
…Part of the reason for the Constitution’s enduring strength is that it is the complement of the Declaration of Independence. The Declaration provided the philosophical basis for a government that exercises legitimate power by “the consent of the governed,” and it defined the conditions of a free people, whose rights and liberty are derived from their Creator. The Constitution delineated the structure of government and the rules for its operation, consistent with the creed of human liberty proclaimed in the Declaration.
Justice Joseph Story, in his Familiar Exposition of the Constitution (1840), described our Founding document in these terms:
We shall treat [our Constitution], not as a mere compact, or league, or confederacy, existing at the mere will of any one or more of the States, during their good pleasure; but, (as it purports on its face to be) as a Constitution of Government, framed and adopted by the people of the United States, and obligatory upon all the States, until it is altered, amended, or abolished by the people, in the manner pointed out in the instrument itself.
By the diffusion of power–horizontally among the three separate branches of the federal government, and vertically in the allocation of power between the central government and the states–the Constitution’s Framers devised a structure of government strong enough to ensure the nation’s future strength and prosperity but without sufficient power to threaten the liberty of the people.
The Constitution and the government it establishes “has a just claim to [our] confidence and respect,” George Washington wrote in his Farewell Address (1796), because it is “the offspring of our choice, uninfluenced and unawed, adopted upon full investigation and mature deliberation, completely free in its principles, in the distribution of its powers uniting security with energy, and containing, within itself, a provision for its own amendment.”
The Constitution was born in crisis, when the very existence of the new United States was in jeopardy. The Framers understood the gravity of their task. As Alexander Hamilton noted in the general introduction to The Federalist,
[A]fter an unequivocal experience of the inefficacy of the subsisting federal government, [the people] are called upon to deliberate on a new Constitution for the United States of America. The subject speaks its own importance; comprehending in its consequences nothing less than the existence of the Union, the safety and welfare of the parts of which it is composed, the fate of an empire in many respects the most interesting in the world.
Several important themes permeated the completed draft of the Constitution. The first, reflecting the mandate of the Declaration of Independence, was the recognition that the ultimate authority of a legitimate government depends on the consent of a free people. Thomas Jefferson had set forth the basic principle in his famous formulation:
We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty, and the pursuit of Happiness. That to secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed.
That “all men are created equal” means that they are equally endowed with unalienable rights. Nature does not single out who is to govern and who is to be governed; there is no divine right of kings. Nor are rights a matter of legal privilege or the benevolence of some ruling class. Fundamental rights exist by nature, prior to government and conventional laws. It is because these individual rights are left unsecured that governments are instituted among men.
Consent is the means by which equality is made politically operable and whereby arbitrary power is thwarted. The natural standard for judging if a government is legitimate is whether that government rests on the consent of the governed. Any political powers not derived from the consent of the governed are, by the laws of nature, illegitimate and hence unjust.
The “consent of the governed” stands in contrast to “the will of the majority,” a view more current in European democracies. The “consent of the governed” describes a situation where the people are self-governing in their communities, religions, and social institutions, and into which the government may intrude only with the people’s consent. There exists between the people and limited government a vast social space in which men and women, in their individual and corporate capacities, may exercise their self-governing liberty. In Europe, the “will of the majority” signals an idea that all decisions are ultimately political and are routed through the government. Thus, limited government is not just a desirable objective; it is the essential bedrock of the American polity.
[CHECKS AND BALANCES]
A second fundamental element of the Constitution is the concept of checks and balances. As James Madison famously wrote in The Federalist No. 51,
In framing a government which is to be administered by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to controul the governed; and in the next place oblige it to controul itself. A dependence on the people is, no doubt, the primary controul on the government; but experience has taught mankind necessity of auxiliary precautions.
These “auxiliary precautions” constitute the improved science of politics offered by the Framers and form the basis of their “Republican remedy for the diseases most incident to Republican Government” (The Federalist No. 10).
The “diseases most incident to Republican Government” were basically two: democratic tyranny and democratic ineptitude The first was the problem of majority faction, the abuse of minority or individual rights by an “interested and overbearing” majority. The second was the problem of making a democratic form of government efficient and effective. The goal was limited but energetic government. The constitutional object was, as the late constitutional scholar Herbert Storing said, “a design of government with the powers to act and a structure to make it act wisely and responsibly.”
The particulars of the Framers’ political science were catalogued by Madison’s celebrated collaborator in The Federalist, Alexander Hamilton. Those particulars included such devices as representation, bicameralism, independent courts of law, and the “regular distribution of powers into distinct departments;’ as Hamilton put it in The Federalist No. 9; these were “means, and powerful means, by which the excellencies of republican government may be retained and its imperfections lessened or avoided.”
Central to their institutional scheme was the principle of separation of powers. As Madison bluntly put it in The Federalist No. 47, the “preservation of liberty requires that the three great departments of power should be separate and distinct,” for, as he also wrote, “The accumulation of all powers, legislative, executive, and judiciary, in the same hands, whether of one, a few, or many, and whether hereditary, self-appointed or elective, may justly be pronounced the very definition of tyranny.”
Madison described in The Federalist No. 51 how structure and human nature could be marshaled to protect liberty:
[T]he great security against a gradual concentration of the several powers in the same department, consists in giving to those who administer each department, the necessary constitutional means, and personal motives to resist encroachments of the others.
Thus, the separation of powers frustrates designs for power and at the same time creates an incentive to collaborate and cooperate, lessening conflict and concretizing a practical community of interest among political leaders.
Equally important to the constitutional design was the concept of federalism. At the Constitutional Convention there was great concern that an overreaction to the inadequacies of the Articles of Confederation might produce a tendency toward a single centralized and all-powerful national government. The resolution to such fears was, as Madison described it in The Federalist, a government that was neither wholly federal nor wholly national but a composite of the two. A half-century later, Alexis de Tocqueville would celebrate democracy in America as precisely the result of the political vitality spawned by this “incomplete” national government.
The institutional design was to divide sovereignty between two different levels of political entities, the nation and the states. This would prevent an unhealthy concentration of power in a single government. It would provide, as Madison said in The Federalist No. 51, a “double security. .. to the rights of the people.” Federalism, along with separation of powers, the Framers thought, would be the basic principled matrix of American constitutional liberty. “The different governments;’ Madison concluded, “will controul each other; at the same time that each will be controulled by itself.”
But institutional restraints on power were not all that federalism was about. There was also a deeper understanding–in fact, a far richer understanding–of why federalism mattered. When the delegates at Philadelphia convened in May 1787 to revise the ineffective Articles of Confederation, it was a foregone conclusion that the basic debate would concern the proper role of the states. Those who favored a diminution of state power, the Nationalists, saw unfettered state sovereignty under the Articles as the problem; not only did it allow the states to undermine congressional efforts to govern, it also rendered individual rights insecure in the hands of “interested and overbearing majorities.” Indeed, Madison, defending the Nationalists’ constitutional handiwork, went so far as to suggest in The Federalist No. 51 that only by way of a “judicious modification” of the federal principle was the new Constitution able to remedy the defects of popular, republican government.
The view of those who doubted the political efficacy of the new Constitution was that good popular government depended quite as much on a political community that would promote civic or public virtue as on a set of institutional devices designed to check the selfish impulses of the majority As Herbert Storing has shown, this concern for community and civic virtue tempered and tamed somewhat the Nationalists’ tendency toward simply a large nation. Their reservations, as Storing put it, echo still through our political history.[1]
It is this understanding, that federalism can contribute to a sense of political community and hence to a kind of public spirit, that is too often ignored in our public discussions about federalism. But in a sense, it is this understanding that makes the American experiment in popular government truly the novel undertaking the Framers thought it to be.
At bottom, in the space left by a limited central government, the people could rule themselves by their own moral and social values, and call on local political institutions to assist them. Where the people, through the Constitution, did consent for the central government to have a role, that role would similarly be guided by the people’s sense of what was valuable and good as articulated through the political institutions of the central government. Thus, at its deepest level popular government means a structure of government that rests not only on the consent of the governed, but also on a structure of government wherein the views of the people and their civic associations can be expressed and translated into public law and public policy, subject, of course, to the limits established by the Constitution. Through deliberation, debate, and compromise, a public consensus is formed about what constitutes the public good. It is this consensus on fundamental principles that knits individuals into a community of citizens. And it is the liberty to determine the morality of a community that is an important part of our liberty protected by the Constitution.
The Constitution is our most fundamental law. It is, in its own words, “the supreme Law of the Land.” Its translation into the legal rules under which we live occurs through the actions of all government entities, federal and state. The entity we know as “constitutional law” is the creation not only of the decisions of the Supreme Court, but also of the various Congresses and of the President.
Yet it is the court system, particularly the decisions of the Supreme Court, that most observers identify as providing the basic corpus of “constitutional law.” This body of law, this judicial handiwork, is, in a fundamental way, unique in our scheme, for the Court is charged routinely, day in and day out, with the awesome task of addressing some of the most basic and most enduring political questions that face our nation. The answers the Court gives are very important to the stability of the law so necessary for good government. But as constitutional historian Charles Warren once noted, what is most important to remember is that “however the Court may interpret the provisions of the Constitution, it is still the Constitution which is the law, not the decisions of the Court.”[2]
By this, of course, Warren did not mean that a constitutional decision by the Supreme Court lacks the character of binding law. He meant that the Constitution remains the Constitution and that observers of the Court may fairly consider whether a particular Supreme Court decision was right or wrong. There remains in the country a vibrant and healthy debate among the members of the Supreme Court, as articulated in its opinions, and between the Court and academics, politicians, columnists and commentators, and the people generally, on whether the Court has correctly understood and applied the fundamental law of the Constitution. We have seen throughout our history that when the Supreme Court greatly misconstrues the Constitution, generations of mischief may follow. The result is that, of its own accord or through the mechanism of the appointment process, the Supreme Court may come to revisit some of its doctrines and try, once again, to adjust its pronouncements to the commands of the Constitution.
This recognition of the distinction between constitutional law and the Constitution itself produces the conclusion that constitutional decisions, including those of the Supreme Court, need not be seen as the last words in constitutional construction. A correlative point is that constitutional interpretation is not the business of courts alone but is also, and properly, the business of all branches of government. Each of the three coordinate branches of government created and empowered by the Constitution–the executive and legislative no less than the judicial–has a duty to interpret the Constitution in the performance of its official functions. In fact, every official takes a solemn oath precisely to that effect. Chief Justice John Marshall, in Marbury v. Madison (1803), noted that the Constitution is a limitation on judicial power as well as on that of the executive and legislative branches. He reiterated that view in McCullough v. Maryland (1819) when he cautioned judges never to forget it is a constitution they are expounding.
The Constitution–the original document of 1787 plus its amendments–is and must be understood to be the standard against which all laws, policies, and interpretations should be measured. It is our fundamental law because it represents the settled and deliberate will of the people, against which the actions of government officials must be squared. In the end, the continued success and viability of our democratic Republic depends on our fidelity to, and the faithful exposition and interpretation of, this Constitution, our great charter of liberty.
[1] Herbert J. Storing, “The Constitution and the Bill of Rights.” in Joseph M. Bessette, ed., Toward a More Perfect Union: Writings of Herbert J. Storing (Washington, D.C.: The AEI Press, 1995).
[2] Charles Warren, The Supreme Court in United States History (Boston: Little, Brown, and Company, 1922-1924), 3 vols., 470-471.
ALL this plays a role in us getting laws.
As an example of how “judicial activism” changes an outcome of a vote that a stae has a right to vote on (BECUASE the enumerated powers in the Constitution were not clear and thus the states get to decide):
- The meaning of marriage.
So a slight majority of California voters voted to say marriage is between a man and a woman. Proposition 8 passed with 52 percent of the vote. One federal judge [Judge Vaughn Walker — himself a gay man] overturned the will of the California people. I think this judge was acting in an “activist” manner, but there is a way to overrule his decision legally… and the percentages to do so were not present, plus the Supreme Court wrongly interfered in this as well — like with Roe v. Wade.
The above is all arguable of course between out varying views of politics — that is not the point.
The POINT IS that this dynamic interferes with “simple math/percentages” idea of those that wish to have a pure democracy.
By way of another point showing the complexity of outcomes not being easily “mathematized,” take the 9th Circuit Upper Court. In 2012, The U.S Supreme Court reversed 86% of the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals rulings that it reviewed. WOW. That is a clear sign of something going on — like Judicial activism. (And this was the time-period where the Supreme Court was more left leaning than now.)
Now however, the Court has moved less from a “the Constitution is a living and breathing document” idea (the progressives view); to a more originalist idea based in president and the authors intent (a conservative view).
- “Trump has effectively flipped the circuit,” said 9th Circuit Judge Milan D. Smith Jr., an appointee of President George W. Bush.
So the outcome of the judicial case regarding such cases like Proposition 8 may end up being much different when in front of the upper courts.
How do you quantify something like that into percentages or fractions?
HINT: You can’t.
So, I noted way up in my Facebook comment that I agree that our form of government is corrupt. I did give an example in my Facebook response that I did not include above — that I will here. And while this example deals with just one aspect, you can apply this to both sides of the aisle in their attempt to distort the will of the people in proper representation in order to aquire power and privilege.
More on this from around the time it was released at REASON.ORG’s post. Here is the video description:
America’s public education system is failing. We’re spending more money on education but not getting better results for our children.
That’s because the machine that runs the K-12 education system isn’t designed to produce better schools. It’s designed to produce more money for unions and more donations for politicians.
For decades, teachers’ unions have been among our nation’s largest political donors. As Reason Foundation’s Lisa Snell has noted, the National Education Association (NEA) alone spent $40 million on the 2010 election cycle (source: http://reason.org/news/printer/big-ed…. As the country’s largest teachers union, the NEA is only one cog in the infernal machine that robs parents of their tax dollars and students of their futures.
Students, teachers, parents, and hardworking Americans are all victims of this political machine–a system that takes money out of taxpayers’ wallets and gives it to union bosses, who put it in the pockets of politicians.
Our kids deserve better.
(With all that in play in the above video… how does that make mathematical equations in outcomes of voting an easy course of action?)
An example of how the corruption in education distorts the will of the people. In a recent survey, 79% of Black parents supported vouchers, 74% supported charter schools, and 78% supported open enrollment. Roughly three in four Black parents (78%) support education savings accounts, which are becoming increasingly popular across the country. This percentage is much higher even than the national average of two-thirds (67%).
You would think that we would already have school choice, however, through the bedfellows of interest groups, unions, and Big-Government (Crony Capitalism, or, Crony Corporatism) — we have outcomes that stifle choice.
All that is debatable as well… but again:
- How do you quantify that?