Shun the Non-Believer…
A CLIP FROM CHARLIE THE UNICORN
Before posting what I did on Facebook as part of a response to a conversation regarding the below graphic… I want to say that by showing vestiges…
- a rudimentary structure in humans corresponding to a functional structureor organ in ancestral animals
…in no way undermines Intelligent Design, or somehow PROVES evolution. Let me explain.
Darwin said he didn’t see an issue with whales evolving from bears, or some bear like creature. In his first edition of Origin of Species, Darwin said this:
- “I can see no difficulty in a race of bears being rendered, by natural selection, more and more aquatic in their structure and habits, with larger and larger mouths,” Darwin concluded, “till a creature was produced as monstrous as a whale.”
ARCHAEOPTERYX
This does not involve “devolution,” a loss of specificity which the below picture captures… but rather, evolution demands an increase in specificity in gene and DNA specificity in the creation of whole new organs and how they act. Similarly, the Archaeopteryx is proffered as an example of evolution, but evolutionists themselves would say that this is only an example of “devolution,” and not an increase of specificity in a species (a clipping from my post: “Was Archaeopteryx Devolving? Thus Losing It’s Ability to Fly?“):
Since other feathered “birds” have been found around the same time or earlier than Archaeopteryx, causing Alan Feduccia to quip, “You can’t be older than your grandfather” (Creation.com)… NATURE has published an article pointing out that Archaeopteryx is JUST LIKE modern flightless birds. And so it could have been losing its ability for flight (like modern birds have).
“We know Archaeopteryx was living on an archipelago during the Jurassic. And with its feathers and bones looking so much like modern flightless island birds, it just makes me wonder,” says…. Michael Habib, a biologist at the University of Southern California….
[….]
“Just because Archaeopteryx was the first feathered dinosaur found, doesn’t mean it has to play a central role in the actual history of the origins of birds,” says palaeontologist Thomas Holtz of the University of Maryland in College Park. “We have to remember it appears 10 million years or so after the oldest known bird-like dinosaurs and so our famous ‘first bird’ may really be a secondarily flightless one.”…
There is just as much [at best] evidence for this proposition as the next. “Devolution” — a loss of specificity/use, may be a more reasonable position to take via observed evidence. We see this all the time (directly below is an example from Lee Spetner’s new book), and EVOLUTION NEWS says that “looks like Archaeopteryx may have to be reclassified as a different sort of icon — symbolizing evolution by loss of function.” Oops.
So these types of examples ACTUALLY COUNT AGAINST the main idea that neo-Darwinism proposed… that I came from a rock.
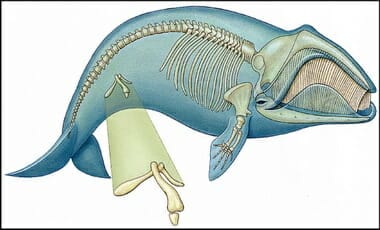
I find it interesting that people think this whale bone pictured above is a vestigial organ. Very similar to the list of a 180 vestigial structures said to be in the human body in the late 1800’s dwindling to effectively zero, and the damage and laziness such thinking cost lives and sciences advancement (see more here):
TONSILS
In the 1930’s over half of all children had their tonsils and adenoids removed. In 1969, 19.5 out of every 1,000 children under the age of nine had undergone a tonsillectomy. By 1971 the frequency had dropped to only 14.8 per 1,000, with the percentage continuing to decrease in subsequent years. Most medical authorities now actively discourage tonsillectomies.[1] Many agree with Wooley, chairman of the department of pediatrics at Wayne State University, who was quoted in Katz: “If there are one million tonsillectomies done in the United States, there are 999,000 that don’t need doing.”
Among the first medical doctors seriously to question the wisdom of tonsillectomies was Albert Kaiser. For ten years he kept complete records of the illnesses of 5,000 children. They were divided into two groups – those who had tonsils removed and those who did not. Kaiser found: “…no significant difference between the two groups in the number of colds, sore throats and other upper respiratory infections.”[2]
Tonsils are important to young people in helping to establish the body’s defense mechanism which produces disease-fighting antibodies. Once these mechanisms are developed, the tonsils shrink to almost nothing in adults, and other organs take over this function.[3] In the Medical World News,[4] a story stated that although removal of tonsils at a young age obviously eliminates tonsillitis (the inflammation of the tonsils) it may significantly increase the incidence of strep-throat and even Hodgkin’s disease. In fact, according to the New York Department of Cancer Control: “…people who have had tonsillectomies are nearly three times as likely to develop Hodgkin’s Disease, a form of cancer that attacks the lymphoid tissue.”[5]
THE POINT
My point is this, the Tonsils were once included in a list of 180 vestigial (“useless, or nearly useless”) organs.[6] And because the assumption was first made that these were organs left over from a previous genetic ancestor (ape, dog, early-man, whatever), that they were deemed useless – ad hoc – because science did not know at that time what their functions were.
So for many years, doctors and scientists that accepted the evolutionary paradigm did not investigate the possible functionality of these organs. Many people suffered and died needlessly due to this philosophical assumption that evolution is true. You will see this assumption play out again and again where medical science and the evolutionary issue intersect. You see, if you come to the table with an understanding that we were created, then these structures serve a purpose, or are a neutral combination of the possible male/female outcome of the fertilized egg (for instance, male nipples[7]). If the assumption is made that these structures are designed, then the medical world would strive to investigate and understand the organ in question, not simply state that it is useless.
[1] Robert P Bolande, “Ritualistic Surgery – circumcision and tonsillectomy,” New England Journal of Medicine, March 13 (1969) pp. 591-595; Alvin Eden, “When Should Tonsils and Adenoids be Removed?” Family Weekly, September 25 (1977), p. 24; Lawrence Galton, “All Those Tonsil Operations: Useless? Dangerous?” Parade, May 2 (1976), pp. 26ff; Dolras Katz, “Tonsillectomy: Boom or Boondoggle?” The Detroit Free Press, April 13 (1972), p. 1-C; Samuel Lipton, “On the Psychology of Childhood Tonsillectomy,” found in: The Psychoanalysis Study of the Child (International Universities Press, New York: 1962).
[2] Galton, p. 26.
[3] Martin L. Gross, The Doctors (Random House, New York: 1966); Simpson Hall, Diseases of the Nose, Throat and Ear (E. and S. Livingston, New York: 1941).
[4] N. J. Vianna, Peter Greenwald, and U. N. Davies, September 10, 1973, p.10
[5] Galton, p. 26-27.
[6] This is an important issue, for instance, during the famous Scopes trial in 1925 – which allowed evolution to be taught alongside creation – zoologist Horatio Hacket Newman, a defense witness, stated: “There are, according to Wiedersheim, no less than 180 vestigial structures in the human body, sufficient to make of a man a veritable walking museum of antiquities.”
[7] Also, if created by a personal God who has created sex to be pleasurable, then the nipples have a purpose other than the neutral canvas of the fertilized egg.
- Jerry Bergman and George F. Howe, Vestigial Organs Are Fully Functional (Creation Research Society Books, Kansas City: MO: 1990).
WHALE TALES
SIMILARLY, the laziness in neo-Darwinian evolutionary propositions in this “example” of a vestigial organ shows the laziness in thought, and, the stalling of advancing science in understanding nature. Now, we know, and even the secular world acknowledges this fact in “discovering” [yet again] that pronouncements made by the evolutionary community of scientists is woefully wrong. Here is an example via THE DAILY MAIL – take note how I and the researches end the article:
Whale Sex Revealed: ‘Useless’ Hips Bones Are Crucial To Reproduction – And Size Really Matters, Study Finds
- Whales and dolphins have pelvic bones, which are evolutionary remnants from when their ancestors walked on land more than 40 million years ago
- Scientists from the University of Southern California and the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County, analysed pelvic bones for four years
- Muscles that control a cetacean’s penis attach directly to its pelvic bones
- They found the bigger the animals’ testis, the bigger their pelvic bone
- Males from more promiscuous species evolve larger penises, so larger pelvic bones are necessary to attach bigger muscles for penis control, they said
- Study changes the way we think about vestigial structures
[…..]
They wrote in the journal Evolution, the muscles that control a cetacean’s highly flexible penis, attach directly to its pelvic bones.
The scientist theorised that the pelvic bones could affect the level of control over the penis that an individual cetacean has, perhaps offering an evolutionary advantage.
To test their idea, they examined hundreds of pelvic bones and used a 3D scanner to make digital models of the curved bones in order to gain an unprecedented level of detail about their shape and size, as well as to compare them.
They then gathered data about testis size relative to the mass of whales. In the natural world, more ‘promiscuous’ species where females mate with many males, create a more competitive mating environment and the males develop larger testes as a way of attracting females.
[…..]
The experts compared the size of pelvic bones to the size of an animal’s testes, relative its body size, and found that the bigger the testes, the bigger the cetacean’s pelvic bone.
Males from more promiscuous species also evolve larger penises, so larger pelvic bones appear necessary to attach larger muscles for penis control, they said.
‘Our research really changes the way we think about the evolution of whale pelvic bones in particular, but more generally about structures we call vestigial,’ Professor Dean said.
‘AS A PARALLEL, WE ARE NOW LEARNING THAT OUR APPENDIX IS ACTUALLY QUITE IMPORTANT IN SEVERAL IMMUNE PROCESSES, NOT A FUNCTIONALLY USELESS STRUCTURE,’ he added….
(emphasis added)
AMBULOCETUS NATANS
In conversation about the above, the person I was speaking with posted a series of evolution from creature-to-creature proving the evolution of the whale.
I have already refuted this clean progression, HERE, but I noted something that this person was not aware of. As most people are not. You see, when you bring your kid to the Natural History Museum, you see this picture of the RED OUTLINED creature in the evidence for whales evolving:

The problem with this evidence is that it is based primarily on an artists rendition. Here is the actual bones all this Ambulocetus Natans is based on — see #3:

I merely commented that his believing and passing along graphics showing full skulls by artists, or the above “skeletal” sequence, reminds me of the movie scene from the Matrix:
In similar fashion, this artistic rendition used in the Scopes “Monkey” Trial was used as evidence proving evolution:
However, this was based off a single tooth. NOT ONLY THAT, but the tooth put forward as hominid, ended up being an extinct pig’s tooth.
APPENDIX
In similar form, many people still think the APPENDIX is a vestigial organ. Here is my response (since updated) to one of my son’s teachers in high school dealing with what was being taught as FACT… that is, that the appendix had no known use:
FULL UPDATED PAPER
Context this short paper was written:
This paper evolved over many years. It was one of the first subjects I debated at a science discussion board on the Internet many years ago prior to the NetZero days. Then I updated it to respond in writing to a Discover magazine article (a much larger paper, of which this takes up two pages).
Finally, as my son has been studying science in seventh grade, his science textbook states many “facts” wrongly, this being only one of the many I have since written about (peppered moths, embryos going through stages of a fish, homology, and the like).
I like to think that the teacher’s role is to not just teach what the “state” requires – this reminds me of the novels 1984, or Animal Farm – but to allow updated information into the classroom that will best challenge these students to become that medical doctor, chemist, or physicist. In other words, I want my son to have the best information that may spark the interest to become, say, a medical doctor. This is all that I argue for.
As it so happened, the teacher merely regurgitated what the “state” wanted her to (even after reading such a cogent and well laid response to her saying “there is no use for the appendix in the human body”). Much like when the dog cubs were taken and “educated” in the novel Animal Farm.
Much thought – and enjoy the read – SeanG!
THE APPENDIX
Dr. Kawanishi,[1] showed that human lymphoid cells in the appendix are immunologically functional as T helper cells and antibody-producing B cells, making IgA molecules in response to immunological challenges. He noted that:
“The human appendix, long considered only an accessory rudimentary organ, could posses a similar antigen uptake role prior to replacement by fibrosed tissue after repeated subclinical infections, or at least in early childhood when it is most prominent.”[2]
The appendix is also rich in argentaffin cells, which can be identified with the use of silver salt staining. The function of these cells has long been obscure, but the evidence suggests that they may be involved with endocrine gland function.[3] Many sources (encyclopedias, textbooks, etc.) still erroneously state that the appendix is useless. Interestingly, the Grolier Multimedia Encyclopedia states in one place: that “In humans the cecum and appendix have no important function,” and in another place that “the appendix is now thought to be one of the sites where immune responses are initiated.”
Dr. Howard R. Bierman… studied several hundred patients with leukemia, Hodgkin’s disease, cancer of the colon and cancer of the ovaries. He found that 84% [of his sample] had [their] appendix removed…. In a control group without cancer, only 25% had it removed.[4]
Bierman himself had concluded that the appendix may be an immunological organ whose premature removal during its functional period permits leukemia and other related forms of cancer to begin their development.[5] Bierman and his associates realized that the lymphoid tissue located on the walls of the appendix may secrete antibodies which protect the body against various viral agents.
While high school and college textbooks today will mention the appendix as vestigial, specialists in their field have for many years stated the necessity of the appendix as useful.
- “There is no longer any justification for regarding the vermiform appendix as a vestigial structure.”[6]
- “For at least 2,000 years, doctors have puzzled over the function of… the thymus gland…. Modern physicians came to regard it, like the appendix, as a useless vestigial organ which had lost its original purpose, if indeed it ever had one. In the last few years, however,… men have proved that, far from being useless, the thymus is really the master gland that regulates the intricate immunity system which protects us against infectious diseases…. Recent experiments have led researchers to believe that the appendix, tonsils, and adenoids may also figure in the antibody responses.”[7]
- “The appendix is not generally credited with significant function; however, current evidence tends to involve it in the immunologic mechanism.”[8]
- “The mucosa and submucosa of the appendix are dominated by lymphoid nodules, and its primary function is as an organ of the lymphatic system.”[9]
The appendix is in fact part of the G.A.L.T. (Gut Associated Lymphoid Tissue) system. The lymphoid follicles develop in the appendix at around two weeks after birth, which is the time when the large bowel begins to be colonized with the necessary bacteria. It is likely that its major function peaks in this neonatal period. Making it anything other than vestigial!
As Dr. Peter Faletra (Ph.D.), who is Senior Science Advisor Office of Science Department of Energy, says in response to a question on an online question-and-answer service for K-12 teachers run by the Argonne National Laboratories:
“As a histologist I see no reason to consider the v. appendix as having no function since it contains numerous lymphoid follicles that produce functional lymphocytes and a rich blood supply to communicate them. The general idea of vestigial organs is to me a measure of ignorance, arrogance and lack of imagination. Ignorance in that we label it as such because we do not know its function; arrogance in that we declare it of no value since we can see none; and lacking in imagination in so far as when we cannot see its function cannot imagine one. I call your attention to that other ‘vestigial organ’ the thymus without which, in early life, we would produce a severely compromised cell-mediated immune system as the ‘nude’ mouse and numerous thymectomized mammalian studies have shown. Although some general reference books still list the v. appendix as ‘vestigial’ most immunologists (I included) would strongly disagree!”[10] (emphises added)
UPDATE
Since the above was removed, I want to embolden the thinking by excerpting a SCIENTIFIC AMERICAN article:[11]
A study in the Journal of Evolutionary Biology finds that many more animals have appendixes than was thought, and that the appendix is not merely a remnant of a digestive organ called the cecum. All of which means that the appendix might not be so useless. Steve Mirsky reports.
Two years ago, Duke University Medical Center researchers said that the supposedly useless appendix is actually where good gut bacteria safely hide out during some unpleasant intestinal conditions.
Now the research team has looked at the appendix over evolutionary history. They found that animals have had appendixes for about 80 million years. And the organ has evolved separately at least twice, once among the weird Australian marsupials and another time in the regular old mammal lineage that we belong to.
Darwin thought that only a few animals have an appendix and that the human version was what was left of a digestive organ called the cecum. But the new study found that 70 percent of rodent and primate groups have species with an appendix….
While Scientific American still tries to relegate it to evolution, they do so by supposition. Almost by metaphysical statements. William Parker, Ph.D., assistant professor of experimental surgery, who conducted the analysis in collaboration with R. Randal Bollinger, M.D., Ph.D., Duke professor emeritus in general surgery – said this:
- “While there is no smoking gun, the abundance of circumstantial evidence makes a strong case for the role of the appendix as a place where the good bacteria can live safe and undisturbed until they are needed”[12]
WIKIPEDIA has a decent section on the appendix’s function as well.[13]
PS – (from the original letter)
This P.S. was to the teacher after she responded to my e-mail, I corrected her on something that any science teacher who isn’t guided by a presupposed philosophy – namely Naturalism – would have correctly defined.
Oh, I forgot, as I was falling asleep last night and running through the day in my head, something occurred to me. You mentioned that theories are, quote:
- “Theories are well tested concepts scientists use to help explain something based on repeated findings.”
Yes, a great quick explanation of a proper theory. However, when the appendix was placed on the vestigial organ list along with 180 other organs by Ernst Haekel in the late 1800‘s – where it has stayed since – no repeatable tests were ever done to confirm the hypothesis that it was useless. In fact, every medical test done of the type of tissue found (argentaffin cells, and lymphoid cells) in the appendix shows that it has a use.
So I would say that the theory that it is useful is quite sound, where as the hypothesis that it is useless is waning and ill founded ~ un-scientific in other words.
FOOTNOTES
[1] H. Kawanishi, “Immunocompetence of Normal Appendiceal Lymphoid cells: in vitro studies,” Immunology, 60(1) (1987), 19-28.
[2] Ibid., 19.
[3] Marti-Ibanez (editor), “Tuber of Life,” M. D. Magazine (1970) #14, p. 240; William J. Banks, Applied Veterinary Histology (Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore: 1981), 390.
[4] Richard G. Culp, Remember thy Creator (Baker Book House, Grand Rapids,; MI: 1975).
[5] Howard R. Bierman, “Human Appendix and Neoplasia,” Cancer 21 (1) (1968), 109-118.
[6] William Straus, Quarterly Review of Biology (1947), 149.
[7] “The Useless Gland that Guards Our Health,” in Reader’s Digest, November (1966), 229, 235.
[8] Henry L. Bockus, Gastroenterology, 2:1134-1148 [chapter The Appendix, by Gordon McHardy], (W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, Pennslyvania: 1976).
[9] Frederic H. Martini, Ph.D., Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology, (Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: 1995), 916
[10] (Since removed) From the site Newton, which is an electronic community for Science, Math, and Computer Science K-12 Educators. Argonne National Laboratory, Division of Educational Programs, Harold Myron, Ph.D., Division Director. Quote: http://www.newton.dep.anl.gov/askasci/mole00/mole00225.htm Home page: http://www.newton.dep.anl.gov/
[11] “That’s No Vestigial Organ, That’s My Appendix,” Scientific American (8-24-2009), found at: http://tinyurl.com/ycb9dcnv
[12] Duke University Medical Center, “Appendix isn’t useless at all: It’s a safe house for bacteria,” EurekaAlert! (AAAS | 10-08-2008); found at: http://tinyurl.com/yadgop2l
[13] Appendix, Functions – found at: http://tinyurl.com/k245vmb