A family member mentioned I should put the recent MRI of my shoulder examination into ChatGPT… Here is the original report:
TECHNIQUE:
Multiplanar, multi sequential MIRI performed) Standard sequences obtained
FINDINGS:
Rotator cuff: Fluid signal extending from the bursal to articular surface of the distal anterior insertion of the supraspinatus tendon consistent with a pinhole full-thickness tear. There is no significant retraction. There Is no muscle atrophy or edema. There Is associated diffuse tendinopathy of the supraspinatus tendon. The infraspinatus tendon is intact There is partial thickness tearing of the subscapularis tendon. The teres minor tendon is intact. There is no significant muscle atrophy or edema. Biceps tendon and labrum: Extensive tendinopathy of the intra-articular portion of the biceps tendon with short segment of longitudinal split tear. Abnormal signal of the superior labrum extending to the biceps anchor most suggestive for SLAP tear. Osseous structures and bone marrow: Cystic changes seen in the superior glenoid. Loss of glenohumeral joint and thinning of the articular cartilage. Moderate AC joint degenerative change, There is no acute fracture, contusion or AVN. No os acromiale or Hill-Sachs fracture. Joint spaces and soft tissues: There is a small joint effusion. There is no significant fluid in the subacromial subdeltoid bursa.
IMPRESSION:
Pinhole full-thickness tear of the distal anterior Insertion of the supraspinatus tendon without significant retraction 2. Partial tearing of the infraspinatus tendon B. Tendinopathy with longitudinal split tear of the biceps tendon 4. Abnormal signal of the superior labrum most suggestive for SLAP tear 5. Osteoarthrosis bf the glenohumeral joint with cystic changes in the superior glenoid G. Moderate AC Joint degenerative change 7. Small joint effusion
Here is how ChatGPT worded it (I add the pics):
Based on the provided findings, the impression of the MRI examination is as follows:
- Pinhole full-thickness tear of the distal anterior insertion of the supraspinatus tendon without significant retraction: This indicates a small tear in the supraspinatus tendon, which is one of the rotator cuff tendons located in the shoulder. The tear extends from the bursal (outer) to the articular (inner) surface of the tendon.
- Partial tearing of the infraspinatus tendon: The infraspinatus tendon, another rotator cuff tendon, appears to have a partial tear. The extent of the tear is not specified.
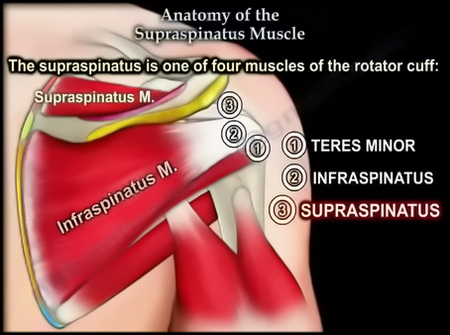
- Tendinopathy with longitudinal split tear of the biceps tendon: The biceps tendon, which runs along the front of the upper arm, shows signs of tendinopathy (tendon damage) and a longitudinal split tear. This tear refers to a tear that runs along the length of the tendon.
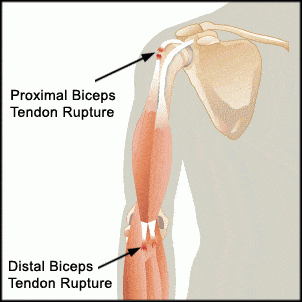
- Abnormal signal of the superior labrum most suggestive for SLAP tear: The superior labrum, also known as the “top” or “upper” labrum, shows abnormal signal intensity. This finding is most suggestive of a SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior) tear. SLAP tears involve the superior part of the labrum and are commonly associated with biceps tendon issues.
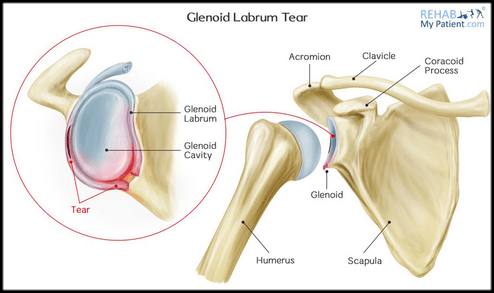
- Osteoarthrosis of the glenohumeral joint with cystic changes in the superior glenoid: The glenohumeral joint, which is the main joint of the shoulder, shows signs of osteoarthrosis, which is a degenerative joint disease. Cystic changes are seen in the superior (upper) part of the glenoid, which is the socket of the shoulder joint.
- Moderate AC Joint degenerative change: The AC (acromioclavicular) joint, which is located at the top of the shoulder, shows moderate degenerative changes. This indicates wear and tear or arthritis in the AC joint.
- Small joint effusion: There is a small amount of fluid within the joint, which could be a sign of inflammation or injury.
Please note that the information provided is based on the findings described and does not constitute a medical diagnosis. It is important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or a specialist, such as an orthopedic surgeon or a radiologist, for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options based on your specific condition.