David Berlinski discusses the fraudulent methods in which evolutionary theory is taught in our schools.
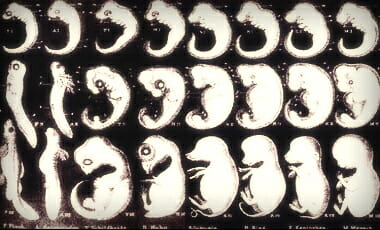
A recommended resource is a recent book entitled, “Haeckel’s Embryos: Images, Evolution, and Fraud” — here is Chicago University Press’ description:
Pictures from the past powerfully shape current views of the world. In books, television programs, and websites, new images appear alongside others that have survived from decades ago. Among the most famous are drawings of embryos by the Darwinist Ernst Haeckel in which humans and other vertebrates begin identical, then diverge toward their adult forms. But these icons of evolution are notorious, too: soon after their publication in 1868, a colleague alleged fraud, and Haeckel’s many enemies have repeated the charge ever since. His embryos nevertheless became a textbook staple until, in 1997, a biologist accused him again, and creationist advocates of intelligent design forced his figures out. How could the most controversial pictures in the history of science have become some of the most widely seen?
In Haeckel’s Embryos, Nick Hopwood tells this extraordinary story in full for the first time. He tracks the drawings and the charges against them from their genesis in the nineteenth century to their continuing involvement in innovation in the present day, and from Germany to Britain and the United States. Emphasizing the changes worked by circulation and copying, interpretation and debate, Hopwood uses the case to explore how pictures succeed and fail, gain acceptance and spark controversy. Along the way, he reveals how embryonic development was made a process that we can see, compare, and discuss, and how copying—usually dismissed as unoriginal—can be creative, contested, and consequential.
With a wealth of expertly contextualized illustrations, Haeckel’s Embryosrecaptures the shocking novelty of pictures that enthralled schoolchildren and outraged priests, and highlights the remarkable ways these images kept on shaping knowledge as they aged.
Another book with a more apolgetic verve is one by Jonathan Wells, “Icons of Evolution: Science or Myth? Why Much of What We Teach About Evolution Is Wrong,” especially chapter five, “Haeckel’s Embryo’s.” Here is the author speaking to it:
Other Examples of SO-SO-STORIES… but first… what is a so-so-story? Here is a quote, and really, a definition of the general theory of evolution (GTE) that G.A. Kerkut defines in his older text, Implication of Evolution (second quote). Here Spetner calls it the neo-Darwinian theory (NDT), it more common name today. Here is Spetner’s relevant quote:
Neo-Darwinian Theory (NDT) is counterintuitive, and is acknowledged as such even by its supporters. All present-day life is assumed to have evolved from some primitive cell, and that cell was supposed to have formed itself from simple chemicals. Nobody seems to know how that cell came to be, but almost all biologists think they understand fairly well how evolution proceeded from that cell to all the life we see today.
There appears to be a vast amount of information contained in trees, fish, elephants, and people. Where did this information come from? It is said to have come from random mutations and natural selection. How can that work? Natural selection is supposed to be the magic that makes evolution happen, but all natural selection does is eliminate the less adaptive organisms and allow the more adaptive ones to survive and proliferate. Where do those more adaptive ones come from? Apparently, that’s what random mutations are supposed to accomplish.
So the information buildup required by Common Descent can come only from random mutations. That means that the buildup of information is a matter of chance. At each step of the evolutionary process, a mutation has to have occurred that grants the organism an advantage. The big question is: Is that reasonable? To see if it is, some people (including me) have made calculations of the probability of mutations building information.
We really don’t have all the data we need to make this calculation. But even if we make some conservative assumptions and give the benefit of all doubts to the Darwinian side, such calculations demonstrate that Common Descent is not reasonable. The Darwinists, however, do not accept these calculations as conclusive — they suggest alternative scenarios that might make the probabilities larger.
In his book Darwin’s Black Box, Michael Behe addressed the unreasonableness of Darwinian evolution. He described some biological systems as what he called “irreducibly complex.” By that he meant that these systems are composed of several critical components in such a way that the system cannot work unless all those components are in place. He then argued that the system could not evolve one small part at a time, because natural selection could not work on less than the whole system. Here, too, the Darwinians countered by suggesting scenarios in which natural selection might work, but again, the Darwinian scenarios are purely hypothetical.
Because the Darwinians can invent scenarios to address any challenge to their theory, they are not convinced by attempts to show that neo-Darwinian evolution cannot work. Therefore, I have concluded that it would be more productive to challenge them to show that it could work — challenge them to do more than just offer vague scenarios of how their theory might work, but to show by calculation that the probability of it working is reasonably high. This is a challenge they must meet to establish their theory on a scientific basis. They have never met this challenge and they cannot. They cannot show that the events they claim to have produced Common Descent have a high enough probability to justify their claim. Their inability to establish the theory of Common Descent means that Common Descent is not an established theory. This is one of the main points of this book.
I cannot overemphasize the importance of probability calculations. NDT is not like Newton’s theory of mechanics, whose equations describe the motion of a physical body under a force. Nor is it like Maxwell’s theory of electromagnetism, whose equations describe the effects of electric and magnetic fields on electric charges. These theories are checked against experiment by solving those equations. NDT describes evolution as the result of random mutations that may or may not yield an adaptive phenotype. These are chance events. The theory can be checked only by calculating the probabilities of the required events to see if they are reasonably large. The theory has not been shown to have passed this test and is therefore not a valid theory. Whatever evidence is given for Common Descent is circumstantial. Circumstantial evidence cannot stand alone. It needs to have a theory tying the evidence to the conclusion. But instead of a theory, imaginary scenarios are offered to suggest how evolution might work. No calculations of probabilities are made.
[….]
Common Descent is a key component of an agenda advocating a natural origin of life. The effort to demonstrate the possibility of such a natural origin is usually divided into two parts: (1) abiogenesis, the origin of a simple life form from naturally occurring chemicals, and (2) the evolution of all life from that single simple beginning. It turns out, however, there is no good evidence for either of these two parts.
Lee Spetner, The Evolution Revolution: Why Thinking People Are Rethinking the Theory of Evolution (Brooklyn, NY: Judaica Press, 2014), 7-9, 15.
(LINKS IN PICTURES)
EYE EVOLUTION IN DRAWINGS:
NEBRASKA MAN (Drawn from from a single — later to be known — pigs tooth)
WHALE EVOLUTION: